Blog > Is Accounts Receivable an Asset or a Liability?
Is Accounts Receivable an Asset or a Liability?
Collecting customer payments can often be a challenging and time-consuming process for businesses. Dealing with various payment terms, managing customer credit, and reconciling payments can require substantial administrative effort. Accounts receivable serve as a critical financial function that helps simplify and streamline collection efforts. This article will explain the nature of accounts receivable, including key AR performance metrics and why AR is listed as an asset rather than a liability on the balance sheet.
Is Accounts Receivable an asset?
Accounts receivable is considered an asset, not a liability. Accounts receivable are assets that represent amounts owed to a company by its customers for goods or services that have been delivered or used but not yet paid for.
What is Accounts Receivable
Accounts receivable (AR) represents a company’s financial claims to payments for goods supplied or services rendered on credit terms. When a company provides goods or services to its customers without immediate payment, it creates an invoice detailing the amount owed. This invoice amount contributes to the company’s accounts receivable.
As an element of the balance sheet, AR is considered a current asset, not a liability, since it represents funds expected to be received by the company. Generally, these are short-term receivables due within one year, making them liquid assets. They’re essential for evaluating a company’s immediate financial positions, such as the accounts receivable turnover ratio and Days Sales Outstanding (DSO).
Assets vs. Liabilities: What’s the difference?
Assets and liabilities are fundamental concepts in accounting, distinguishing a company’s financial position on a balance sheet. Assets represent things of value owned by a company that provides economic benefit, either now or in the future. Assets are categorized as either current assets, like cash and accounts receivable, or non-current assets, such as machinery, real estate, or intellectual property. These can further be classified as liquid (easily convertible to cash) or fixed assets, like equipment. Liabilities, on the other hand, signify the company’s debts or obligations that arise during business operations and are settled over time through the transfer of economic benefits such as money or services.

Now that you understand what accounts receivable is, you should understand how this tool improves everyday collection processes.
Accounts receivable: A critical asset on your balance sheet
Unlike long-term assets like real estate or tangible assets such as machinery, accounts receivable typically convert into cash quickly, contributing to a company’s liquid assets. AR is integral in assessing a company’s financial position as it indicates pending income, which can directly influence cash flow. Here are a few ways AR streamlines the payment collection process:
Stabilizing cash flow and working capital
Accounts receivable play a pivotal role in stabilizing cash flow and managing working capital, which is the lifeblood of any business. The cycle of selling goods or services on credit and then collecting payment dictates the rhythm of cash inflows. Consequently, punctual payments from receivables ensure consistent cash flow and help maintain stable working capital levels.
An imbalance in accounts receivable, such as poor cash flow due to unpaid invoices, can hamper operational efficiency. By making informed decisions, like extending credit only to customers with good credit scores or through credit checks, a business owner can mitigate risks associated with bad debt expenses while optimizing cash flow.
Active receivable management, facilitated by receivable automation software, allows firms to forecast cash flow accurately, plan for future expenditures, and make strategic business decisions, contributing to a solid financial footing.
Building strong customer relationships
Beyond numbers, effective accounts receivable management is crucial for fostering healthy customer relationships. Granting credit terms is often a sign of trust between the business and its clients. When a company offers services on credit, it allows the client to pay after delivery, which can improve customer satisfaction and loyalty. High Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) might indicate that a company is lenient with payment terms, which can enhance relationships but could risk the financial position due to unpaid invoice balances. Striking a balance is key, as maintaining customer goodwill while ensuring that payments are collected promptly is an art that smart receivables management can achieve.
Decreasing collection expenses
Efficiently managing accounts receivable can lead to a decrease in collection expenses. Bad debt and the time spent chasing down unpaid invoices tie up resources and can be costly for businesses. By employing stringent credit policies, consistently following up on receivable balances, and using automation software for reminders and collection processes, companies can reduce the cost associated with recovering debts.
