Blog > What Are Embedded Payments?
What Are Embedded Payments?
How we pay for goods and services constantly evolves, from bartering to banknotes to modern times with digital wallets and embedded payments.
Embedded payments represent the latest frontier of integrating financial transactions into everyday software. Think Uber rides paid directly in the app or buying groceries using a smart fridge interface — that’s the power of embedded payments. This approach transforms industries, and knowledge of its workings is increasingly indispensable.

Therefore, understanding embedded payments is crucial for businesses and consumers alike as they offer a glimpse into the future of commerce.
What are embedded payments?
Embedded payments are the seamless integration of payment processing into business software to streamline financial transactions for users without redirecting them to external payment gateways.

Embedding payments means directly incorporating payment functions into a digital service or application. This integration enhances user experience by providing a frictionless payment method, allowing transactions within the app or a platform’s ecosystem.
What types of software can you embed payments into?
Numerous software systems can integrate embedded payment systems to improve functionality and user experience.
Businesses can embed payments into standard business software, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and accounting, eCommerce, Customer Relationship Management (CRM), and transportation systems.
ERP / Accounting
Embedding payments in ERP and accounting software enables businesses to manage their financial operations more efficiently.

By incorporating payment processing, these systems allow for direct invoicing and immediate settlement of transactions, enhancing cash flow management and financial reporting. This means companies can handle all aspects of their finances, from payroll to supplier payments, within a unified system, reducing the need for manual entries and minimizing errors.
eCommerce
The capacity to embed payment solutions is paramount for eCommerce platforms. Online retailers can process payments directly on their shopping sites, offering a streamlined checkout experience that can increase conversion rates.

By embedding payments, these platforms eliminate the disruption of redirecting customers to third-party payment gateways for faster and more secure transactions, which may increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
CRM
Embedded payments can be very beneficial when your business integrates them into CRM software.

With payment functions integrated, businesses can process and track payments within the context of their sales pipeline and customer interactions. This leads to a more cohesive understanding of customer behavior, as financial transactions are tied directly to client profiles and histories, enabling more personalized and efficient service offerings.
Transportation
Transportation software, crucial for coordinating logistics and fleet management, also reaps benefits from embedding payment capabilities.

For ride-sharing, freight billing, or public transport ticketing, embedded payments can facilitate immediate fare collection and processing, helping operators and passengers by offering convenient and efficient transaction methods.
Since there are many different outlets for embedded payments, it’s essential to know how these payments work.
