Blog > Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio: Understanding Its Significance and How to Calculate It
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio: Understanding Its Significance and How to Calculate It
Accounts receivable turnover ratio is a measure that determines the efficiency of a business’s payment collections process.
What is the accounts receivable turnover ratio?
The accounts receivable turnover ratio is a financial metric that measures how efficiently a company collects payment on credit sales. This ratio is essential for businesses to assess their ability to manage and collect outstanding accounts receivable in a given period.
By calculating the accounts receivable turnover ratio, companies can gain valuable insights into their cash flow and the effectiveness of their credit policies. This ratio provides a better understanding of the frequency with which your business collects outstanding payments and assists in making more informed decisions about credit terms and collection strategies.
Despite the many essential accounting ratios and calculations, the accounts receivable turnover ratio is critical in providing more clarity into payment collections.
Why is the AR turnover ratio important?
As 2024 brings many economic challenges, staying ahead of your finances is more important than ever. Therefore, tools like the accounts receivable (AR) turnover ratio are vital since it can have several implications for customer relations.
A high AR turnover ratio may indicate stringent credit policies, potentially straining customer relationships. Conversely, a low ratio could mean lenient credit policies, which may foster strong customer relations and result in delayed cash revenue.
Ultimately, the AR turnover ratio is crucial in understanding a company’s financial health, cash flow management, and customer relationships. Your business can calculate this ratio by following three simple steps.
How to calculate the accounts receivable turnover ratio
Understanding the AR turnover ratio calculation will set your company up for success by helping you determine if you need to make changes to avoid negative cash flow situations.
Your business can follow these three steps to calculate its AR turnover ratio:
