Blog > Third-Party Payment Processing: What You Need to Know
Third-Party Payment Processing: What You Need to Know
If you’re running an online or brick-and-mortar business, you’re likely familiar with payment processing to accept and verify customer payments for goods or services. Did you know you can outsource payment processing to a third party?
Third-party payment processors can handle this process to relieve companies of the hassle of collecting payments in-house.
As businesses move away from traditional payment methods and embrace online transactions, third-party payment processors have become increasingly popular.
This article will explore the world of third-party payment processing, its benefits, risks, and top considerations when choosing a provider.
What is third-party payment processing?
Before diving further into the technical process, your company should understand the third-party payment processor definition and all it entails to help you decide if it’s right for your business.
Third-party payment processing is defined as a service that enables businesses to accept electronic payments from customers without having to establish their merchant account with a bank. It involves an intermediary (the payment processor) that collects payment information from the customer, processes the payment, and transfers the funds to the seller’s account after deducting a processing fee.
Third-party payment processing eliminates the need for businesses to worry about processing payments in-house or setting up a merchant account since processors manage incoming payments to simplify the accounts receivable (AR) operations.
While third-party payment processing may seem complicated, the technical process can be explained in a few steps.
The process of third-party payment processing
Luckily, third-party payment processing is much more straightforward than it sounds.
When customers make payments, their information is sent securely using the third-party payment gateway to the payment processor for verification. Once the payment is verified, the payment processor transfers the funds to your business bank account after deducting their processing fees.
This means your business doesn’t have to handle the payment process and can rely on the expertise and technology of the payment processor to handle the transaction for you.
It’s important to note that not all third-party payment processors work similarly. Some may hold the funds for a certain amount of time before releasing them to your account, while others may charge different fees depending on the type of transaction. Therefore, your business must conduct thorough research to choose a reputable and transparent third-party payment processor that meets its needs.
Despite many third-party processing services on the market, a few key players in the industry stand out.
Examples of third-party payment processors
Selecting a third-party payment provider is challenging, considering the many contenders in the payment processing industry.
To help your business narrow down its options, here are four of the top third-party payment providers to look into:
- EBizCharge
- PayPal
- Stripe
- Square
EBizCharge
EBizCharge provides many features, including online and mobile credit card processing, unlimited transaction history, customizable reports, electronic invoicing, secure encryption and tokenization, email payment links, a customer payment portal, and more.
EBizCharge has an abundance of integrations, including over 100+ integrations with accounting, ERP, eCommerce, and CRP software. Your company can accept payments directly within these integrations, providing a seamless customer payment experience.
With flexible and customized pricing plans, your company can be certain that you’ll be getting the fairest price. EBizCharge doesn’t have any hidden fees, cancellation fees, no long contracts, and price matching.
Not only are the prices of EBizCharge something that stands out, but their level of security is top class. In 2021, EBizCharge was awarded the best PCI compliance provider by the CNP awards, making sure their customer’s data was safely stored.
PayPal
For businesses needing a payment solution trusted by millions of users worldwide, PayPal is a popular choice. With its user-friendly interface and seamless integration with various shopping carts and invoicing software, PayPal can help you accept payments from customers across the globe. PayPal also offers advanced security features, including buyer and seller protection, to help you avoid fraudulent transactions and disputes.
Despite PayPal’s popularity, it does come at a price. PayPal’s fees are around 3% + $0.10 per transaction.
Stripe
If you’re looking for a robust payment gateway with a wide range of eCommerce integrations, Stripe is a solid choice. With its flexible API and developer-friendly tools, Stripe makes it easy to accept payments online and customize your checkout process. Stripe’s fraud prevention and dispute resolution features can help protect your business from chargebacks and other payment-related issues.
Like PayPal, Stripe has higher credit card processing fees. Stripe’s prices average 2.8% + $0.18 per transaction.
Square
Square is another popular payment gateway that provides many features and integrations to help businesses accept online and in-person payments with its user-friendly interface and easy-to-use tools. Additionally, Square’s advanced security features, such as encryption and two-factor authentication, help protect your business and customers from fraud and unauthorized access.
However, Square isn’t compatible with Windows desktops or tablets and only works on iOS and Android phones and tablets. This may be a dealbreaker for companies solely utilizing Windows for business practices.