How do embedded payments work?
Embedded payment systems offer financial services solutions within digital platforms, software, or mobile apps to accelerate and improve the transaction process.
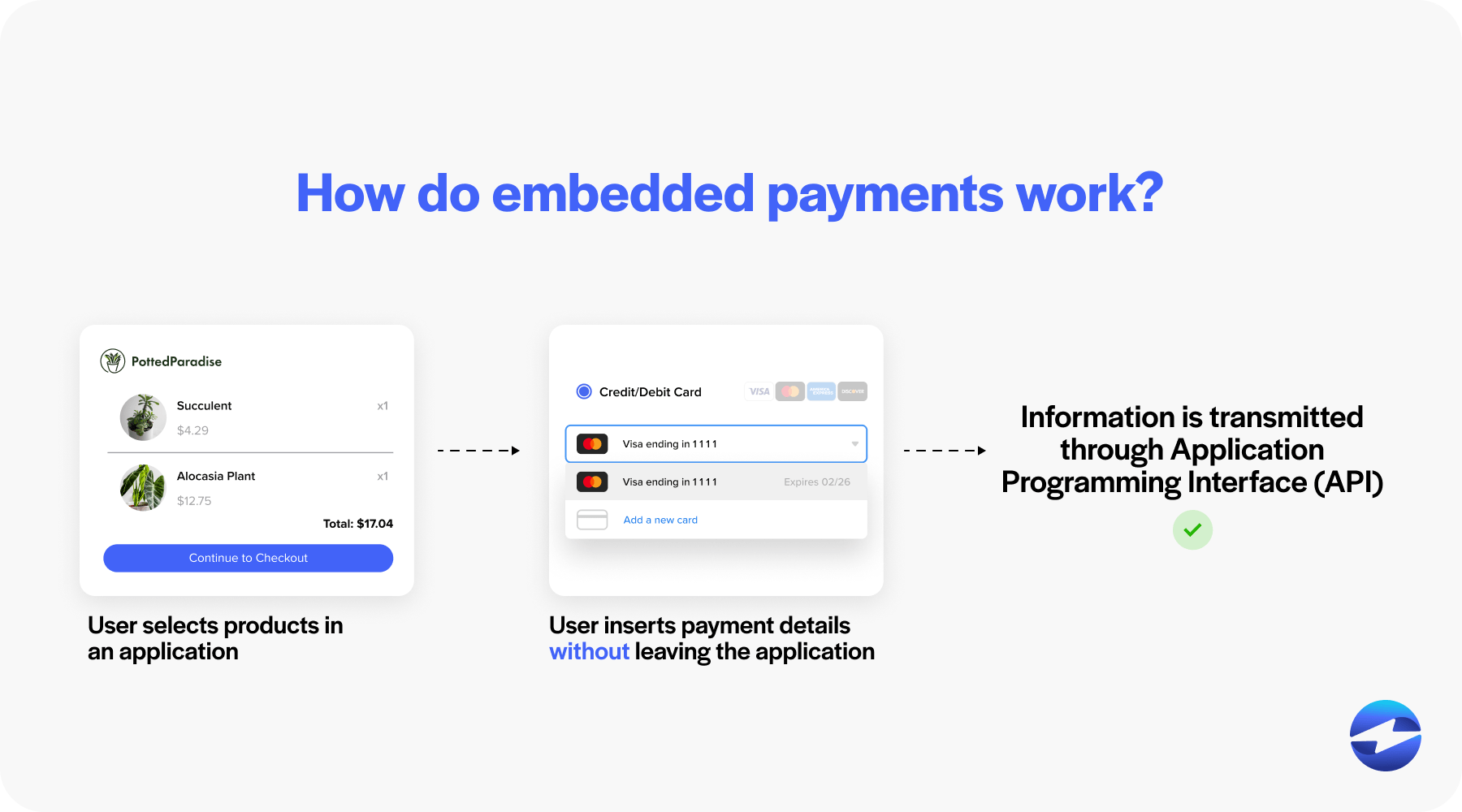
With an embedded payment, a user selects a product or service within an application. Users can input their payment details directly within the application rather than being directed to an external website or payment gateway to complete the transaction. This convenience is achieved through backend integrations that connect the app to payment processors.
Once a user confirms a payment, this information is transmitted via the payment form through the Application Programming Interface (API) to the payment processors who authorize and complete the payment. The result? A frictionless transaction that has the potential to bolster user satisfaction and loyalty.
APIs from payment providers are used in embedded payments to connect the app’s infrastructure to financial solutions that transfer secure funds. These payments ensure financial data protection via encryption and comply with banking services regulations.
Overall, embedded payments minimize the steps and time required to complete a traditional transaction to improve customer experience.
Real life application of embedded payments
To better grasp the power of embedded payments, the following examples will display different scenarios in which these payments are applied.
Example 1
A prime example of an embedded payment is the checkout process within a ride-sharing mobile app like Uber or Lyft.
When customers book a ride, their payment details are stored securely within the app. Upon reaching their destination, the fare is automatically charged to the customer’s pre-selected payment method without needing cash exchange or manual card swiping.
This method facilitates frictionless financial transactions, demonstrating a robust payment solution that can effectively boost conversion rates for businesses that adopt similar embedded payment systems.

Example 2
Embedded payment solutions also revolutionize transactions by integrating into non-financial environments – for example, a travel booking website.
When customers search for flights or hotels, they not only see the options available but also can book and pay for them directly on the website without being redirected to another platform.
This approach elevates user experience and boosts the travel company’s conversion rates by reducing the time and effort associated with standalone payment methods.
Embedded payments in such websites bridge the gap between digital platforms, payment gateways, and user-friendly financial solutions to cater to evolving customer payment preferences.
7 benefits of embedded payments
Embedded payments have become pivotal in expanding financial services within various business models, which can lead to multiple benefits across numerous industries.
Here are seven benefits of using embedded payments:

- Revenue growth
- Enhanced user experience
- Improved security
- Increased conversions
- Better insights and analytics
- Operational efficiency
- Reduced infrastructure costs
1. Revenue growth
Discrete payment solutions pose numerous friction points that can deter transactions, affecting a company’s profit generation. However, embedded payments offer new revenue streams by facilitating smooth financial transactions directly within digital platforms.