- Determine your net credit sales.
- Calculate your average accounts receivable.
- Divide your net credit sales by the average accounts receivable.
Step 1: Determine your net credit sales
To calculate your net credit sales, start by adding your total credit sales. This includes all sales made on credit rather than cash or other forms of payment.
Then, subtract any returns or allowances from this total to reach your net credit sales figure. Returns are products that customers have returned for a refund, while allowances are reductions in the selling price of products due to defects or other issues.

Net credit sales = Gross Credit Sales – Returns – Discounts – Allowances
You can find this figure on your annual income statement or balance sheet, which should provide a breakdown of your sales and any adjustments for returns and allowances.
Step 2: Calculate your average accounts receivable
After retrieving the beginning and ending accounts receivable numbers from your balance sheet, the next step is to calculate the average accounts receivable (AR).
To do this, add the beginning accounts receivable to the ending accounts receivable and divide the sum by two. This will give you the average accounts receivable for the period you’re analyzing.
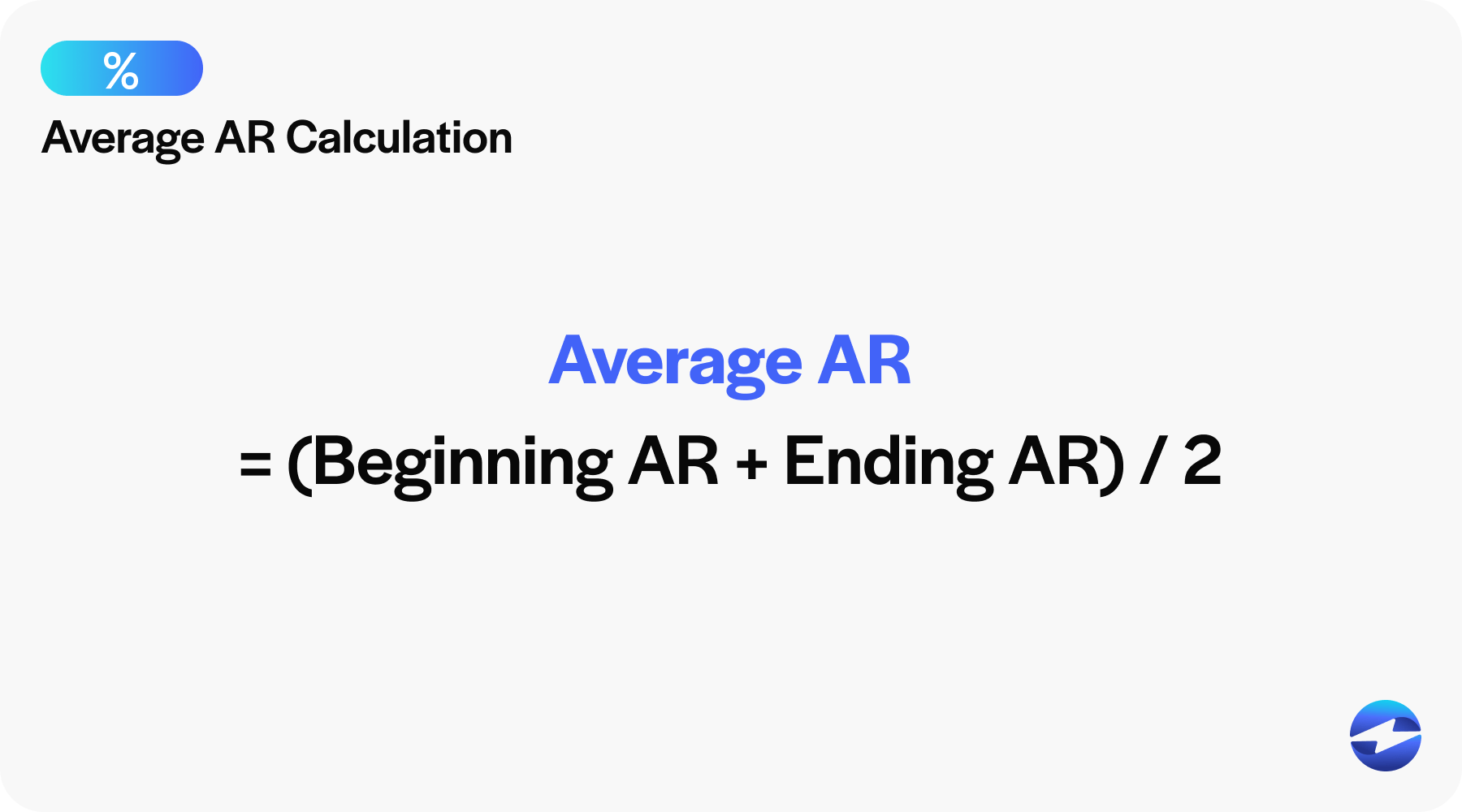
Average accounts receivable = (Beginning AR + Ending AR) / 2
For example, if your beginning AR is $50,000 and your ending AR is $70,000, you’ll add these figures to get $120,000 and divide by 2 to earn an average AR of $60,000.
Step 3: Divide your net credit sales by the average accounts receivable
The next step in calculating the accounts receivable turnover is to divide your net credit sales by the average accounts receivable.
After determining the net credit sales figure and calculating the average AR balance (using the first steps above), divide the net credit sales figure by the average AR balance to determine the accounts receivable turnover.

Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio = Net credit sales / Average accounts receivable
The following section will provide an example to show you how the accounts receivable turnover ratio works in action.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio example
