Blog > Understanding Accounts Receivable Forecasting
Understanding Accounts Receivable Forecasting
Understanding how to accurately forecast accounts receivable (AR) is essential for maintaining healthy financial operations. AR forecasting not only aids companies in planning their cash flow but also provides insights into customer behavior and payment trends. Factors like customer payment behavior, invoicing practices, and market volatility play significant roles in how businesses forecast receivables. By grasping these elements, organizations can refine their financial strategies and bolster their bottom line.
This article will explore the concept of accounts receivable forecasting, exploring its definition, influencing factors, and significance.
What does forecasting accounts receivable mean?
Forecasting accounts receivable (AR) refers to predicting future cash inflows from credit sales, allowing business owners to make informed financial decisions. This process involves estimating when outstanding invoices will be paid by analyzing key components such as historical sales data, payment terms, days sales outstanding (DSO), and market conditions.

Historical sales data provides insight into past trends to help predict future performance, while payment terms and DSO offer a clearer picture of how long customers typically take to settle invoices. Additionally, market conditions are considered to account for any external factors that might affect customer payments.
The benefits of AR forecasting include improved cash flow management, as it aids in planning for future financial needs, as well as accurate financial planning, which supports budget creation and strategic decision-making. It also helps maintain a better receivable balance by monitoring outstanding debts and ensuring a steady cash inflow.

It’s important to diligently track your AR, as there are numerous factors that can affect it.
6 factors that can affect accounts receivable
Understanding what influences accounts receivable is crucial for predicting future cash inflows. Being aware of these factors helps businesses make informed decisions and manage their cash flow effectively.
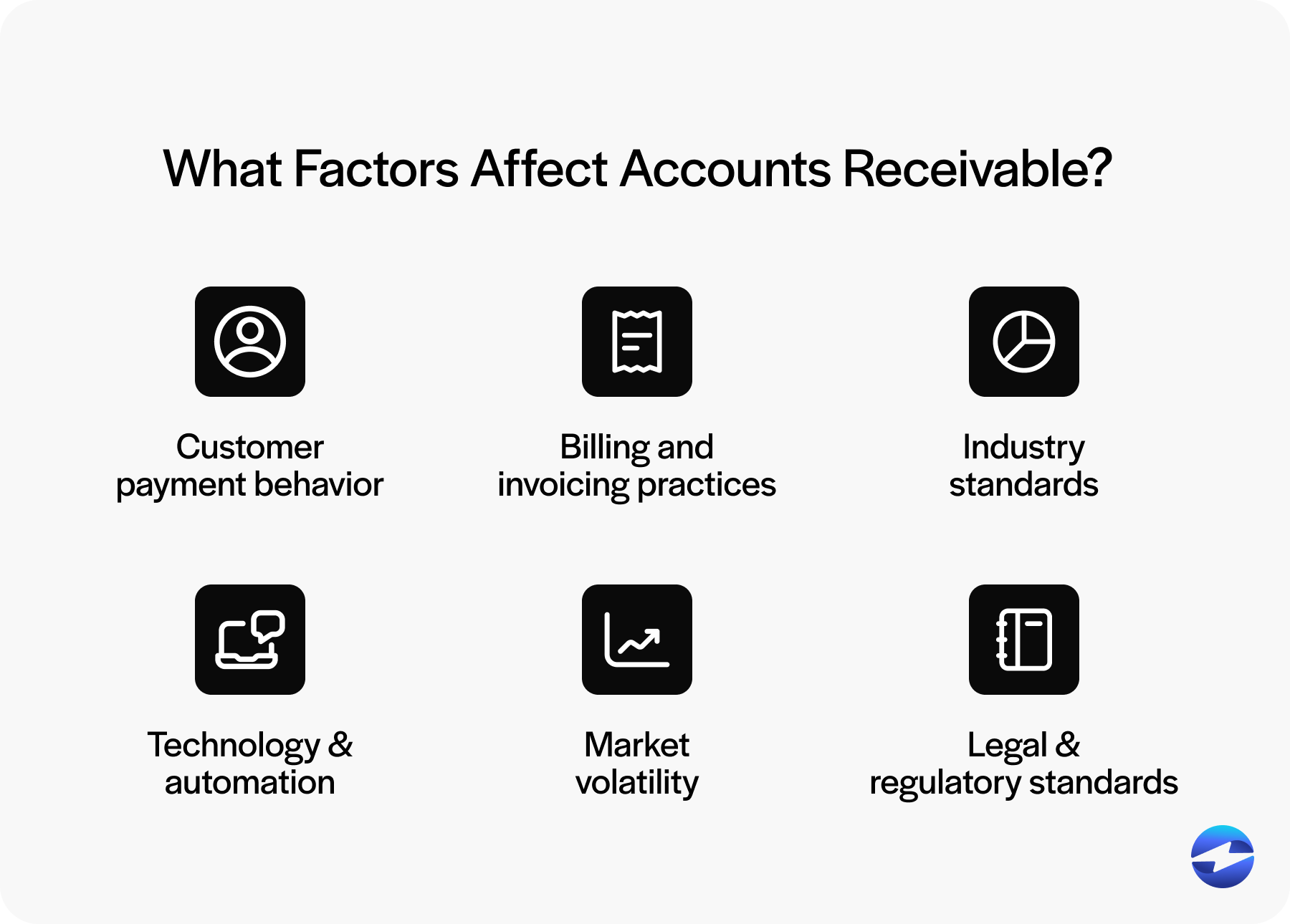
Customer payment behavior: Customer payment habits directly impact the receivable forecast. Some customers may pay on time, while others are delayed. Analyzing these behaviors helps create more accurate forecasts and better manage cash flow.
Billing and invoicing practices: Efficient billing and invoicing ensure timely payments. Inaccurate or delayed invoices can confuse customers and lead to late payments. Clear and prompt invoicing practices help maintain a healthy receivable balance.
Industry standards: Industry norms can guide payment terms and expectations. For instance, industries differ on how many days they allow for payment. Knowing these standards helps in setting realistic goals for accounts receivable and staying competitive.
Technology and automation: Advanced technology streamlines the collections process and improves forecast accuracy. Automated invoicing and reminders can speed up payments, reducing DSO and improving cash flow management.
Market volatility: Fluctuations in the market can affect how quickly customers pay invoices. Economic downturns may lead to slower payments. Monitoring market conditions allows businesses to prepare for changes.
Legal and regulatory standards: Laws and regulations can influence payment terms and collection processes. Compliance ensures that your business avoids legal issues that might affect receivable collection. It’s vital to stay updated with any changes in these standards for effective financial planning.
All of these factors can affect your accounts receivable turnover ratio, a metric that’s crucial to keep track of. The following section will explain how to calculate it.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: What is it?
The accounts receivable turnover ratio is a metric used to measure how efficiently a business collects debts from its credit sales, providing valuable insight into how well the company manages its accounts receivable. It’s calculated using this formula:
Receivable turnover ratio = Net credit sales / average accounts receivable
For example, if a company has net credit sales of $100,000 and an average accounts receivable of $25,000, the calculation would be $100,000 divided by $25,000, resulting in a turnover ratio of 4. This indicates that the company collects its average receivables four times per year.
How to calculate accounts receivable
Understanding how to calculate accounts receivable is vital for cash flow management and financial planning. Accounts receivable represents the money owed to your business from customers who made purchases on credit. Calculating this figure helps you forecast future cash flow and make informed decisions.
The basic formula for calculating accounts receivable is:
Accounts receivable = Total credit sales – payments received

Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Determine total credit sales: Sum up all sales made on credit within a specific time period.
- Subtract payments received: Deduct total payments received from customers during that period.
For example, if total credit sales in January amount to $10,000 and payments received total $3,000, the accounts receivable balance would be $7,000. This receivable balance is essential for projecting future cash inflows and managing outstanding invoices. By maintaining accurate forecasts, businesses can better control their financial health.
How to forecast accounts receivable
To create reliable forecasts, it’s essential to analyze key metrics, predict future sales, and apply the right formulas. A systematic approach ensures that your accounts receivable projections are both precise and actionable.
Here is a quick breakdown of how to forecast accounts receivable:
1. Understand and calculate DSO
The first step in forecasting accounts receivable is understanding Days Sales Outstanding (DSO). This metric tells you how long it takes to collect cash from credit sales.
Here’s how to calculate it:
DSO = (Accounts receivable / Total credit sales) x Number of days in period

A shorter DSO period is ideal. It indicates faster payment collection. Knowing your DSO helps you predict when future payments will arrive. Correctly calculating DSO supports your AR forecasting by estimating how quickly you’ll receive cash.
2. Forecast your sales
Next, you need to forecast your sales. Predicting future credit sales is essential for an accurate accounts receivable forecast. Start by analyzing historical sales trends. Consider market conditions and adjust for seasonal changes. You can use past sales data to make sales forecasts. A realistic sales forecast gives you a base for calculating future accounts receivable.
3. Use the accounts receivable formula
The final step is to apply the accounts receivable formula. Use the predicted sales and your DSO to forecast your future accounts receivable.
Forecast accounts receivable = (DSO / 365) x Sales forecast

This calculation will help you project your cash inflows.
By following these steps, you ensure precise and accurate forecasts. This will improve your financial planning and assist in effectively managing your business’s receivable balance.
The importance of forecasting accounts receivable
Accurate forecasting allows business owners to make well-informed decisions about financial planning and adapt to changing market conditions. Accurate forecasts provide stability and predictability by improving cash flow, enabling strategic planning through metrics like days sales outstanding and average accounts. Additionally, forecasting facilitates a more efficient collections process by identifying payment delays and allowing for timely interventions.
EBizCharge enhances accounts receivable forecasting through advanced analytics, customizable reports, automated alerts, and seamless integration with accounting software. Its advanced analytics provide valuable insights into credit sales and historical sales trends, while customizable reports enable precise forecasting tailored to specific financial periods. Automated alerts notify businesses of upcoming due dates and overdue invoices, helping reduce outstanding balances. Integration with accounting software simplifies the process by linking accounts payable and sales data, ensuring forecast accuracy. These features collectively support better financial forecasting and improved cash flow management.
