Blog > Credit Card Fraud Detection: Best Methods of 2024
Credit Card Fraud Detection: Best Methods of 2024
In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital transactions, the battle against credit card fraud remains a critical concern for both consumers and financial institutions alike. As technology advances, so do the tactics employed by fraudsters, necessitating continuous innovation in fraud detection methods.
What Is credit card fraud?
Credit card fraud is a type of financial deception involving unauthorized use of someone’s credit card information. This fraudulent activity can come in many forms, such as:
- Stolen card information used to make purchases.
- Fake card creation with stolen account details.
- Unauthorized online transactions.

The culprits behind credit card fraud aim to carry out unlawful transactions, which can result in significant financial losses for both consumers and businesses. Cardholders might only be aware of these activities once they notice suspicious charges on their accounts or receive an alert from their bank. Credit card fraud detection thus plays a crucial role in identifying and preventing these dishonest acts, ensuring that both financial transactions and cardholders’ sensitive information are safeguarded.
While credit card fraud covers a large area, there are a couple of different types of credit card fraud that clear up the confusion.
Types of credit card fraud
When discussing credit card fraud detection, understanding the types of fraud that may occur is crucial for both consumers and merchants. There are two primary types of credit card fraud that cardholders and businesses should be aware of: card present fraud and card-not-present fraud. Each manifests differently and requires unique approaches for detection and prevention. Here’s what the two types of credit card fraud entail.
Card present fraud

Card present fraud refers to situations where the physical credit card is used for making unauthorized transactions. This type of fraud can occur when a card is lost, stolen, and used by a fraudster before the cardholder can report its disappearance. Likewise, skimming devices, which secretly record card details during a legitimate transaction, also pave the way for this sort of fraud. Businesses often rely on stringent checks like asking for identification or using chip-enabled POS (Point of Sale) systems to combat this fraud. Understanding and detecting card present fraud is vital for protecting financial transactions that occur in person.
Card-not-present fraud
Contrary to card present fraud, card-not-present fraud happens when the fraudster does not physically display the credit card during the transaction. This is common in online transactions, where details such as the card number, expiration date, and CVV are required to complete a purchase. It’s also seen in phone or mail orders. Given the absence of the card, verifying the user’s identity is challenging, making it a prevalent fraud risk for e-commerce spaces. Digital security measures, such as encryption and transaction alerts, are critical tools in detecting credit card fraud that occurs without a physical card.
Both forms of fraud threaten the integrity of credit card usage and are important to consider when implementing credit card fraud detection systems. It’s essential for businesses and consumers alike to be conversant with these fraud types to protect themselves against potential risks.
The risks of credit card fraud
Credit card fraud detection isn’t just about stopping unauthorized purchases; it’s about safeguarding against a range of risks that can have far-reaching consequences. While it may be easy to focus solely on the immediate financial ramifications, the true impact of credit card fraud extends into several critical areas that affect both individuals and businesses.
Financial loss
Perhaps the most prominent risk associated with credit card fraud is financial loss. In 2021, the U.S. had 389,737 credit card fraud reports amounting to $32.34 billion (about $100 per person in the US) lost.

Whether an individual is victimized by fraudulent charges or business deals with chargebacks resulting from unauthorized transactions, the monetary consequences can be severe. Proactively detecting credit card fraud is integral in minimizing these financial hits. For businesses, repeated incidents can lead to increased transaction fees or even higher insurance premiums, placing more strain on the bottom line.
Damage to reputation
Credit card fraud can do more than just empty your wallet; it can tarnish your good name. Businesses that frequently fall victim to card fraud detection failures may find their reputation at risk as customers lose trust in the security of their financial transactions. Rebuilding customer confidence can take considerable time and effort, often far exceeding the duration and cost of rectifying the initial financial damages caused by the fraudulent activities.
Operational disruption
When a business is hit by credit card fraud, it’s not just about the money and reputation. The operational disruption can be significant. Detecting credit card fraud typically involves investigation and resolution activities, which can divert resources from regular business operations and lead to inefficiencies and lost productivity. Businesses must dedicate time to address and resolve fraudulent transactions, which could otherwise be spent on growth and expansion activities.
Legal and regulatory consequences
The legal and regulatory consequences of credit card fraud cannot be ignored. If card fraud detection does not work effectively, both individuals and businesses may find themselves navigating a complex legal landscape. There may be punitive fines for failing to adhere to industry standards like PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard), and in some cases, businesses might even face lawsuits or other legal actions as a result of fraudulent activities.