Embedding payments into the customer journey improves the ease of completing a purchase, which can lead to higher transaction volumes and revenue growth.
2. Enhanced user experience
Embedded payments transform the customer journey by eliminating disruptions, ensuring a seamless checkout process.
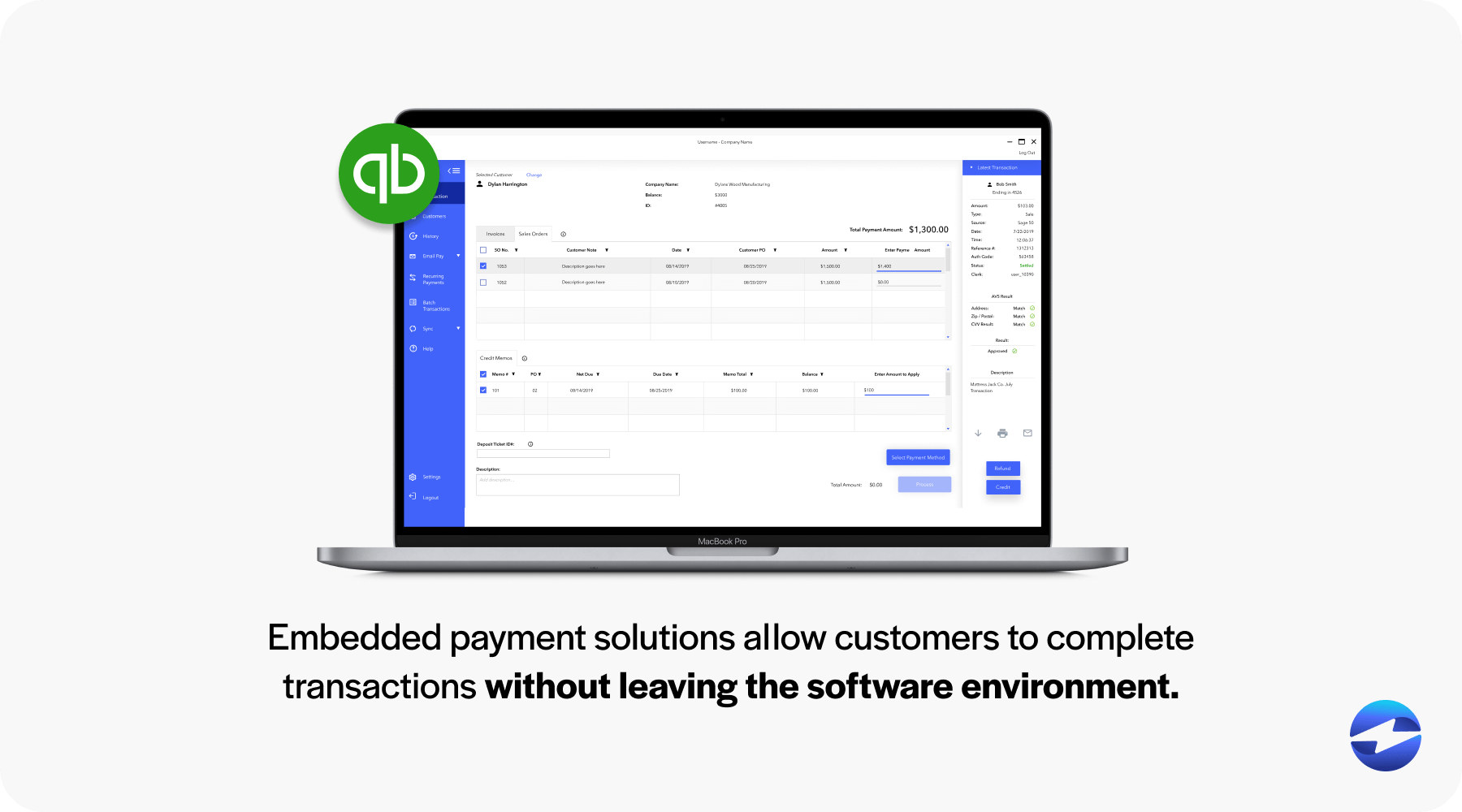
Embedded payment solutions allow customers to complete transactions without leaving the software or mobile app environment, resulting in a more intuitive and satisfying interaction. By prioritizing user experience, businesses can foster stronger customer relationships, leading to repeat business and referrals.