Moreover, a business with a low accounts receivable turnover ratio can take steps to improve it, thus reducing bad debt expenses and enhancing its cash position without incurring additional collection costs. By focusing on reducing bad debt expenses and enhancing its cash position without incurring additional collection costs.
Now that you understand the importance of healthy accounts receivable management, you should also familiarize yourself with the metrics used to measure AR performance.
Understanding AR performance metrics
Performance metrics are essential tools companies use to measure the efficiency and effectiveness of their accounts receivable processes. These metrics provide insights into how well the company is managing its credit sales and collections, which, in turn, affects its liquidity, cash flow, and overall financial health. By monitoring and analyzing these metrics, business owners can make more informed decisions, identify areas for improvement, and safeguard the company’s financial position.
The collection effectiveness index (CEI) is a measure of a business’s ability to collect funds from its customers. It’s calculated by comparing the amount of receivables a company has successfully collected during a specific period to the amount of receivables available for collection at the beginning of the period, including any new sales on credit. The CEI is presented as a percentage, with a higher percentage indicating more effective collection practices. This index helps a company evaluate the effectiveness of its AR collection policies and practices over time.
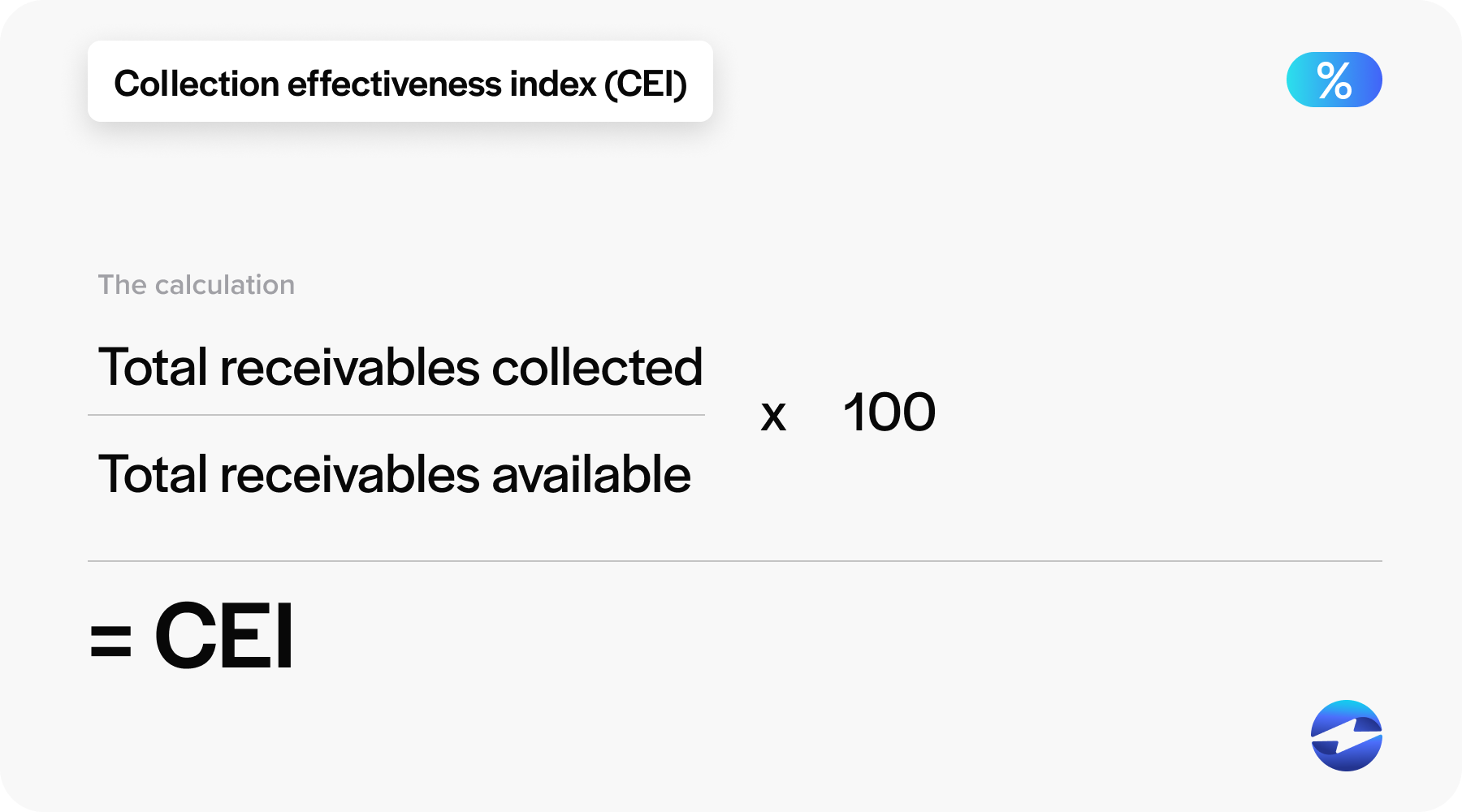