For Square’s easy-to-use interface and tools, it comes at a higher price. On average, Square charges 3% + $0.18 per transaction.
Despite the various third-party processing options available, knowing if specific providers must be used in your industry or business is essential.
Are you required to use third-party payment processing?
While some companies handle payment processing in-house, many will use third-party payment processors to simplify payment collections and focus on other aspects of their business.
By outsourcing payment processing to a third party, corporations can avoid the need to build their payment infrastructure, which can be expensive and time-consuming. Additionally, third-party payment processors often offer various payment options, including credit and debit cards, ACH payments, digital wallets, etc. This can be especially important for businesses that operate in different regions or countries with other popular payment methods.
Whether or not you need a third-party payment processor depends on the size and complexity of your business. Small businesses with lower transaction volumes may handle payment processing on their own. Whereas mid-size and larger enterprises with higher transaction volumes may benefit from outsourcing payment processing to a third-party payment processor.
If you outsource these payment processing operations to a third party, your company can reap many benefits.
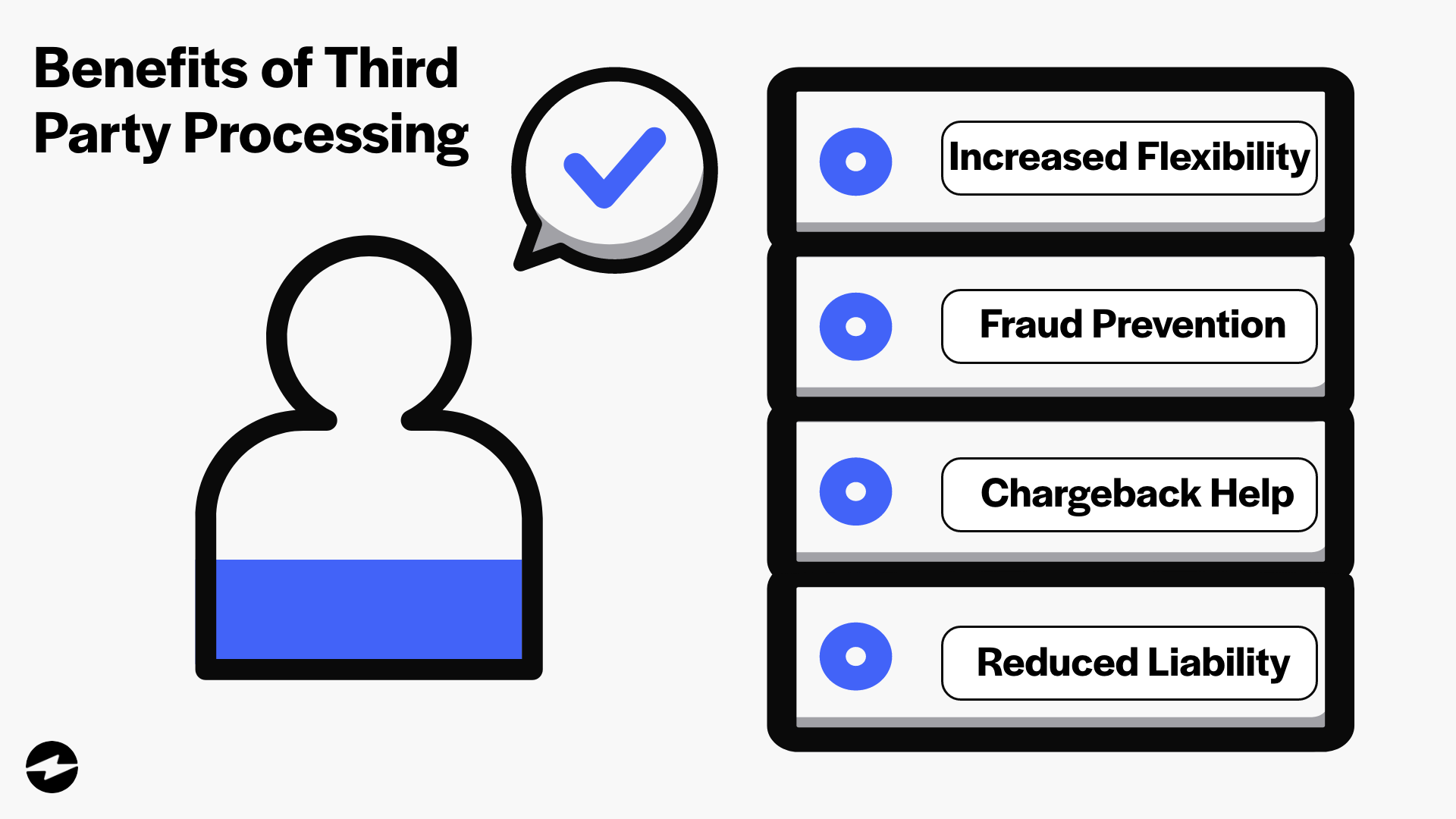
4 Main benefits of using a third-party payment processor
Using a third-party payment processor can offer several benefits for your business that can enhance payment security and improve the overall payment experience.
