Blog > Fraud Protection: Everything You Need to Know About Payment Security
Fraud Protection: Everything You Need to Know About Payment Security
Since cardholder data is a major target of breaches, payment security remains at the forefront of concerns for most businesses trying to secure their infrastructures.
Payment security typically involves specific regulations and security measures that focus on protecting cardholder data that is stored, transmitted, or being processed.
In this article, businesses will learn about the ins and outs of payment security which include:
- PCI compliance standards
- Security features to protect your infrastructure
- Best practices to secure payments
- Building the right payment security strategy
Become PCI compliant to enhance payment security and prevent threats
For a well-rounded payment security strategy, businesses that process or handle cardholder data must adhere to the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), also known as PCI compliance standards.
PCI compliance standards refer to a set of global payment card security requirements that consist of various security guidelines, applications, and tools to protect cardholder data.
When a merchant becomes and remains PCI compliant, they’re using the necessary protocols and security applications to enhance payment security by actively addressing, preventing, and mitigating fraudulent activity and data breaches. PCI DSS requirements vary by business, as they’re determined by your PCI level — transaction volumes.
To become compliant, you can reference this comprehensive PCI Checklist.
In addition to becoming PCI compliant, it’s imperative to evaluate the many types of payment security to determine which programs and strategies are right for your business.
Payment security features to protect your business
Payment security is not a one size fits all approach, as there are a variety of businesses like online stores and brick-and-mortar merchants that have different needs.
Luckily, you can choose from many payment security options to secure your payments. Here are 6 payment security features to help you protect sensitive cardholder data:
- Tokenization
- 3D Secure
- Multi- or Two-Factor Authentication
- Data Encryption
- Card Verification Value
- Address Verification System
Before determining which method of payment security is best for your business, read on to learn about what each entails.
1. Tokenization
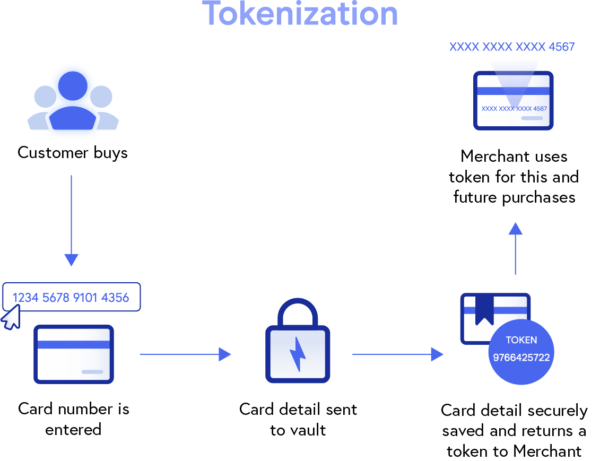
Tokenization provides payment security for merchants by replacing sensitive cardholder data, like card or bank account numbers, with random characters known as tokens.
Tokens are automatically generated during the payment process and can be transmitted (over the Internet or on networks) and stored without exposing the actual card information. Replacing cardholder data, rendering it useless to hackers, will help prevent fraudulent activity or breaches from occurring, and enhance payment security for both merchants and their customers.
2. 3D Secure
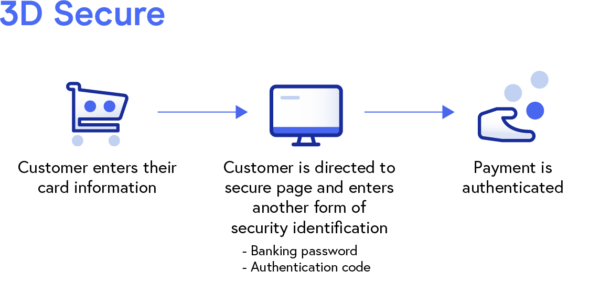
Three Domain Secure, commonly referred to as 3D Secure or 3DS, is a valuable security protocol that adds an extra level of authentication for eCommerce merchants looking to improve their online payment security.
3D Secure works to prevent the unauthorized use of cards by directing customers to a secure page (hosted by their card providers) where they’re required to enter a banking password or authentication code before payments can be processed.
Once a customer enters this information, the merchant, card network, and financial institutions share it with each other and work together to process the transaction request, assess any risks, and lastly, move to authenticate or challenge the payment.
3D Secure is a useful payment security tool for high-risk transactions and can help protect eCommerce merchants from fraudulent activity and unauthorized chargebacks.
3. Multi- or two-factor authentication
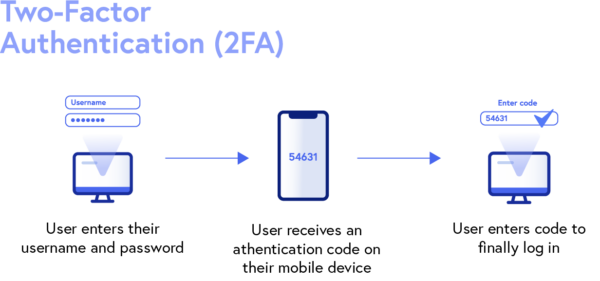
Businesses can also apply other payment security protocols like multi-factor (MFA) or two-factor (2FA) authentication to validate their transactions.
MFA and 2FA require cardholders to verify their identities by completing multiple authentication steps before accessing their accounts. Authentication factors include verification codes (via email or SMS messages), security questions, one-time passwords, push notifications, and more.