CEI = (Total receivables collected/ total receivables available) x 100
Days sales outstanding (DSO) is a common metric used to measure the average number of days it takes for a company to collect payment after a sale has been made. It provides insight into the length of time a company’s cash is tied up in receivables. DSO is calculated by dividing the total receivable balance by the total credit sales and then multiplying the result by the number of days in the period. A lower DSO value indicates that the company is collecting receivables more quickly, which is generally a sign of good financial health.
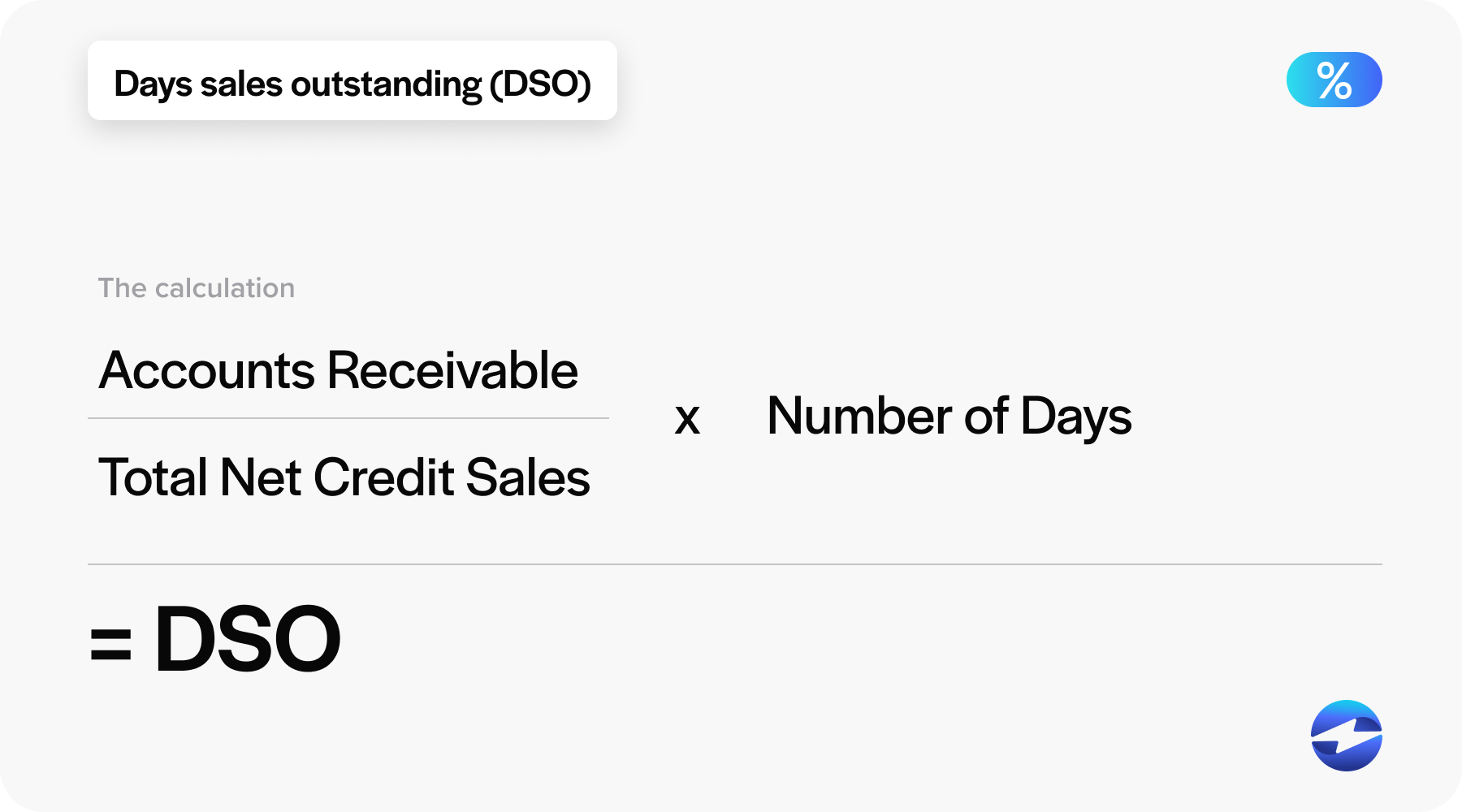
DSO = (Accounts receivables/ total credit sales) x number of days