It is vital to take fraud risk seriously and to implement robust detection systems to avoid such costly legal and regulatory outcomes.
What Is credit card fraud detection?
Credit card fraud detection is a critical process financial institutions and merchants use to identify unauthorized or suspicious transactions that can lead to economic losses. It’s a system of tools and techniques designed to spot when a credit card is being used without the cardholder’s consent. By detecting credit card fraud, companies aim to prevent fraudulent activities, protecting their customers and business interests.
The process involves real-time monitoring of credit card transactions to filter out legitimate transactions from potential fraud. Various technologies are employed to achieve this, including machine learning models, which analyze patterns in data to recognize fraud risk, and rules-based systems, which trigger alerts for suspicious activities. Detecting credit card fraud is a balancing act, as systems must minimize false positives (legitimate transactions flagged as fraudulent) and false negatives (fraudulent transactions missed by the system), ensuring a seamless experience for genuine card users while keeping imposters at bay. As fraudsters become more sophisticated, so do credit card fraud detection methods, constantly evolving to outsmart new types of fraud and defend against financial fraud.
The improvements in card security
Over the years, credit card security has significantly advanced to outsmart fraudsters. Initially, basics like signature verification and physical card scrutiny were primary. The magnetic stripe came next, storing card data, followed by EMV chips – a leap forward, with unique data generation making duplication more challenging. Then came the online evolution: card-not-present transactions spurring new checks like CVV numbers, 2-factor authentication, and 3D Secure to ensure the person making online transactions is a legitimate cardholder.
Security measures continued to get more innovative with the help of technology. Real-time monitoring and AI-driven systems track and flag suspicious activities, reducing false positives while quickly identifying potential fraud and adopting tokenization and end-to-end encryption to shield data during the transaction process. This timeline reflects a constant battle wherein credit card companies employ cutting-edge tools and methods to stay ahead of fraudsters, safeguarding our financial transactions with every swipe, insert, or click.
| Era | Security Features |
|---|---|
| Early Days | Signature verification |
| Magnetic Stripe | Storage of card data |
| Chip Technology | EMV chips, unique data for each transaction |
| Online Security | CVV, 2-factor authentication, 3D secure |
| Current Tech | AI monitoring, real-time alerts, encryption, tokenization |
