Blog > Your Ultimate Guide to Secure Payment Processing Systems
Your Ultimate Guide to Secure Payment Processing Systems
In today’s digital economy, securing financial transactions is more critical than ever. Whether you’re a small business owner or managing a large online store, protecting customers’ payment data is essential to maintaining trust and long-term success.
With cyber threats on the rise and consumer security expectations at an all-time high, implementing a secure payment processing system has become a foundational business requirement — not just a best practice.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about secure payment processing systems, from how they work and why encryption and tokenization matter to practical steps for avoiding chargebacks and choosing the best gateway.
Understanding and applying these concepts will allow you to protect your business while enhancing the user experience to foster lasting customer loyalty.
What are secure payment processing systems?
Secure payment processing systems act as a bridge between businesses and financial institutions to facilitate safe and efficient transactions.

These systems operate via secure payment gateways that transfer funds between merchants and financial institutions while protecting sensitive financial data, such as credit and debit card information.
With minimal transaction fees and strong data protection, secure payment solutions help build trust between merchants and their customers.
Payment processing systems with reliable security will also employ advanced encryption protocols and comply with regulatory requirements to guard against fraudulent activity.
How secure payment processing systems work
Since secure payment processing systems are vital technologies designed to safely manage transactions, knowing what protocols they enforce to protect data is essential.
Whether handling credit cards, debit cards, or Automated Clearing House (ACH)/eChecks, the focus is on secure payments that enhance customer satisfaction.
To meet evolving security standards, payment processing systems consist of numerous security methods, including encryption, tokenization, authentication, and various standard compliances.
Encryption
Encryption is integral to secure payment processing systems, ensuring all financial transactions are shielded from unauthorized eyes.
Encryption converts sensitive customer and payment data into a coded format during online transactions. This means that even if a malicious party intercepts the data, it can’t read it without the decryption key.