Average days delinquent is a metric used to assess the average number of days that pass before unpaid invoices are settled. This measure is critical for business owners to understand how efficient their receivable processes are and to identify issues related to poor cash flow that may stem from late payments.
To calculate this metric, one would typically add the number of days invoices are overdue for a given period and then divide it by the total number of invoices issued during that time. Average days delinquent is a crucial component when examining the days sales outstanding (DSO), which is another key indicator of a company’s accounts receivable management effectiveness.
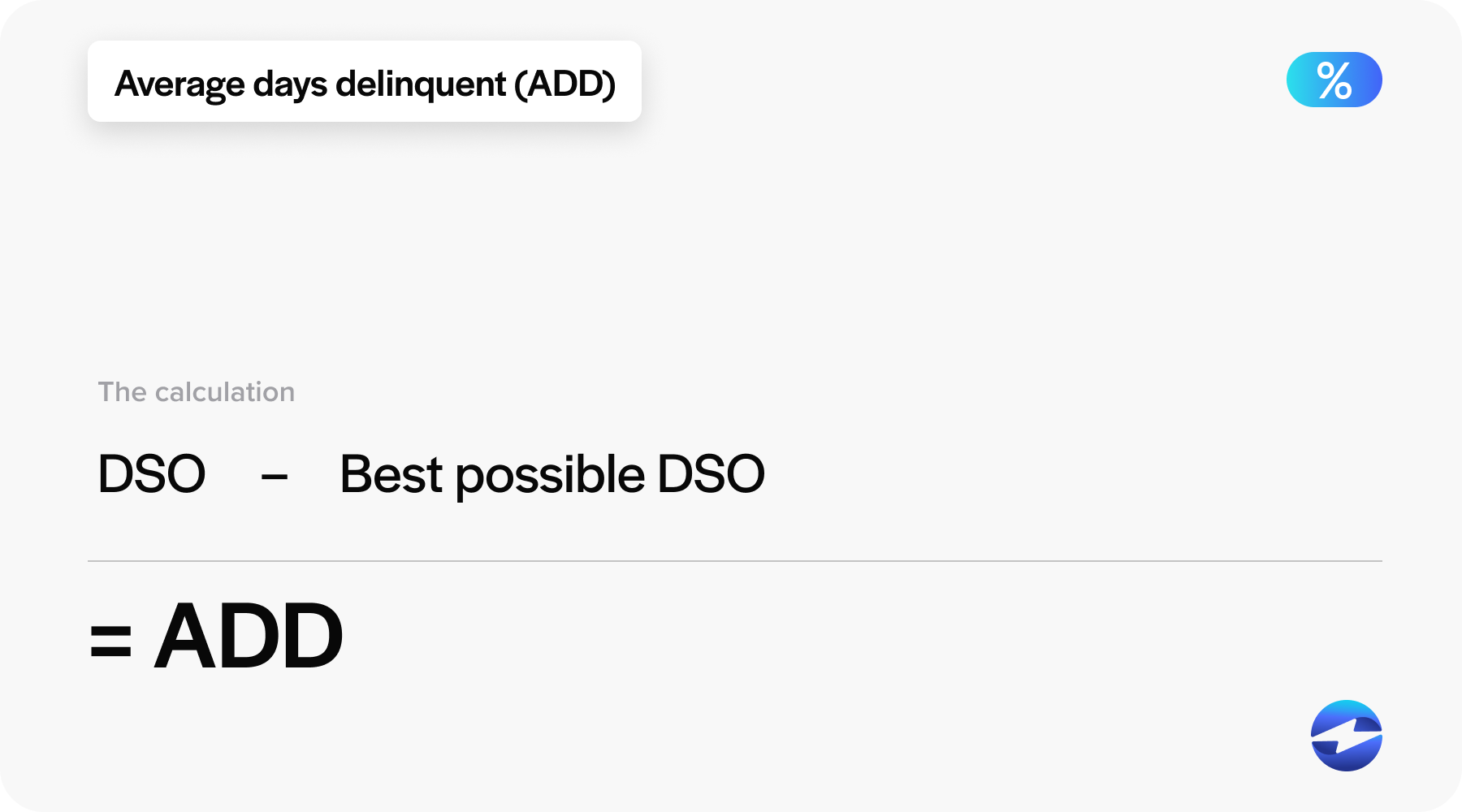
ADD = DSO – Best possible DSO
The bad debt to sales ratio quantifies the relationship between the amounts written off due to non-payment and the total sales over a given