3. Improved security
Embedding payment processing into business software requires rigorous security protocols managed by specialized payment processors. Advanced encryption and compliance with strict financial standards can reduce the risk of data breaches and fraud.
Embedded payments also often leverage tokenization, where payment details are replaced with secure tokens, thus providing an additional layer of security for financial transactions. This minimizes the exposure of sensitive data, giving customers peace of mind.
4. Increased conversion rates
When customers arrive at the payment stage, a cumbersome process can result in cart abandonment. Embedded payments help boost conversions by simplifying the payment process.
Embedding payments reduce checkout steps and can quickly guide the user from selection to successful payment, which helps prevent potential drop-offs. A sleek payment form can significantly impact the decision to finalize a purchase.
5. Better insights and analytics
Integrating embedded payment solutions into a business’s digital infrastructure offers access to more in-depth transactional data. Companies leverage this data to understand purchasing behavior, customer preferences, and other critical metrics.
Enhanced analytics provided by embedded payments can inform strategic decisions for tailored marketing initiatives, product development, and personalized customer experiences, leading to more effective business growth strategies.
6. Operational efficiency
By embedding payment processing into existing operations, businesses can improve operational efficiency.
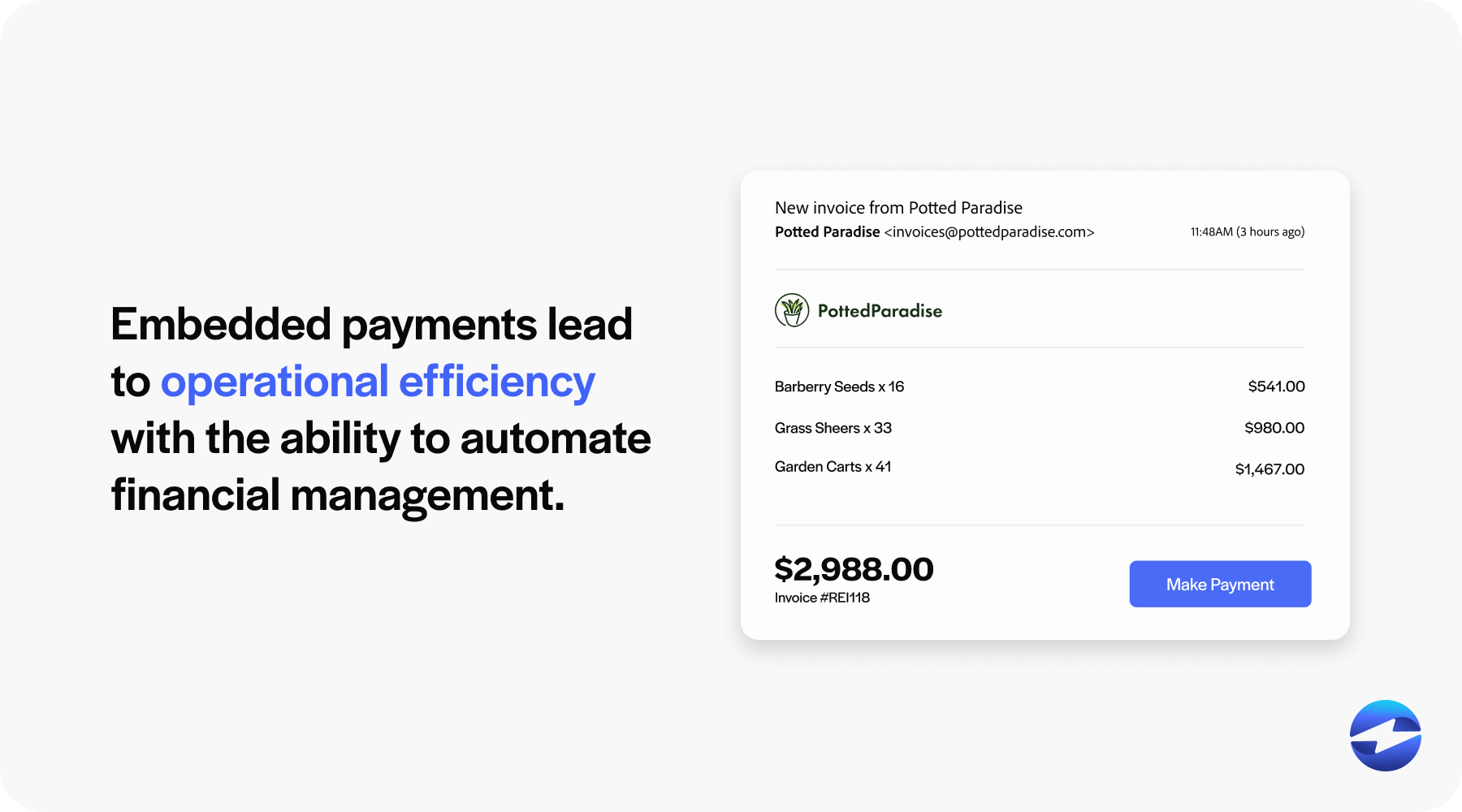
Embedded payments often automate several aspects of financial management, such as invoicing, billing, and reconciliation, thereby reducing manual interventions and errors.