In this example, Sal’s Supplies store is reviewing its finances for the year to determine its turnover ratio. Here’s the financial data it’s collected so far:
- Net credit sales: $500,000
- Beginning AR (on Jan. 1 or beginning of period): $58,000
- Ending AR (on Dec. 31 or end of period): $68,000
You can calculate Sal’s Supplies store’s turnover by inputting the above information into the average AR formula and the AR turnover formula:
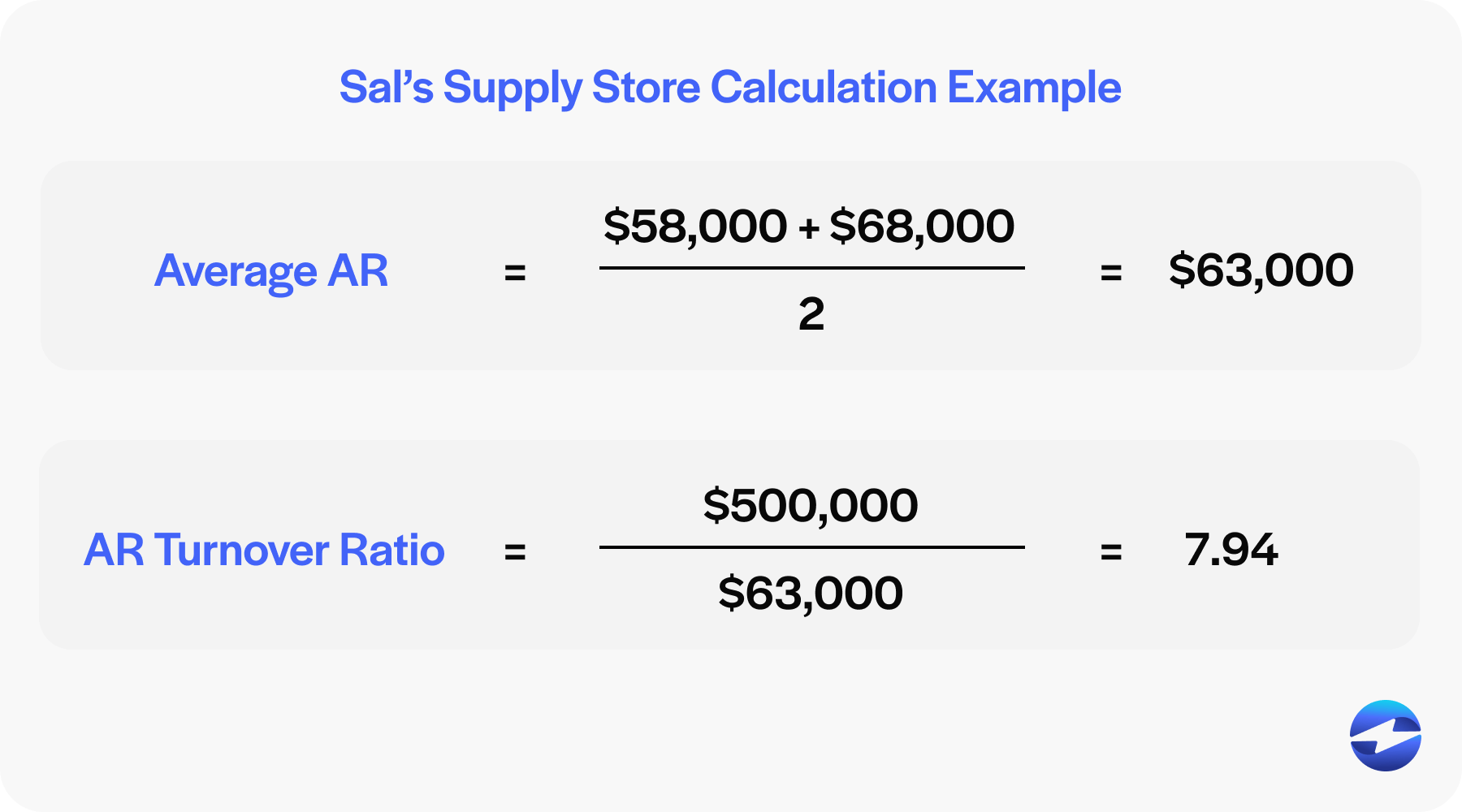
Average accounts receivable = ($58,000 + $68,000) / 2 = $63,000
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio = $500,000 / $63,000= 7.94
These results suggest that Sal’s Supplies received cash for its receivables 7.94x on average for that period of time.
Companies can conduct this annual, quarterly, or monthly financial analysis to better understand their AR turnover.
The AR turnover ratio can also be converted into days by dividing the AR turnover ratio by 365 (days in a year). This provides the same information as the first but gives companies a more specific picture of when they can expect to get paid by their customers.
Here’s how the AR turnover rate in days can be calculated for Sal’s Supplies:
AR turnover in days = 365 / 7.94 = 45.97
Therefore, Sal’s Supplies can expect its customers to pay their receivables within roughly 46 days.
Businesses can use the AR turnover ratio to compare their collection process efficiency to industry averages or competitors to see if any improvements are necessary.
High vs. low accounts receivable turnover ratios
Determining whether or not your AR turnover ratio is good is essential since this can indicate if your company effectively manages its credit policies and promptly collects outstanding debts.
High accounts receivable turnover ratio
A high accounts receivable turnover ratio typically suggests that a business efficiently collects customer payments. This can be attributed to several factors, such as strict credit approval requirements and ensuring that only customers with good credit history are credited.
Additionally, structured invoicing and payment processing systems help to streamline the billing and collection process. The business may also offer incentivized payment schedules to encourage customers to settle their accounts promptly.