period. It’s an important financial ratio highlighting the percentage of revenue that can’t be collected. This ratio is critical for assessing the impact of bad debts on the company’s profitability and for evaluating the effectiveness of credit policies and risk management practices.
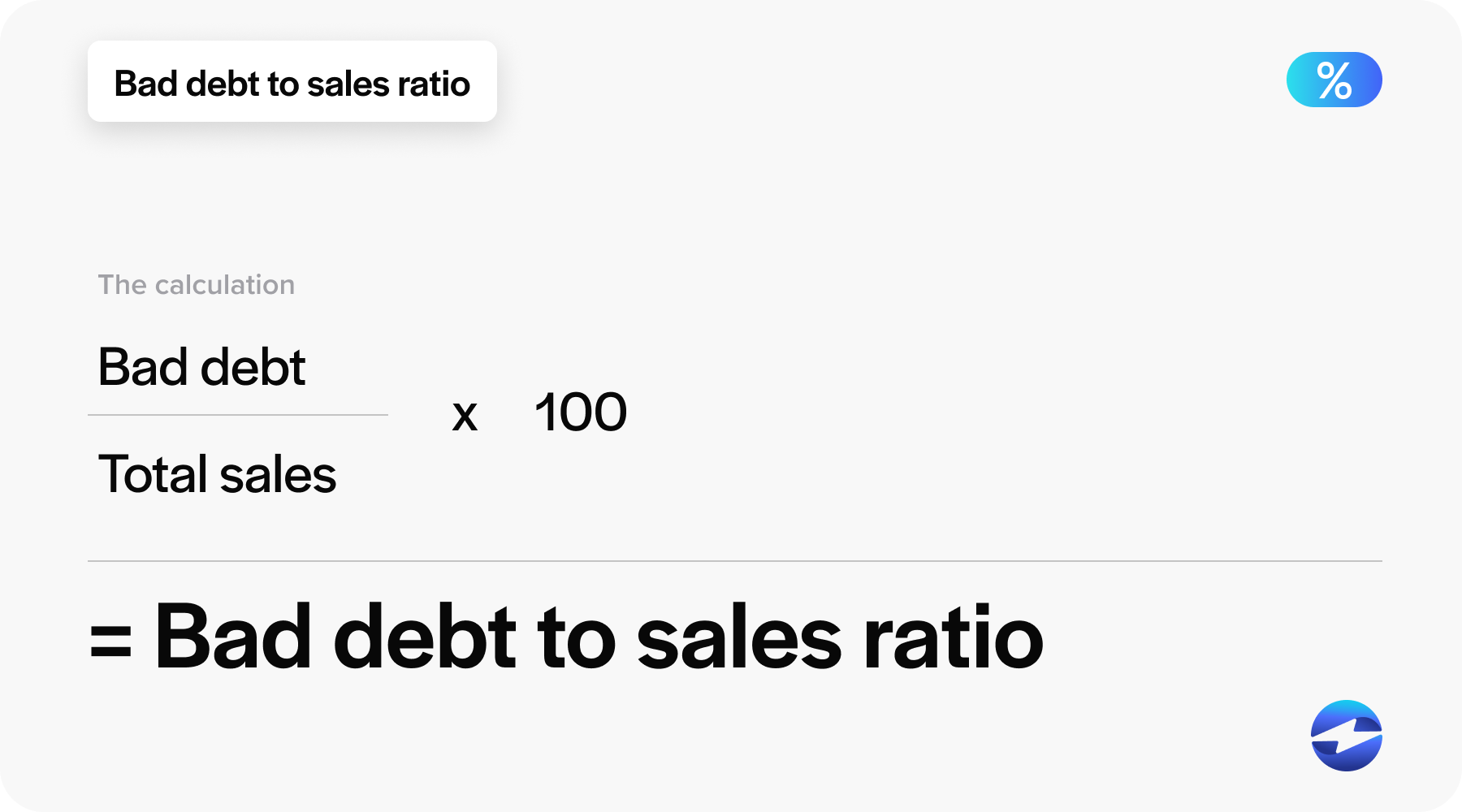
Bad debt to sales ratio = (bad debt/ total sales) x 100
The percentage of high-risk accounts metric identifies the proportion of receivable accounts that have a greater risk of non-payment. Identifying such accounts allows the company to monitor these risks more closely, adjust credit terms as necessary, and implement strategies to mitigate potential bad debt expenses. Maintaining a low level of high-risk accounts is indicative of strong credit management and stable financial operations.
