Blog > ACH Debit vs. ACH Credit: What’s the Difference?
ACH Debit vs. ACH Credit: What’s the Difference?
Digital transfers are a fast, convenient, and cost-effective method of transferring funds from one financial account to another. With so many different types of digital transfers, it’s crucial to understand how they differ to determine which works best for your business.
One of the most popular forms of digital transfers is Automated Clearing House (ACH) payments, which continues to amass growth in the U.S. According to the National Automated Clearing House Association (NACHA), the value of ACH payments increased by $1 trillion in 2022 for the 10th consecutive year.
This article will dive into the characteristics of each ACH transfer, their differences, and their network to help you determine if these payments suit your business.
What is ACH?
ACH stands for Automated Clearing House, a payment processing system used in the U.S. designed for digital transfers between bank accounts.
The ACH network is regulated by both NACHA and the Federal Reserve, which establish the rules and regulations for processing ACH transactions. In doing so, they ensure each transaction is efficiently completed and adheres to the necessary security measures.
The ACH network processes billions of transactions each year — these transactions can consist of various payment methods and ACH types.
ACH transfers fall under two categories: ACH credit and ACH debit, also known as push and pull payments.
What are the different types of ACH transactions?
ACH transactions can include various transfers, such as direct deposits, withdrawals, bill payments, business-to-business payments, peer-to-peer (P2P) transfers, and more.
All these transfers can be categorized into two categories: ACH credit transactions and ACH debit transactions.
What is ACH Credit?
ACH electronic credit transfers, or push payments, push funds from one financial institution to another.
These transfers are typically used for the direct deposit of payroll, tax refunds, and other government benefits.
What is ACH Debit?
ACH electronic debit transfers, or pull payments, withdraw funds from a financial institution and transfer them to another. ACH debit transfers are commonly used for recurring payments, such as subscriptions or bills, where the recipient needs to receive payments regularly.
ACH debit can be initiated through various methods, such as bank transfers, direct debits, or online payment systems.
Regardless of the transaction your ACH transfer falls under, it’s essential to understand how it’s processed.
The 6-step process behind ACH transfers
The process of ACH transfers is incredibly secure and efficient as these transfers are highly regulated and standardized by NACHA.
Here are the six steps involved in processing ACH transactions include:
![]() 1. Initiation of the transfer request
1. Initiation of the transfer request
2. Authorization of funds
3. Batch processing
4. Routing funds
5. Posting to the recipient’s account
6. Notifying all parties involved
1. Initiation of the transfer request
The ACH transfer process begins with the initiation of the transfer request. This is done through the initiator’s financial institution using either digital methods or by filling out the proper paperwork provided by the respective institution, such as an ACH payment authorization form.
2. Authorization of funds
The next step after initiation is authorization. Once the transfer request is initiated, the financial institution verifies the associated account holds sufficient funds to complete the transaction.
The institution also confirms the appropriate party authorized the transfer request.
3. Batch processing
Batch processing is when the sender’s bank or payment service provider combines multiple ACH transfers into a single batch for submission to the ACH network.
Batches are usually created to set daily intervals to streamline the processing and settlement of ACH transfers.
4. Routing funds
The routing step of the transfer process is when funds are transferred from the sender’s bank to the recipient’s bank through the ACH network using the recipient’s routing number.
During this step, the ACH network identifies the sender’s and recipient’s banks by their unique routing numbers. These routing numbers are 9-digit codes assigned to each bank by the Federal Reserve Bank.
5. Posting to the recipient’s account
During this step, the recipient’s bank receives the ACH file and verifies the transaction details.
Once verified, the ACH network processes the payment, and the recipient’s bank credits the deposited funds to the recipient’s account and makes the funds available for use.
6. Notifying all parties involved
The final step of the transfer process involves financial institutions notifying both the sender and the recipient regarding the transfer status.
The notification includes a summary of the transfer details, such as the account number associated with the deposit, the amount being deposited, and the date the funds will be available.
Now that you know the process behind ACH transfers, it’s essential to understand the main differentiators between ACH credit and debit transactions.
Primary differences between ACH credit and ACH debit
Two critical differences set ACH credit and debit transactions apart, which include the direction of these transfers and the processing timelines for each.