Multi-factor and two-factor authentication will enhance your payment security by preventing hackers from accessing and stealing sensitive cardholder data.
4. Data encryption
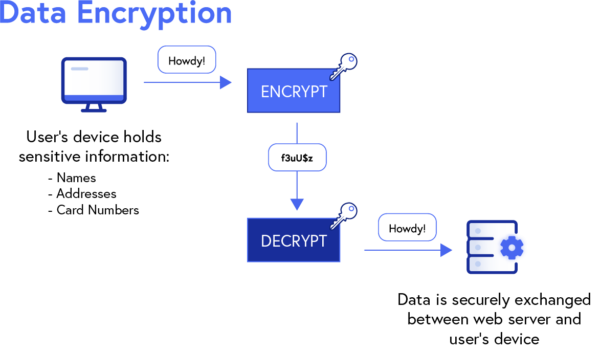
Data encryption is a vital part of any payment security infrastructure, as it consists of several protocols like Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS).
SSL is a widely used security measure that encrypts data transmitted during online transactions to prevent sensitive information (names, addresses, card numbers, etc.) from being exposed.
While newer providers offer the updated and stronger encryption known as TLS, this term is often interchanged with SSL since it’s more widely known.
Once you’ve obtained an SSL or TLS certificate from a reliable provider, a lock symbol and HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) will appear in the address bar next to your URL to show visitors your site is secure.
5. Card Verification Value (CVV)
Card Verification Value (CVV) is the three- or four-digit code on the back of credit cards that’s used to verify card-not-present (CNP) transactions processed online or over the phone.
While CVV codes aren’t immune to fraudulent activity, they can add to payment security and make it more difficult for breaches to occur by allowing merchants to authenticate a transaction without storing these numbers.
In addition to verifying CVVs, merchants would be wise to add extra authentication protocols to protect sensitive cardholder data and enhance their payment security.
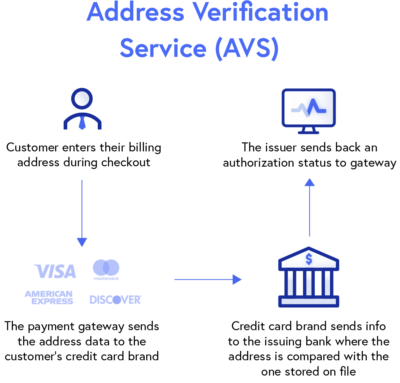
6. Address Verification System (AVS)
Similar to CVV protocol, Address Verification System (AVV) verifies a transaction by matching the provided billing address to the address on file with the customer’s card-issuing bank.
AVS provides another level of payment security by preventing the use of unauthorized cards which can reduce fraudulent transactions and chargebacks. This security measure has been widely adopted by many online merchants, payment gateways, and eCommerce platforms.
Now that you have an idea of the payment security features your business can implement, you can decide what the best practices are to take to better secure your payments.
4 best practices to secure your payments
While there are several strategies that can be used to enhance your payment security, there are a few best practices every business should include in its operations.
According to the PCI Data Security Standard, businesses can tackle payment security using three key steps: assess, remediate, and report.
To take it a step further, you can also apply a fourth practice into your infrastructure by using an all-in-one payment processor to ensure secure payments.
Assess all areas of your business for payment security vulnerabilities
Assessing all areas of your business to identify any vulnerabilities in your operations and payment processing system is an essential part of strengthening payment security.
During these assessments, your business should take inventory of all the systems and technology it uses to capture and store sensitive card data. You can then identify vulnerabilities in your payment infrastructure that need to be addressed.
Remediate any payment security vulnerabilities in your infrastructure
Once a thorough assessment has been conducted, your business can remediate these payment security vulnerabilities.
The remediation process includes:
- Scanning networks
- Mitigating and resolving any vulnerabilities
- Categorizing and ranking vulnerabilities to prioritize high-risk areas
- Applying patches or changes to systems and operational vulnerabilities
After you’ve completed the remediation process, your business must run an additional scan to ensure all payment security vulnerabilities and problems have been resolved.
Report remediation and compliance efforts to the necessary parties
Now that you’ve identified and addressed payment security vulnerabilities, your business must compile and submit a remediation report.
This report, also known as an Attestation of Compliance (AOC), will include all the payment security efforts you took to mitigate these vulnerabilities and should be sent to all acquiring banks and card networks you work with.
Use an all-in-one payment processor
Lastly, an all-in-one payment processor will help your business secure its payments by providing the necessary tools and measures to meet PCI compliance and other payment security needs.
In addition to full PCI compliance, an all-in-one payment processor can provide payment security features like tokenization, encryption, off-site data storage, and more.
What’s the right payment security strategy for your business?
After evaluating the various payment security tools and best practices for preventing data breaches, you may be wondering what strategy is right for your business.
Payment security looks a little different for each merchant but the best strategies focus on risk and vulnerability reduction and improving the payment experience for consumers. With these goals in mind, you can decide which security measures and software are right for your business.
Take advantage of reliable resources to build a powerful payment security system
While sensitive cardholder data remains an area of concern, various tools and technology are readily available to alleviate this stress. Merchants can take advantage of these resources to uphold PCI compliance standards, implement strong security protocols and software, and build a powerful payment security infrastructure.
 Is you business PCI compliant? Take this 1-min quiz to find out.
Is you business PCI compliant? Take this 1-min quiz to find out. 