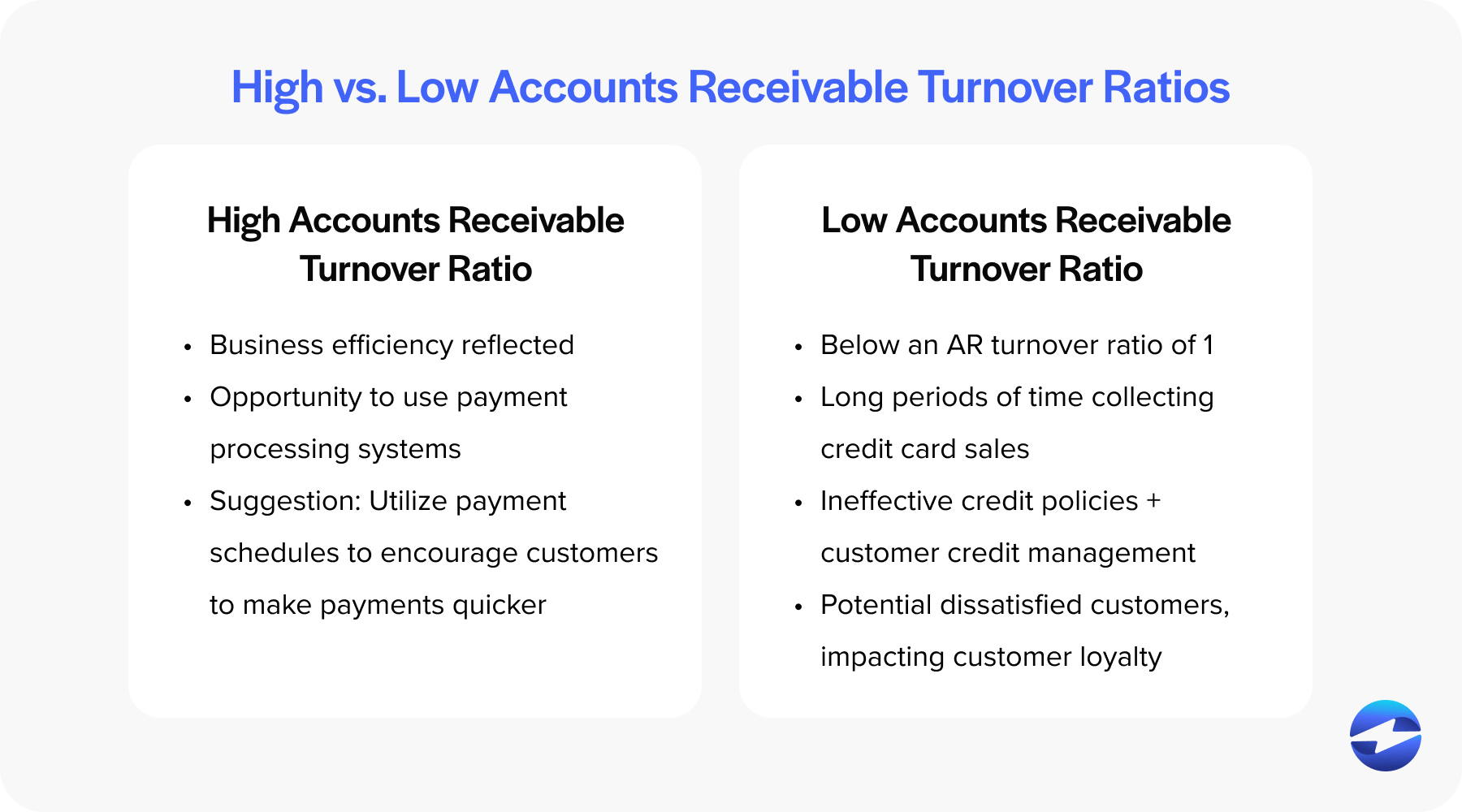
Low accounts receivable turnover ratio
A low ratio suggests that a business takes a long time to collect on its credit sales, which can lead to several operational disruptions. A low ratio is typically any value below an AR turnover ratio of 1.