Directions of ACH credit vs. debit transfers
One primary difference between ACH credit and ACH debit transactions is the direction of the transfer, which depends on who initiates it. ACH credit and debit transfers are also referred to as “pull” payments and “push” payments, as these terms reference the direction of each transfer.
In ACH debit payments, the recipient requests or “pulls” the payment from the payer. In other words, the recipient initiates the payment transaction by requesting funds from the payer’s account rather than the payer pushing the payment to the recipient.
In ACH credit payments, these payments are pushed or transferred in the opposite direction. In other words, a push payment is where the payer initiates the transfer and sends the funds to the recipient’s account without the recipient having to take action to request the payment.
ACH credit and debit transfers also differ in processing timelines.
Processing times for ACH credit and debit transfers
While a typical ACH transfer takes one to three days to process, the processing timelines for ACH credit and debit transactions can vary depending on a few factors.
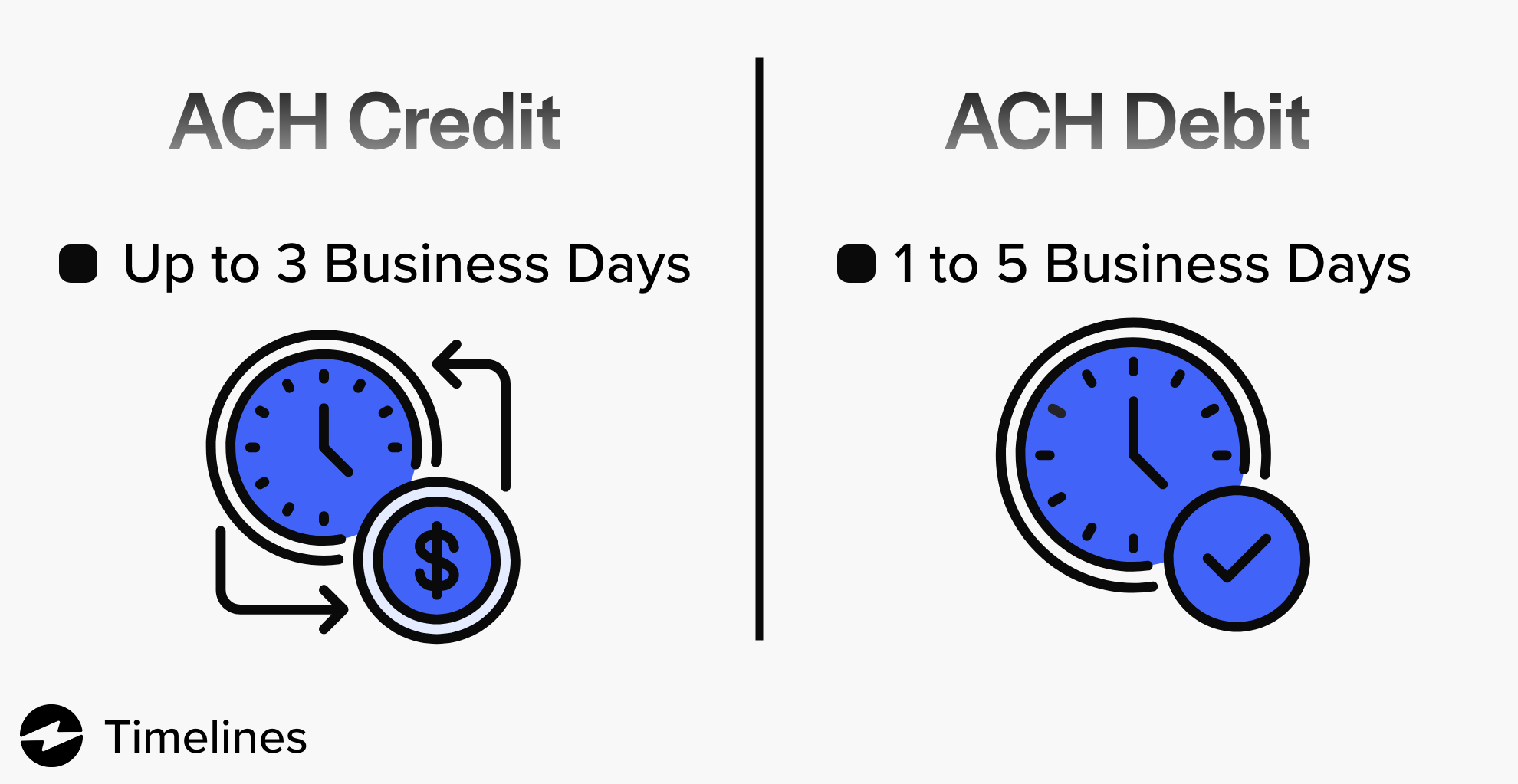
ACH credit processing timeline
For an ACH credit transfer, funds typically take up to three business days to become available in the payee’s account. Time frames can vary based on the bank involved and the time of day when the transfer is initiated.