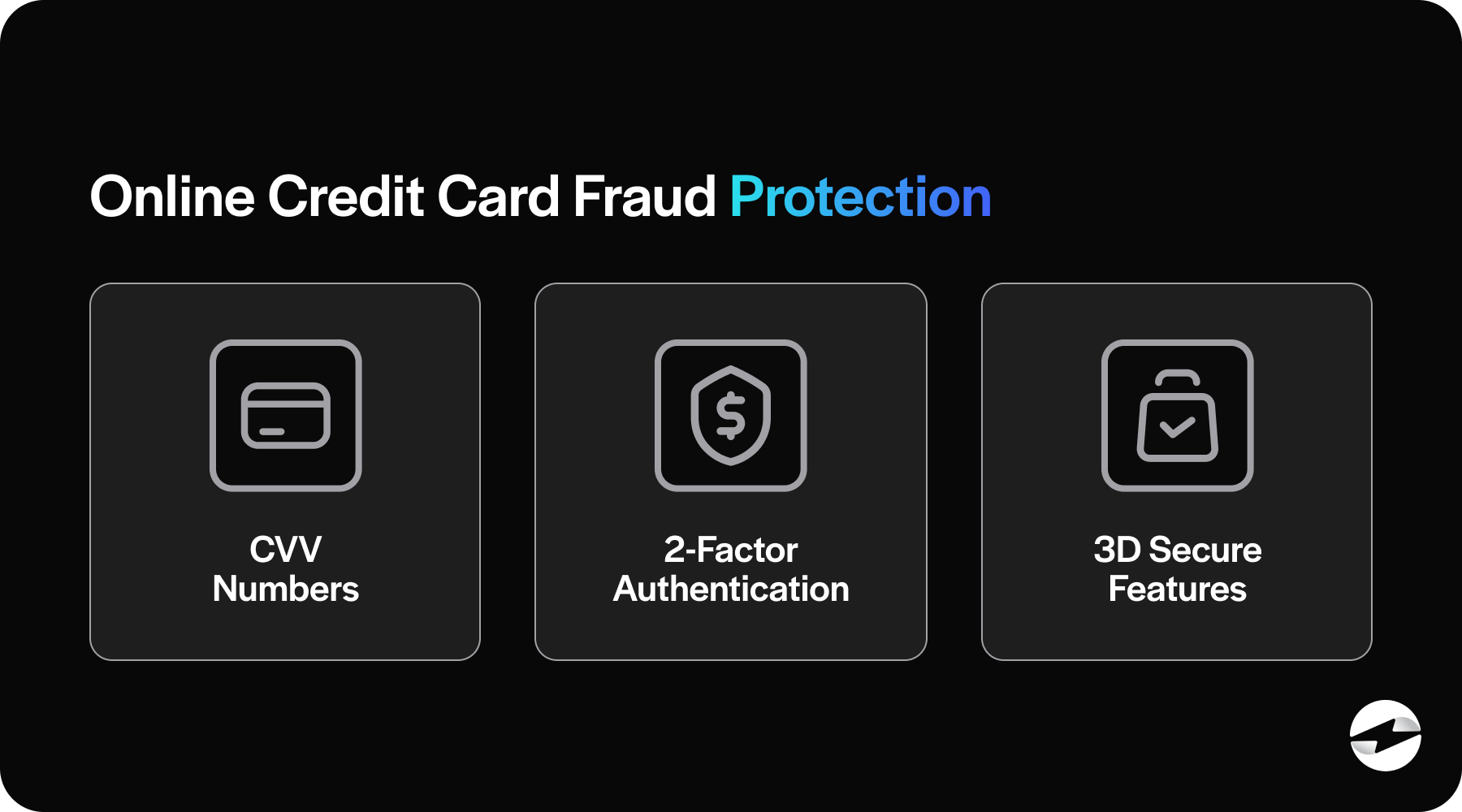
By staying abreast of technological enhancements, credit card security has become more robust and responsive, reducing financial losses due to fraud.
What should your fraud detection strategy help you achieve?
A robust fraud detection strategy should enable your business to pinpoint suspicious activities promptly and accurately. The primary goals are to safeguard customer data, prevent unauthorized transactions, and reduce financial losses due to fraudulent activities. A good strategy must be vigilant, versatile, and adaptive. It should be capable of evolving with fraudsters’ tactics and minimize any inconvenience to legitimate customers. Your strategy should detect current fraud patterns and anticipate future threats.
Outlier Models
Outlier models, essential in fraud detection, utilize predefined thresholds to identify transactions deviating from expected patterns, aiding in spotting irregular spending behavior or unusual transaction amounts, crucial indicators of credit card fraud.
Outlier models are statistical tools that help in fraud detection by flagging transactions that fall outside the expected range or pattern of behavior. These models work on predefined thresholds, which, when exceeded, signal a transaction as suspicious. Outlier detection can be beneficial for spotting erratic spending behavior or unusual transaction amounts, which are significant red flags for credit card fraud. The main challenge is to calibrate the model to detect genuine fraud while avoiding the unnecessary blocking of valid purchases.
Predictive Modeling

Predictive modeling uses historical transaction data and machine learning algorithms to predict the likelihood of a transaction being fraudulent. A predictive model gauges each transaction’s fraud risk by considering various factors, such as the time of purchase, location, and purchase amount. The strength of predictive modeling lies in its ability to adapt to evolving fraud patterns and nuanced types of fraud. The constant refinement of models ensures they stay effective even as fraudsters change their tactics. Predictive modeling aspires to balance sensitivity to fraud with the need to limit inconvenience, striving for a user-friendly financial environment with robust security.
Anomaly Detection
Anomaly detection is one of the core components of a fraud detection strategy. This method involves monitoring credit card usage and identifying transactions that deviate from a user’s typical spending patterns. For instance, if a cardholder typically makes small purchases within their local area, a sudden high-value transaction from a foreign country would be flagged as anomalous. Anomaly detection systems continuously learn from transaction data, which helps reduce false positives over time and enhances the detection of genuine fraudulent transactions.