Low AR turnover ratios can affect cash flow, as the delayed collection of receivables means less cash is available for day-to-day operations and investment. Additionally, it can signal ineffective credit policies and poor customer credit management, leading to potential bad debts and financial instability. It can also result in dissatisfied customers who may feel neglected or experience delays in their cash flow, impacting customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Industry averages for accounts receivable turnover ratio
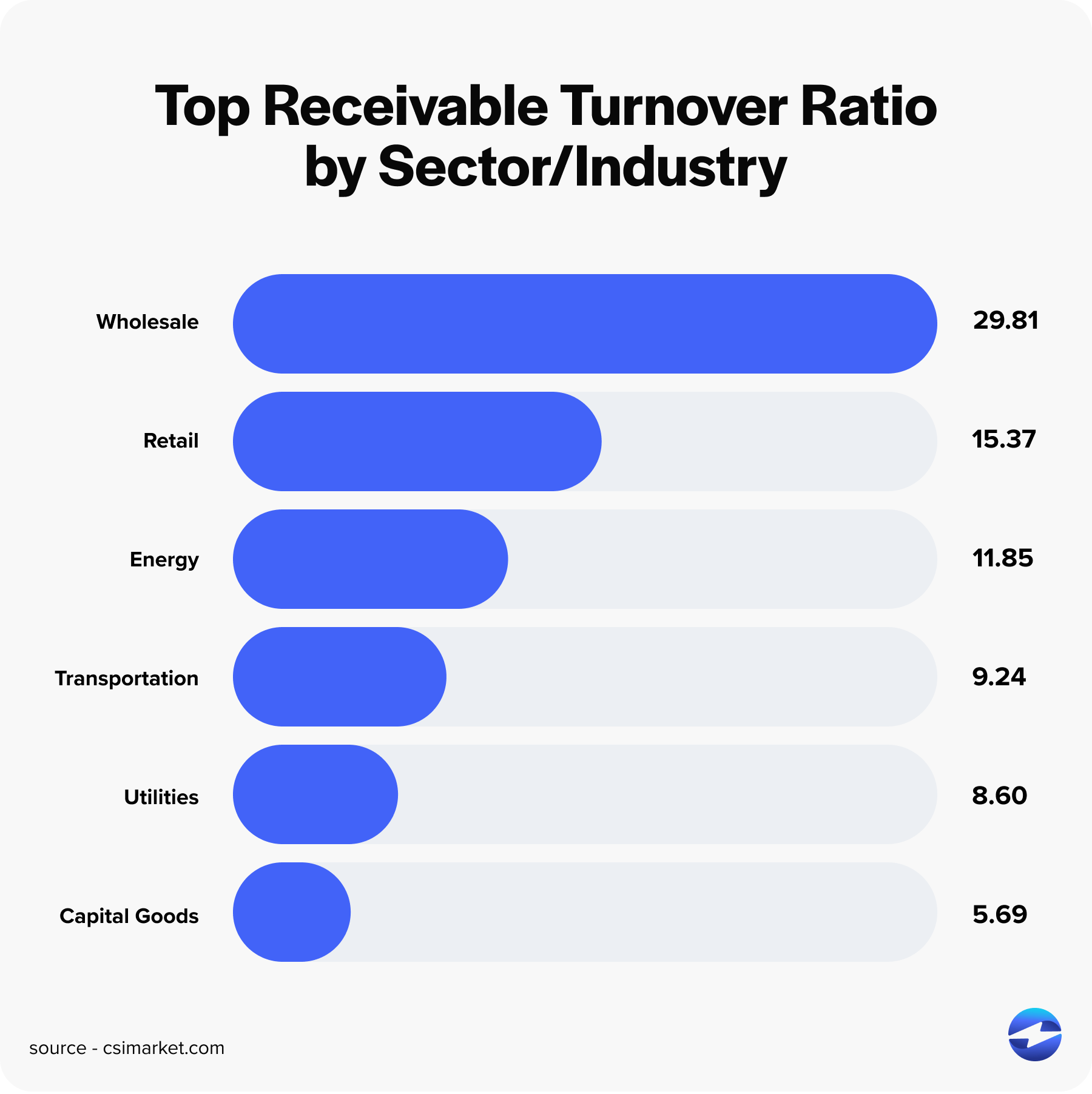
When evaluating your accounts receivable turnover, your industry’s average is a good baseline for your company to go off of.
Here’s a list of the top-ranking industries for AR turnover ratio in Q4 2023:
Regardless of the industry you’re in, the AR turnover ratio does come with some limitations.
AR turnover ratio limitations
Before using the AR turnover ratio, your business should be aware of the limitations associated with this formula.
The AR turnover ratio may be inaccurate if using total sales instead of net sales. Total sales include cash and credit sales, whereas net sales only include credit sales, providing a more accurate reflection of accounts receivable. Total sales could inflate the AR turnover ratio for businesses with significant cash sales.
Seasonal businesses also face challenges with the AR turnover ratio, as their accounts receivable tend to fluctuate throughout the year. This variation can skew the ratio, making it less reliable for year-round comparisons.