Some banks have more efficient systems to process transfers quicker, while others may take longer. Initiation times can also delay these funds — if a transfer is initiated later in the day, it may take longer to deposit in the payee’s account. Weekends and holidays can also impact ACH credit processing times.
ACH debit processing timeline
For an ACH debit transfer, funds typically take one to five business days to become available.
The time the ACH file is initially submitted to the bank is important because banks may have different cut-off times for receiving ACH files. If a file is submitted after the cut-off time, the request will likely not be processed until the next day. Therefore, confirming specific cut-off times with your bank is imperative.
ACH debit payments can also fail due to incorrect file formats, insufficient funds in the customer’s account, and inaccurate payment details. To ensure your ACH debit is successfully processed, double-check all information and formatting before submission and check with your bank for any specific requirements.
Another factor to consider when looking into ACH payments are the various benefits they yield for your business and its customers.
4 benefits of ACH credit and ACH debit transfers
There are several benefits of ACH debit and credit transfers, such as transaction fees, processing times, security, and convenience. However, these benefits may vary depending on the type of ACH payment you’re using.
ACH credit and debit transactions can yield various benefits for businesses and customers, such as:
- Lower transaction costs
- Enhanced security and reduced fraud
- Added convenience
Lower transaction costs
ACH transfers are typically cheaper than other payment methods, such as wire transfers or credit card transactions. One of the reasons for this is that ACH transfers process their transactions in batches, allowing multiple transactions to process at once.
ACH transfers usually involve large transactions, meaning the cost per transaction can spread over a larger dollar amount. Therefore, ACH debit and credit transactions are cost-effective for transferring funds between bank accounts.
Although ACH costs can vary by the financial institution, ACH debit transfers generally accrue lower transaction fees than ACH credit transfers because they’re considered less risky. This is because ACH debit transfers require authorization from the sender before the transaction can occur, providing an additional layer of security that reduces the risk of fraud and chargebacks.
Enhanced security and reduced fraud
ACH credit transfers are safer than paper checks for a multitude of reasons. The main reason being there’s no physical check to be lost or stolen and, therefore, no risk of alteration or forgery.
On the other hand, ACH debit transfers have a lower risk of fraud than ACH credit transfers because the sender must provide authorization before the funds are transferred. This authorization can come in a signed agreement or recorded phone conversation, providing a clear trail of consent to verify the transaction’s authenticity.
Added convenience
ACH transactions are a convenient method of transferring funds as they eliminate the need for physical checks, reduce the risk of fraud and errors, and offer reliable processing. They’re also an excellent option for recurring payments, as they can be processed automatically to help to reduce the risk of late or missed payments.
ACH debit transactions can be more convenient for the payee since the payee initiates them, and the funds are automatically withdrawn from the recipient’s account. ACH credit transactions are also a convenient method of transferring funds since they’re simple to set up, processed quickly, and can be used for various payment types.
In addition to these benefits, you can assess the transactions you’re handling when deciding whether ACH debit or credit is a better fit. If you consistently take recurring payments, ACH debit may be the right option. Alternatively, ACH credits may be the right fit if you find yourself processing direct deposits of payroll and tax refunds.
Streamline your payment process with ACH payments
When it comes to ACH credit or debit transactions, both offer excellent options for businesses and individuals looking to quickly and efficiently transfer funds electronically between accounts.
ACH payments can streamline your payment process and improve financial management and performance. For a more seamless experience, you can use a reliable payment processor to process ACH transfers and provide quality service, enhanced security, advanced collection tools, and complimentary customer support.
 EBizCharge is the most robust ACH/eCheck solution on the market. Start collecting payments today.
EBizCharge is the most robust ACH/eCheck solution on the market. Start collecting payments today.