Here are four main benefits of using a third-party payment processor:
3rd party payment services
- Expanded payment options: Third-party payment processors typically offer various payment options, including credit and debit cards, ACH, mobile payments, and more. With more payment options comes more flexibility and ease for your customers.
- Fraud detection and prevention: Many third-party payment processors provide tools and services that utilize artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms synced with your company’s data to suggest rules and detect and block potential fraud.
- Chargeback management: If a customer disputes a charge, third-party payment processors often have services to manage the chargeback process. These services will generally be a team of specialists who will walk you through dispute management in real-time before they become an issue.
- Reduced liability: Outsourcing payment processing to a third party can reduce your business’s liability in case of a security breach or fraud.
While there are clear benefits to using a third party as your payment processor, there are also some risks associated with outsourcing these services.
The risks of using a third-party payment processor
Businesses must consider the risks of working with a third-party payment processor before deciding if it’s the right fit.
Common third-party payment processing risks include data security threats and too much dependence on providers.
Data security risks
One potential drawback of using third-party payment processors is the risk of data security breaches.
Processors store sensitive customer information, including credit card details and personal data. If your payment processor experiences a security breach or hack, this information may be compromised, leading to legal and financial consequences for your business.
Therefore, choosing a reputable payment processor with a reliable track record and advanced security measures is essential to minimize this risk.
Dependence on third-party providers
When you use a third-party merchant service provider, your business depends on the provider for payment processing. If your payment processor experiences downtime or technical issues, it may disrupt your business operations and lead to a loss in sales and revenue.
Since your business doesn’t have direct control over its payment processing system, choosing a trustworthy third-party processor is vital in minimizing disruptions.
It can be stressful trusting another company to handle your payment processing and customers’ confidential information. Thankfully, businesses can be at ease knowing many payment processors follow the Payment Card Industry (PCI) requirements and other security protocols to securely accept payments and apply high-quality payment software to streamline AR operations.
5 Things to consider when using third-party payments
When choosing between a third-party payment processor, businesses should evaluate features, functionality, pricing, and more to select the right one for their needs.
To help with this decision, here are five areas to consider when comparing third-party providers:
- Software integrations
- Hardware integrations
- Pricing
- Policies
- Support
1. Software integrations
Choosing a processor that seamlessly integrates with your existing software solutions, such as accounting and ERP systems and eCommerce platforms, can ensure an efficient payment processing experience for you and your customers.
Integrating your software solution with your payment processor can enhance and accelerate your payment collections and help you better manage your finances.
2. Hardware integrations
Hardware compatibility is an important consideration when selecting a payment processor, especially if you plan to accept in-person payments.
Finding a payment processor with card readers and terminals that are compatible with your devices and support the payment types you intend to accept is essential.
3. Pricing
Pricing is a major deciding factor when deciding on a third-party payment provider. Payment processing costs can include transaction fees, setup fees, and other charges.
Therefore, evaluating and comparing different payment processors’ prices will help to ensure you get the best value for your money. Many processing companies have hidden fees they won’t tell you about upfront, so it’s essential to ask the necessary questions to avoid them.
4. Policies
Reviewing payment processors’ policies on chargebacks, refunds, and dispute resolution is essential before signing up for their services.
Chargebacks occur when a customer disputes a charge on their card, which the card issuer reverses, causing the payment processor to return the funds to the customer. A payment processor’s policy on chargebacks should include the following:
- Clear guidelines on how chargebacks will be handled.