Encryption protocols safeguard payment details, like credit card numbers and bank account information, adding a robust layer of security.
Tokenization
Tokenization is a security measure that replaces sensitive payment information with non-sensitive tokens. It plays a significant role in preventing data breaches and fraudulent transactions by removing legitimate payment data from transactions.

When customers use credit or debit cards, the actual card numbers are substituted with a token. This token is meaningless to anyone without the decryption mechanisms set up by the secure payment gateway. Even if cybercriminals access the token, they can’t use it to perform unauthorized transactions.
In addition to improving security, tokenization technology simplifies compliance with regulatory standards by reducing sensitive cardholder data that businesses need to store.
Insecure systems lacking tokenization face greater challenges when protecting payment processor data and financial transactions.
Adherence to regulatory standards
Secure payment systems must adhere to various regulatory standards to protect sensitive data and ensure safe transactions.
These standards include:
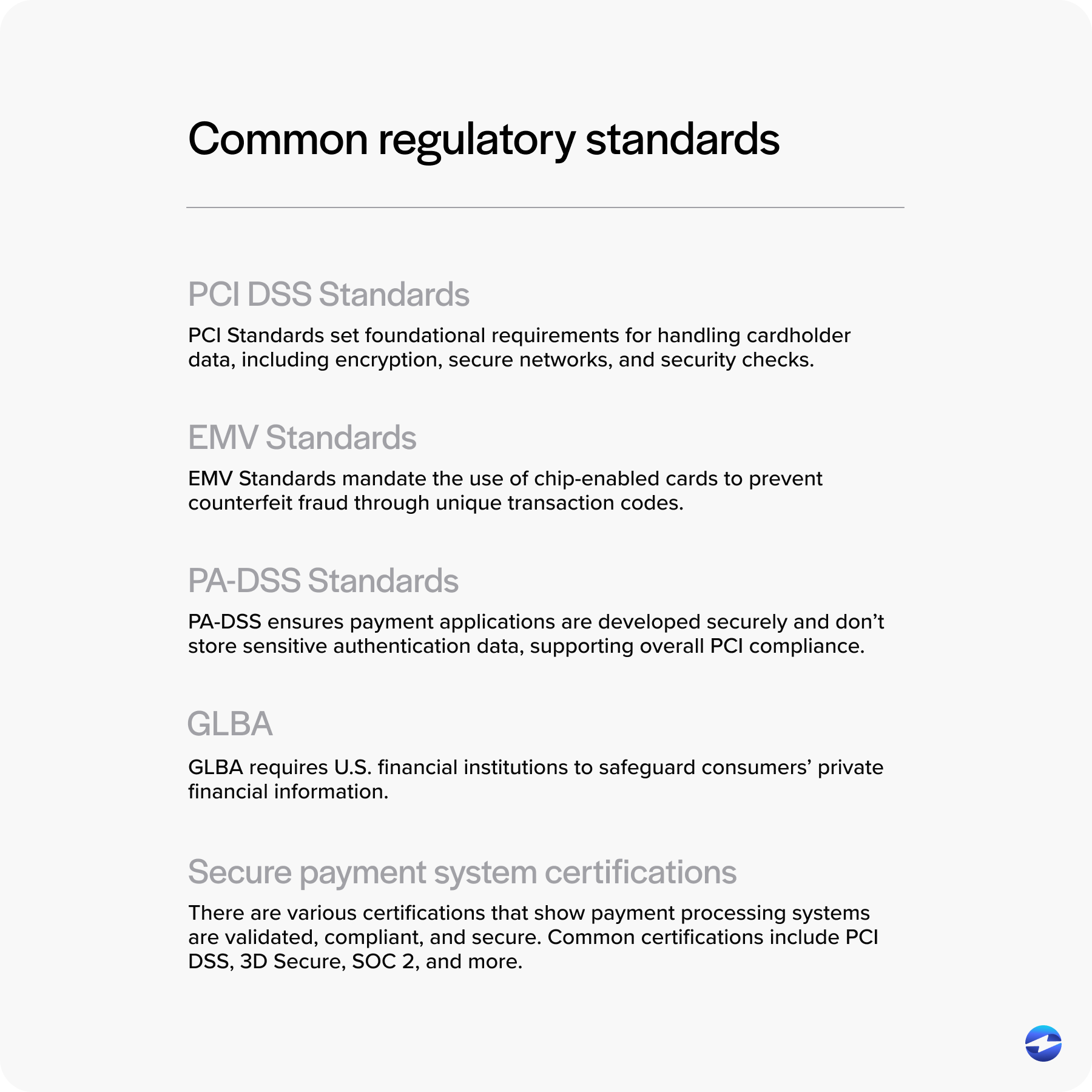
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS): PCI Standards set foundational requirements for handling cardholder data, including encryption, secure networks, and security checks.
- Europay, Mastercard, and Visa (EMV) Standards: EMV Standards mandate the use of chip-enabled cards to prevent counterfeit fraud through unique transaction codes.
- Payment Application Data Security Standards (PA-DSS): PA-DSS ensures payment applications are developed securely and don’t store sensitive authentication data, supporting overall PCI compliance.
- Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA): GLBA requires U.S. financial institutions to safeguard consumers’ private financial information.
- Secure payment system certifications: There are various certifications that show payment processing systems are validated, compliant, and secure. Common certifications include PCI DSS, 3D Secure (3DS), System and Organization Controls (SOC 2), and more.
International systems will likely be subject to additional standards and regulations.
Authentication mechanisms
Authentication mechanisms are essential components of a secure payment processing system, ensuring each transaction is authorized by a legitimate user.
Authentication goes beyond basic passwords to provide multiple layers of identity verification, helping merchants prevent fraud and protect customer data.