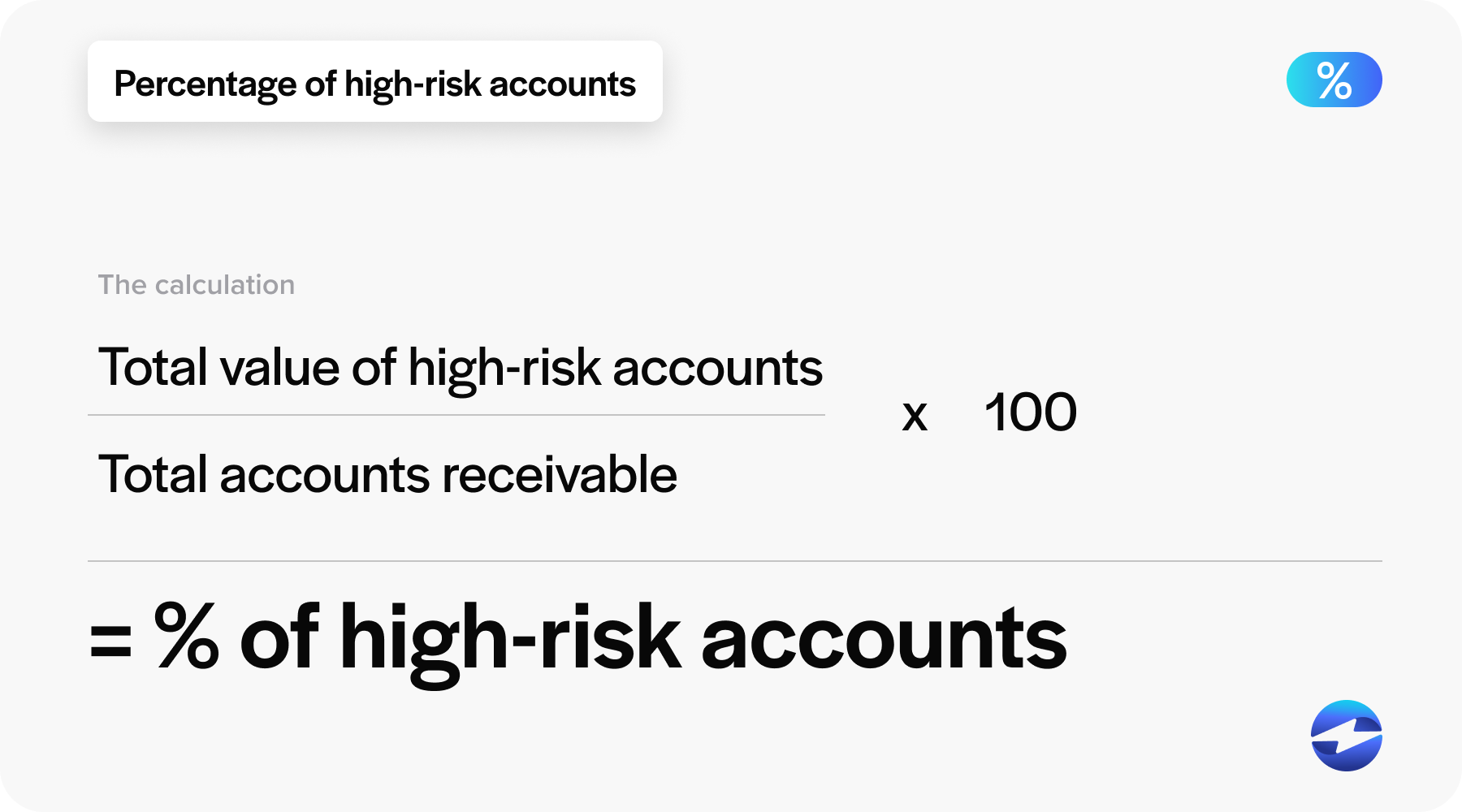
Percentage of high-risk accounts = (total value of high-risk accounts/ total accounts receivable) x 100
By effectively tracking these metrics, businesses can take proactive measures to address potential issues in their accounts receivable processes, improving cash flow and reducing the chances of accumulating significant bad debt.
Streamlining accounts receivable with EBizCharge
EBizCharge offers a robust and comprehensive solution for streamlining and simplifying accounts receivable management. By automating key processes such as invoicing, payment reminders, and collection efforts, EBizCharge minimizes the manual workload and reduces the risk of errors. Its seamless integration with various business systems
allows for real-time tracking of payments and easy reconciliation, enhancing overall efficiency. The platform supports multiple payment methods, providing customers with flexibility and convenience, which in turn helps businesses collect payments faster and maintain healthy cash flow. Additionally, EBizCharge offers advanced reporting and analytics tools that give businesses valuable insights into their accounts receivable performance, enabling proactive management and strategic decision-making. By leveraging this top-rated payment processing solution, businesses can significantly decrease collection costs, improve customer relationships, and ensure a more stable financial position.