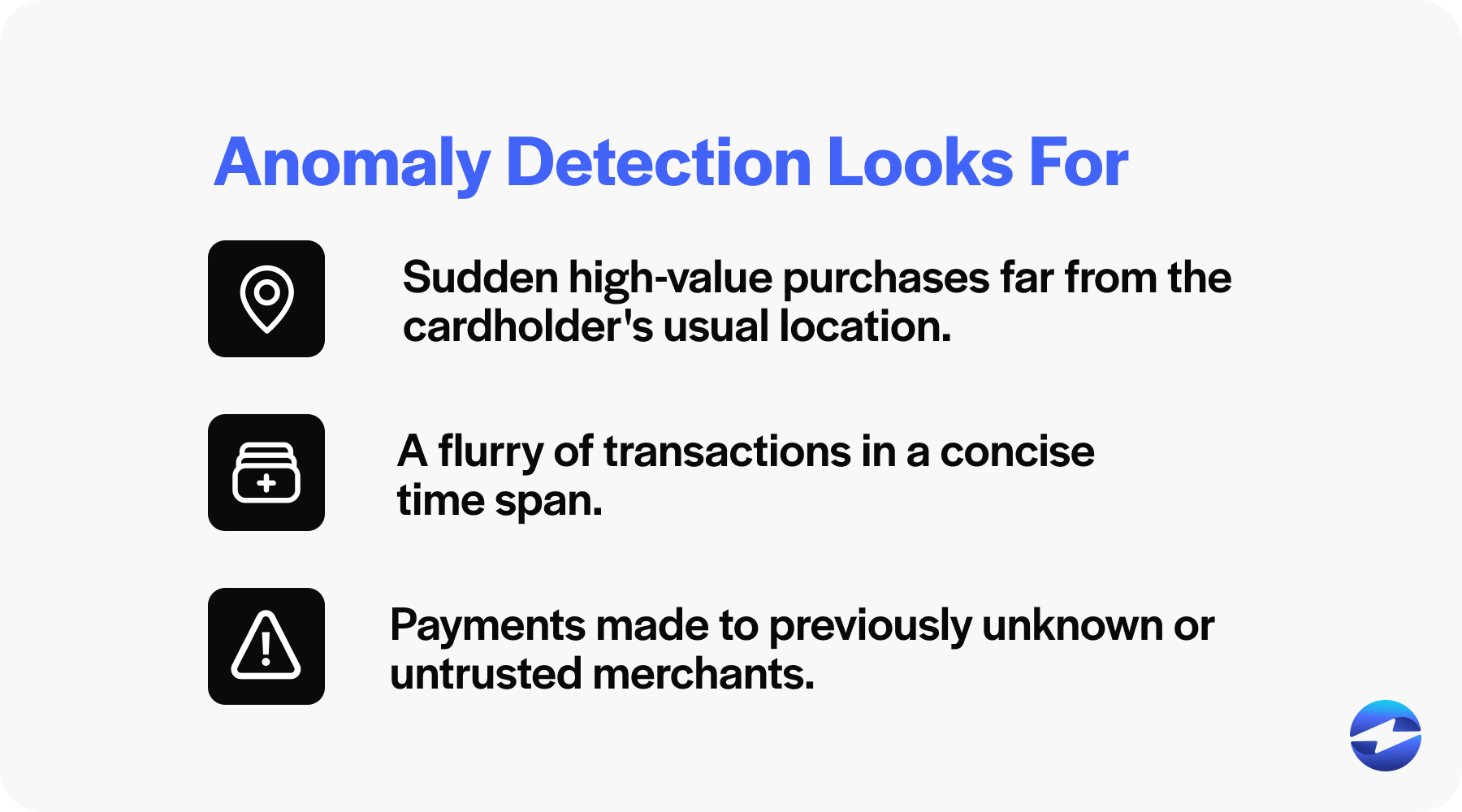
What can be an anomaly?
An anomaly, in the context of anomaly detection, refers to an occurrence that deviates from what is considered normal. These irregularities often signal suspicious activities or potential issues within a system. When considering financial transactions, anomalies might indicate credit card fraud, as they present patterns inconsistent with an account holder’s typical behavior.
Examples of anomalies could include:
- Sudden high-value purchases far from the cardholder’s usual location.
- A flurry of transactions in a concise time span.
- Payments made to previously unknown or untrusted merchants.
Anomaly detection is a crucial mechanism for systematically identifying outliers. It often employs sophisticated algorithms to sift through vast amounts of data to flag unusual occurrences for further investigation.
Mastering your CC fraud detection for 2024
Staying abreast of the most advanced methods for credit card fraud detection in 2024 is crucial for safeguarding against financial losses due to fraudulent transactions. With the integration of sophisticated technologies such as machine learning models, neural networks, and deep learning, detecting credit card fraud has become more accurate, reducing false positives and false negatives.
Remember, effective fraud detection is about balance—minimizing the risk of fraud while ensuring an uninterrupted, no fee credit card processing experience for users. By utilizing the best methods available, individuals and businesses can protect themselves from the various types of fraud while maintaining model performance and fraud risk management. Always stay informed and be vigilant to ensure that the fight against credit card fraud continues to be a winning battle.
 Is you business PCI compliant? Take this 1-min quiz to find out.
Is you business PCI compliant? Take this 1-min quiz to find out.