- The timelines for submitting chargeback disputes.
- Any fees associated with chargebacks.
Refund policies should also be reviewed to understand the timelines for issuing refunds, any fees associated with rebates, and the process for initiating a refund.
Lastly, dispute resolution policies outline how the payment processor handles disputes between the merchant and the customer and the steps involved in resolving such disputes.
Understanding these policies and others will help your business avoid unexpected fees and conflicts with payment processors.
5. Customer Support
Using a payment processor with reliable customer support, such as phone or chat support, is necessary to maintain efficient payment processing operations.
Support is vital, especially when encountering technical issues with the payment processing service. Merchant service providers with 24/7 in-house customer support are typically the best options for businesses. A responsive customer support team can help minimize disruptions or delays in processing payments and keep your business running smoothly.
Considering these factors and others will help your company select the best third-party payment system and service for your business model and customers.
Cracking the code of credit card processing pricing structures
Understanding the costs and fees associated with credit card processing and knowing the right questions to ask will help your business find the most cost-effective solution and avoid unnecessary fees.
With different payment processing companies come different pricing structures and fees.
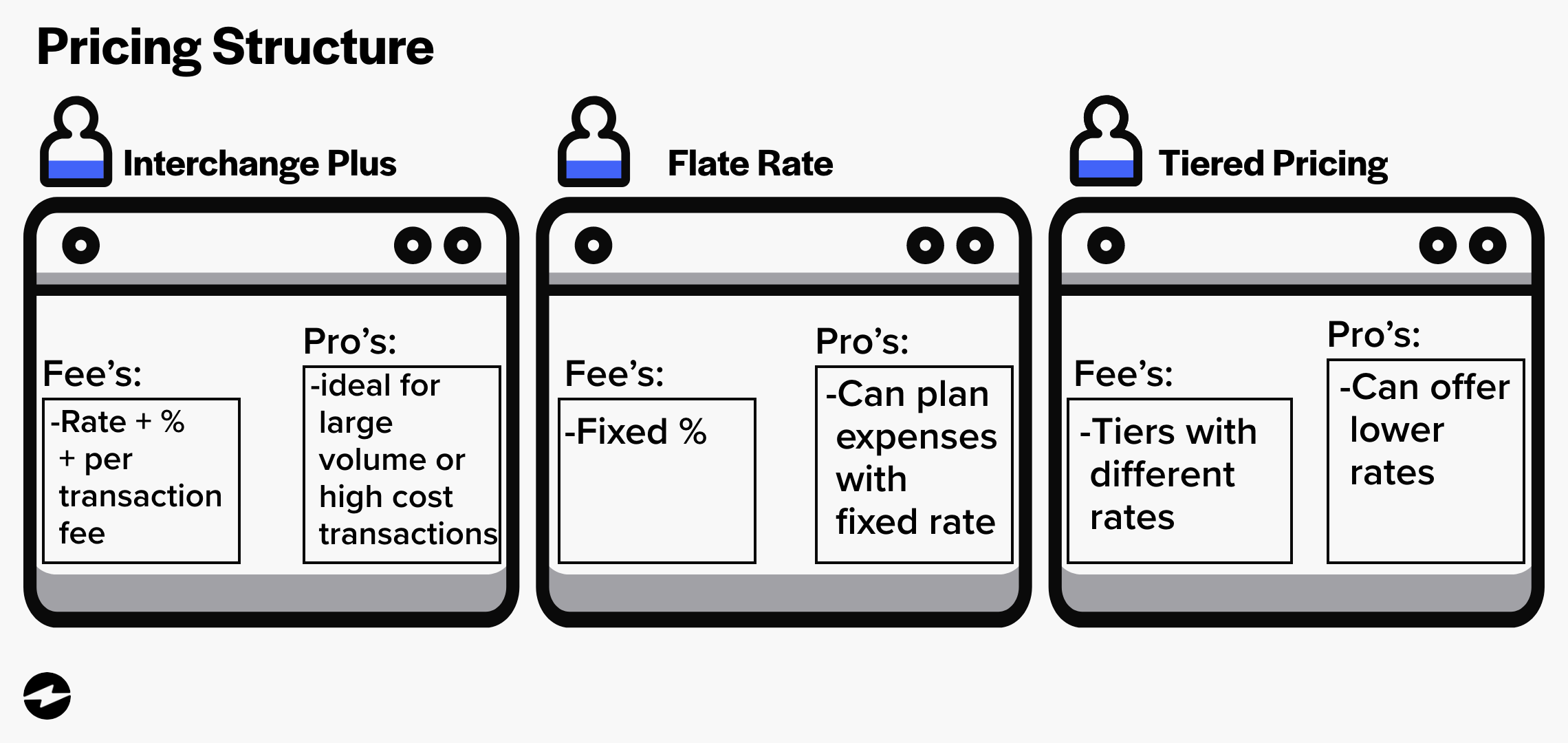
Typically, these costs will be broken down into interchange plus, flat rate, and tiered pricing.