Popular authentication tools include:
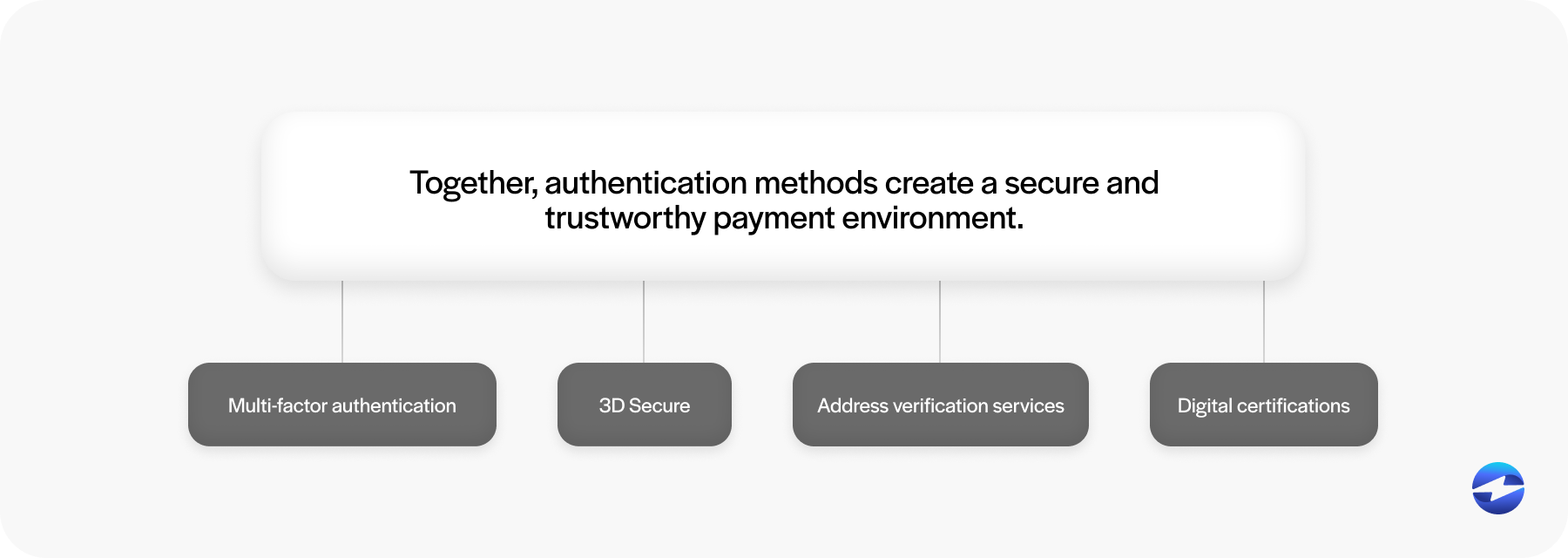
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): MFA requires users to confirm their identity using two or more different factors, typically a password and one-time code, sent via SMS or email. Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a popular authentication method for modern transactions, although more authentication factors may be required for industries with more stringent measures.
- 3D Secure: 3DS, developed by major card networks like Visa and Mastercard, prompts customers to complete an extra verification step for online transactions, such as entering a code or responding to an app notification, during checkout.
- Address verification services (AVS) are fraud prevention tools payment processors use to verify that customer billing addresses match addresses on file with credit card issuers. During a transaction, AVS verifies the numeric portions of the billing address (street number, ZIP code, etc.) to confirm the cardholder’s identity. If the information doesn’t match, the transaction may be flagged or declined to reduce unauthorized purchases.
- Digital certificates: Digital certificates verify the legitimacy of a website or payment gateway. Issued by trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs), these certificates enable Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) connections, encrypting sensitive data exchanged during a transaction. A padlock icon in the browser or a URL beginning with “https” will indicate a secure site to ensure customers that their payment information is handled safely.
Together, these authentication methods can create a secure and trustworthy payment environment to reduce fraud, protect data, and boost customer confidence.
With the proper parameters, secure payment processing systems can provide numerous benefits for businesses, including mitigating chargebacks.
How to avoid chargebacks
Chargebacks are disputes initiated by customers through their bank or credit card issuer, typically resulting in the reversal of a completed transaction.

While intended as a consumer protection mechanism (especially in cases of fraud or merchant error), chargebacks can pose significant and reputational risks for businesses.
Secure payment processing systems play a critical role in mitigating and managing chargebacks since these systems are equipped with features designed to detect and prevent fraudulent activity before a transaction is finalized.
For example, encryption protocols protect sensitive payment data during transmission, making it difficult for hackers to intercept or misuse information. MFA and biometric verification help ensure the authorized cardholder is initiating the transaction. Together, these tools reduce the likelihood of unauthorized transactions, which are a significant cause of chargebacks.
Secure payment systems also provide detailed transaction records and real-time reporting features, which can help merchants effectively respond to chargeback claims. A transparent and traceable transaction history allows businesses to present compelling evidence when disputing illegitimate chargeback requests.
For a secure payment experience, businesses should look for trusted payment gateway solutions with industry-compliant security features.
Securing your online store with a payment gateway

A payment gateway is an intermediatory between consumers and merchants equipped with technology to process online transactions safely and efficiently.
One of the primary advantages of using a payment gateway is its ability to encrypt sensitive customer data, which prevents unauthorized access during transmission.
Additionally, these systems are equipped with fraud prevention tools that help detect and block suspicious activities, reinforcing the integrity of the payment process.
Compliance with the PCI Standards is another crucial benefit, as payment gateways help ensure that your online store meets the necessary security requirements, particularly when handling credit card transactions.