Enhanced operations can lead to more accurate and effective business practices, freeing up resources that can be allocated to other growth-focused activities.
7. Reduced infrastructure costs
Businesses that implement embedded payment systems typically can invest less heavily in developing their payment processing infrastructure.
Payment Facilitators and gateways take on the burden of maintaining the payment ecosystem, thus saving companies from substantial capital investments and operational costs associated with standalone payment systems.
Furthermore, this can lead to significant savings in time and money, allowing resources to be invested back into essential business services.
In addition to the benefits embedded payments offer, there are a few payment models that offer embedded payments.
Embedded payment models
Embedded payment models define the various structural approaches businesses can employ to integrate payment processing capabilities into their products and services.
These models differ based on the levels of involvement and control the company has over the payment process, the extent of the required infrastructure, and the responsibility assumed in handling transactions.
The ISO Referral and Payment Facilitator models are two commonly adopted embedded payment models.
ISO referral model
The Independent Sales Organization (ISO) referral model is foundational for embedding payment functionalities into a business offering. In this model, a company partners with an established ISO, effectively acting as a referrer.
Upon successful referral, the business identifies potential merchants for the ISO and receives a commission for each customer lead, resulting in a new account. The significant advantage of the ISO Referral Model lies in the simplicity of the referring business being spared of the complexities of managing the payment process, as the ISO handles all aspects of payment processing, customer support, and compliance. This allows companies to leverage the ISO’s payment infrastructure without making substantial investments.
Payment Facilitator model
The Payment Facilitator (PayFac) model offers businesses more control over the payment process than the ISO referral model.
A PayFac is an intermediary between the merchant and the payment processors or acquiring banks. By adopting the PayFac model, a company becomes a mini acquirer, able to onboard clients, manage transactions, and assume a financial services provider’s associated risks and compliance responsibilities.
The PayFac model typically requires more substantial infrastructure investment and adherence to more stringent financial regulations. However, it can yield higher returns through transaction fees and presents an opportunity to offer value-added services to customers, enhancing customer relationships and satisfaction.
The difference between embedded payments and integrated payments
While both modern approaches to streamlining transactions, embedded and integrated payments differ in application and integration level.
Embedded payments are seamlessly incorporated within the service or product, meaning the payment process occurs without the user stepping out of the application or platform experience.
Integrated payments connect payment processing capabilities with other business systems like accounting, ERP, CRM, or eCommerce software. Still, integrated payments are more invisibly woven into the user journey than embedded payments.
Embedded payments enhance the user experience by making transactions almost unnoticeable, whereas integrated payments focus more on the efficiency and effectiveness of the business’s operational side.
| Feature | Embedded Payments | Integrated Payments |
|---|---|---|
| Integration Depth | Deeply incorporated into the product | Connected to external business systems |
| User Experience | Near-invisible transactions within platform | Simplified payment operations alongside usage the |
| Primary Benefit | Enhances customers satisfaction | Streamlines backend processes |
| Example Usage | Paying for a ride within a ride-sharing app | Processing a card payment through accounting software |
| Focus | End-user interface | Business efficiency and workflow improvement |
Embedded and integrated payments both have crucial roles in payment processing, but it’s important to understand when to use one over the other.
Optimize transactions with embedded payments
Embedded payments centralize financial transactions by syncing into software platforms for a more optimized user experience.
As the payments industry evolves, financial services are increasingly being integrated into mobile apps and websites to offer companies more unified user interfaces. With the right strategy, you can adopt embedded payment solutions to transform your business model and financial solutions.