Interchange plus pricing
With interchange plus pricing, businesses have a more transparent, upfront breakdown of costs to help them understand what they’re paying for.
Third-party payment systems charge a percentage above the interchange rate with this pricing model. The interchange rate is the fee set by major card brands — Visa, Mastercard, American Express, etc. — for using their payment network and is passed to the payment processor.
The payment processor’s percentage, added on top of the interchange rate, is typically a small percentage ranging from 0.2% to 0.5%. In addition to this percentage, the payment processor also charges a per-transaction fee. This per-transaction fee covers the payment processor’s operational costs, such as the cost of technology and infrastructure.
Interchange plus pricing is ideal for businesses that process a large volume of credit card transactions or have high average transaction amounts.
While interchange plus pricing is generally more transparent than other pricing models, there may be more cost-effective options on the market.
Flat rate pricing
With the flat rate pricing model, the payment processor charges a fixed percentage for every transaction, regardless of the type of card used or the transaction amount.
For example, if a payment processor charges a flat rate of 2.9% plus 30 cents per transaction, every transaction will be charged this same percentage and fee.
Flat rate pricing is beneficial because it’s easy to calculate and predict the fees for each transaction, making it more straightforward for businesses to budget and plan their expenses. Additionally, this pricing model can be advantageous for companies that process a large volume of small transactions, as the per-transaction fee is typically lower than other pricing models.
However, there may be cheaper pricing models for businesses that process more high-value transactions since other structures can charge a lower percentage for these payments.
Tiered pricing
Tiered pricing is typically more complicated than the interchange plus and flat rate pricing models.
Tiered pricing categorizes credit card transactions into different tiers, each with its own rate. Payment processors use various criteria to determine a transaction’s level, including the type of card used, the transaction amount, and the payment method (in-person or online).
The tiers involved in this pricing structure include:
- Qualified rate: The qualified rate is the lowest tier and is usually charged for standard credit cards.
- Mid-qualified rate: The mid-qualified rate is charged for transactions that don’t meet the criteria for the qualified rate, such as rewards or corporate credit cards.
- Non-qualified rate: The non-qualified rate is the highest tier charged for transactions not meeting specific criteria, such as manually keyed-in or international transactions.
While tiered pricing may offer lower rates, it can be more expensive in the long run since payment processors may categorize transactions as non-qualified to yield higher processing fees.
This pricing model can also be confusing and difficult to compare across different payment processors. Therefore, it’s essential to read the terms and conditions carefully to understand the criteria used for each tier and the associated fees.
Third-party payment processing for your company
Running a business comes with many challenges, especially when collecting payments efficiently and securely from your customers. Luckily, reliable and secure third-party payment processors can handle these operations to alleviate stress and allow your business to focus on other priorities.
A seamless and PCI-compliant third-party credit card processor like EBizCharge allows businesses to effortlessly and securely accept payments while protecting sensitive card data. With advanced security features, complimentary collection tools, robust reporting options, and more, EBizCharge provides an enhanced payment experience for your customers to easily make payments on time.
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions
Summary
- What is third-party payment processing?
- The process of third-party payment processing
- Examples of third-party payment processors
- Are you required to use third-party payment processing?
- 4 Main benefits of using a third-party payment processor
- The risks of using a third-party payment processor
- 5 Things to consider when using third-party payments
- Cracking the code of credit card processing pricing structures
- Third-party payment processing for your company
- Frequently Asked Questions