Beyond basic security, payment gateways support multiple secure payment methods, including credit and debit cards, ACH/eChecks, and digital wallets. Many also incorporate advanced security layers such as 2FA and biometric verification, providing extra safeguards against cyber threats. These features collectively contribute to a secure and seamless payment experience for customers.
By integrating a reliable payment gateway into your online storefront, you not only protect your business from security breaches but also enhance the overall customer experience.
In addition to using a dedicated payment gateway, businesses should stay updated on best practices for secure payment processing.
4 best practices to deliver secure payment processing
Merchants must understand and implement best practices for secure payment processing to protect sensitive payment data and reduce data breaches and fraud.
The following sections will provide four best practices your business can apply to its payment security strategy.

1. Implement stringent security measures
First and foremost, any business collecting customer payments must incorporate the necessary security measures into its infrastructure.
Security measures like encryption and tokenization, 2FA and MFA, 3D Secure, biometric authentication, and more can safeguard transactions.
Encryption protocols convert sensitive payment details into a code format, making it hard for unauthorized parties to access them. On the other hand, tokenization replaces sensitive information with an unexploitable value or “token” outside the payment system.
MFA and/or 2FA enforce additional security layers that require users to verify their identities. While 3D Secure requires a password, SMS code, or biometric to verify the cardholder’s identity.
Lastly, biometric authentication uses unique biological traits to confirm the identities of authorized users.
2. Only collect necessary data
Collecting only essential information is another best practice in secure payment processing, as it limits the amount of sensitive customer data handled during transactions.
Minimizing data collection reduces the potential for data breaches since less sensitive payment information is available to hackers. Storing less data also aligns with compliance requirements.
Many financial institutions and regulatory bodies emphasize limited data storage to safeguard consumers. Reducing data collection minimizes risks and simplifies compliance with regulations.
Merchants should only ask for information required to complete a transaction and avoid storing unnecessary details such as excessive customer profiling data.
Proper data collection practices can foster more trust by giving consumers a better sense of security and protecting their sensitive information, thus encouraging more return purchases and brand loyalty.
3. Conduct regular system updates and patches
Routine system updates and patches are vital for maintaining secure payment processing and deterring malicious actors from exploiting vulnerabilities.
Software developers often release patches to address known weaknesses. By applying these patches, businesses set up robust defenses against potential threats.
Merchants should establish a schedule for routine system maintenance and assessments to allow for the timely application of updates and security patches. With this proactive approach, you can prevent cyberattacks and increase online payment security.
Regular maintenance also ensures that your system complies with evolving PCI, EMV, and other regulatory compliance standards. As a result, businesses and customers enjoy a worry-free payment experience.
4. Choose the right payment processor
Choosing a reliable payment processor is key to securing your payment processing system — a trustworthy payment processing provider will provide the necessary security software and measures to deliver seamless, secure transactions that enhance the user experience.
When deciding between providers, focus on the various payment security features they offer to see if they match your expectations. Processors with encryption tools, fraud detection, authentication measures, 3D Secure, PCI-compliant solutions, and other security protocols are more likely to protect your payments and sensitive financial data.
Customer reviews and industry reputation are also helpful to consider, as they can help your business determine a processor’s track record and gauge their reliability and commitment to secure payments.
Payment processors should also be compatible with your current infrastructure, support popular payments, and provide secure payment solutions that sync with top business systems to meet diverse needs.
Partnering with a reputable payment processor builds a secure foundation for your financial operations and can result in more efficient, safe transactions that enhance your overall success.
How EBizCharge delivers secure payment processing
EBizCharge provides a robust and secure payment processing system tailored to streamline payment operations for businesses of all sizes and industries.
By integrating seamlessly with 100+ existing platforms, including accounting, ERP, customer relationship management (CRM), and eCommerce software, EBizCharge simplifies the complexities of managing payments.
This top-rated payment processing solution supports various flexible payment options, including credit, debit, and ACH/eCheck payments, allowing businesses to meet diverse customer preferences.
At its core, EBizCharge employs advanced encryption and tokenization protocols, creating a fortified barrier against data breaches. The EBizCharge software is also fully PCI-compliant and provides features like offsite data storage, TLS protocols, fraud detection and prevention, chargeback management, and more.
EBizCharge is packed with comprehensive payment security features and payment collection tools that reduce the risk of fraud while elevating the invoicing experience for more consumer satisfaction. By securing transactions and automating key financial operations, merchants are free to focus on growth and operational efficiency.
In short, EBizCharge is a trusted partner in payment processing that strengthens security, streamlines invoicing operations, and enhances the overall customer experience.