When calculating the average AR for the AR turnover ratio, choosing the correct beginning and ending values is essential. Incorrect values can result in misleading conclusions about a company’s collection efficiency.
While these limitations may be a challenge for your company to work around, there are several ways that AR automation can improve your turnover ratio.
4 ways automation can improve your AR turnover ratio
AR automation tools like EBizCharge are excellent software that can significantly improve the time it takes for your customers to pay you.
Here are four ways this AR automation software can enhance your AR turnover ratio:
- Improved accuracy and reduced errors
- Reminders are automatically sent before the bill is due
- Optimized payment collections workflow
- Accelerated invoicing and payment processing
1. Improved accuracy and reduced errors
Implementing accounting software with automated AR tracking can significantly improve the accuracy of the AR turnover ratio and reduce errors in the process.
By automating the monitoring of accounts receivable, the software can ensure all transactions and customer payments are recorded accurately and promptly to reduce the risk of errors with manual data entry and reconciliation.
Furthermore, AR automation software can provide real-time insights into the accounts receivable turnover ratio, accounts receivable ratio, and accounts receivable turnover in days, allowing businesses to make informed decisions based on up-to-date information. With these real-time insights into the accounts receivable aspect of the company, businesses can better strategize how to receive payments from their customers.
Businesses can also reduce the time and effort spent on manual tasks to focus on more high-priority tasks. This can improve efficiency and productivity within the finance department.
2. Reminders are automatically sent before the bill is due
Setting up an automatic reminder system can be a game-changer in ensuring timely customer payment.
Using your billing system, you can schedule reminders to be sent a few days before the due date, giving customers enough time to settle their bills. This not only streamlines the payment process but also minimizes the risk of late payments.
3. Optimized payment collections workflow
Incorporating AR automation software and efficient collection procedures can significantly optimize your payment collections workflow.
Automated AR platforms can help with timely follow-ups on overdue invoices and simplify the payment collection process. This software offers many payment features that seamlessly integrate into invoicing software for companies to avoid collection issues and streamline their workflow. Efficient collection procedures, such as offering discounts for early payments, can also incentivize customers to pay on time.
Streamlining collections workflows can also improve your cash flow and reduce days sales outstanding.
4. Accelerated invoicing and payment processing
Accelerating invoices and payment processing operations is essential in improving your AR turnover and ensuring timely customer payments.
An efficient payment gateway is key to accelerating payments, as it enables customers to use credit cards, debit cards, and eChecks to pay in person, over the phone, online, and on the go. Gateways should typically provide multiple payment methods to expedite the payment process, such as credit cards, debit cards, eChecks, and digital wallets.
Finding a gateway provider with robust payment integrations can further streamline invoices by syncing with your company’s accounting or ERP software to allow you to process payments directly inside this system.
Tools like online portals or automated reminders can also speed up the collection process and improve customer satisfaction.
Other tips to improve your AR turnover ratio
It’s evident that an automated AR system can drastically transform your AR turnover ratio, but other strategies can also significantly improve this ratio.
Implementing transparent payment terms and offering discounts can enhance your AR turnover rate by ensuring more timely payments, better cash flow, and fewer late payments. These terms and incentives can increase financial stability, strengthen customer relationships, and optimize working capital.
Businesses can further improve their AR turnover by consistently communicating with customers to quickly address discrepancies and reinforce payment expectations. Incorporating a regular invoicing schedule can also prompt faster and more accurate payment collections.
If your company struggles with customer payments and AR turnover, you can follow these tips to get paid faster and more efficiently.
Mastering AR turnover ratio to enhance your financial performance
Mastering your accounts receivable turnover and company finances isn’t the easiest task. Thankfully, valuable formulas like the AR turnover ratio and automated payment processing software like EBizCharge can assist in transforming your payment collections and revenue.
For the most effective financial performance, your business should regularly review its finances and AR turnover figures and implement reliable AR software systems and powerful strategies to increase cash flow, reduce late invoices, and enhance overall financial operations.
Summary
- What is the accounts receivable turnover ratio?
- Why is the AR turnover ratio important?
- How to calculate the accounts receivable turnover ratio
- Accounts receivable turnover ratio example
- High vs. low accounts receivable turnover ratios
- AR turnover ratio limitations
- 4 ways automation can improve your AR turnover ratio
- Mastering AR turnover ratio to enhance your financial performance
 EBizCharge is proven to help businesses collect customer payments 3X faster than average.
EBizCharge is proven to help businesses collect customer payments 3X faster than average.