Blog > What are SKUs and how Beneficial are they for your Business?
What are SKUs and how Beneficial are they for your Business?
Whether you’re a large-scale retailer or a small online store, effectively managing inventory is essential for meeting customer demands and maximizing profitability.
At the heart of this intricate process lies a seemingly simple yet powerful tool: the SKU. The acronym SKU is short for stock keeping unit, which is crucial in streamlining operations, optimizing inventory control, and driving business growth.
What is the purpose of SKUs?
At its core, stock keeping units are unique identifiers assigned to a specific product within a company’s inventory system. SKUs distinguish products from each other based on the products’ categories, are typically composed of alphanumeric characters (generally eight digits), and can be customized to fit the needs of individual businesses.
SKUs enable accurate and efficient tracking of products throughout the inventory management process. By assigning a unique SKU to each item, businesses gain the ability to monitor and manage their inventory in a granular and organized manner.
In addition to enhancing operational efficiency, using SKUs in inventory can yield many other benefits for businesses.
6 benefits of using SKUs
From precise product identification and tracking to streamlined order fulfillment, SKU systems play a vital role in driving success in inventory management.
Here are six benefits SKUs can provide for your company:
- Identification
- Tracking and inventory control
- Order fulfillment
- Data analysis
- Valuable sales insights
- Improved internal communication and collaboration
1. Identification
SKUs provide a means to identify and differentiate products based on their unique attributes, such as size, color, style, or any other relevant characteristic.
This level of specificity allows for precise categorization and tracking of individual items.
2. Tracking and inventory control
With SKU systems in place, businesses can accurately track the movement of products within their inventory. This includes monitoring stock levels, conducting regular audits, and ensuring optimal inventory control.
SKUs create an environment designed to make product organization much easier and prevent stockouts or overstocking.
3. Order fulfillment
SKUs play a vital role in efficiently fulfilling customer orders. By associating SKUs with specific products, businesses can streamline the picking, packing, and shipping processes to ensure the right products reach the right customers in a timely manner.
4. Data analysis
SKUs provide valuable data for businesses to analyze, measure, and use to produce helpful reports.
Businesses can make informed decisions about product assortment, pricing, and overall inventory management strategies by monitoring SKU-specific metrics such as sales performance, customer preferences, and inventory turnover.
5. Valuable sales insights
In addition to analyzing and building useful reports, SKU data can identify sales patterns, popular items, and customer preferences.
This data-driven approach allows businesses to make informed decisions about inventory management, marketing strategies, and product development.
6. Improved internal communication and collaboration
Standardized SKUs can facilitate efficient communication and collaboration across departments within a business, reducing errors and improving overall workflow. SKUs do this by keeping track of the amount of stock a company has and communicating (or automatically ordering) with employees if a product gets low in stock.
With SKU systems, businesses can enjoy enhanced operational efficiency, improved customer satisfaction, and tremendous success in their inventory management endeavors.
The difference between SKU and UPC codes
The terms SKU and UPC are commonly used in the world of retail. SKUs and UPCs are similar in that they’re both associated with products but differ in uses.
SKU
SKUs are internal codes businesses craft to track and identify products within their inventory systems. These codes serve as unique identifiers, containing valuable information such as product attributes, variants, and other specific details relevant to the business.
SKUs can also include additional details like internal codes or supplier information, enabling streamlined processes and providing insights into product performance.
UPC
In contrast, Universal Product Codes (UPCs) are standardized product identification codes that predominantly facilitate point-of-sale transactions. UPCs follow a universal format, are widely recognized and accepted globally, and are typically associated with the barcodes printed on product packaging.
UPC codes are crucial in retail environments, enabling seamless scanning and efficient checkout processes. These codes provide a unique identifier for each product, allowing retailers to quickly and accurately retrieve product information, retrieve pricing details, and manage inventory at the point of sale. The uniformity of UPCs ensures compatibility across different retail systems, making them universally applicable in various POS environments.
Now that there’s a clear distinction between SKU and UPC, it’s important to understand how SKU management can enhance your company’s inventory.
Effective SKU management to simplify your inventory
Properly managing SKU systems is essential to ensure your company has the necessary inventory to fulfill customer demands and maintain financial stability. Accurate inventory tracking through SKUs helps you avoid overstocking, which can result in high carrying costs, obsolescence, or markdowns.
Efficient SKU management is crucial for seamless inventory control and can be accomplished manually or using an automated approach.
Manual SKU management
Businesses rely on spreadsheets or other record-keeping methods in manual SKU management to assign and track their SKUs.
This approach is often suitable for small-scale operations or businesses with relatively simple inventories. However, manual SKU management can become increasingly challenging as companies grow or deal with more extensive stocks and frequent product updates.
When it comes to manual SKU management, you’ll need to understand how to calculate the ratio first.
Calculating the SKU ratio
If your business decides to go the manual route, you’ll need to know how to calculate SKUs. To do so, you’ll need your company’s product list to compile all the SKUs into a spreadsheet and the price, the COGS (cost of goods sold), and the gross profit of each SKU.
Once the spreadsheet is complete, create gross profit ranges ($0-$10, $10-$19.99, etc.) to note how many SKUs are in each gross profit range. You’ll then divide the total number of SKUs to get the SKU ratio for each range you’ve established.
If the manual method of calculating SKUs is too tedious, there’s an automated way of managing SKUs that simplify the inventory process.
Automated SKU management
Automated SKU management utilizes specialized inventory management software to streamline the creation, tracking, and organization of SKUs. These systems often integrate with other business processes, such as sales and procurement, providing real-time data and enhancing overall inventory control efficiency.
SKU management automation is just one of many of the best practices for managing SKUs for your business. However, there are many other methods of optimizing SKU management that your company can implement to improve your overall inventory efficiency.
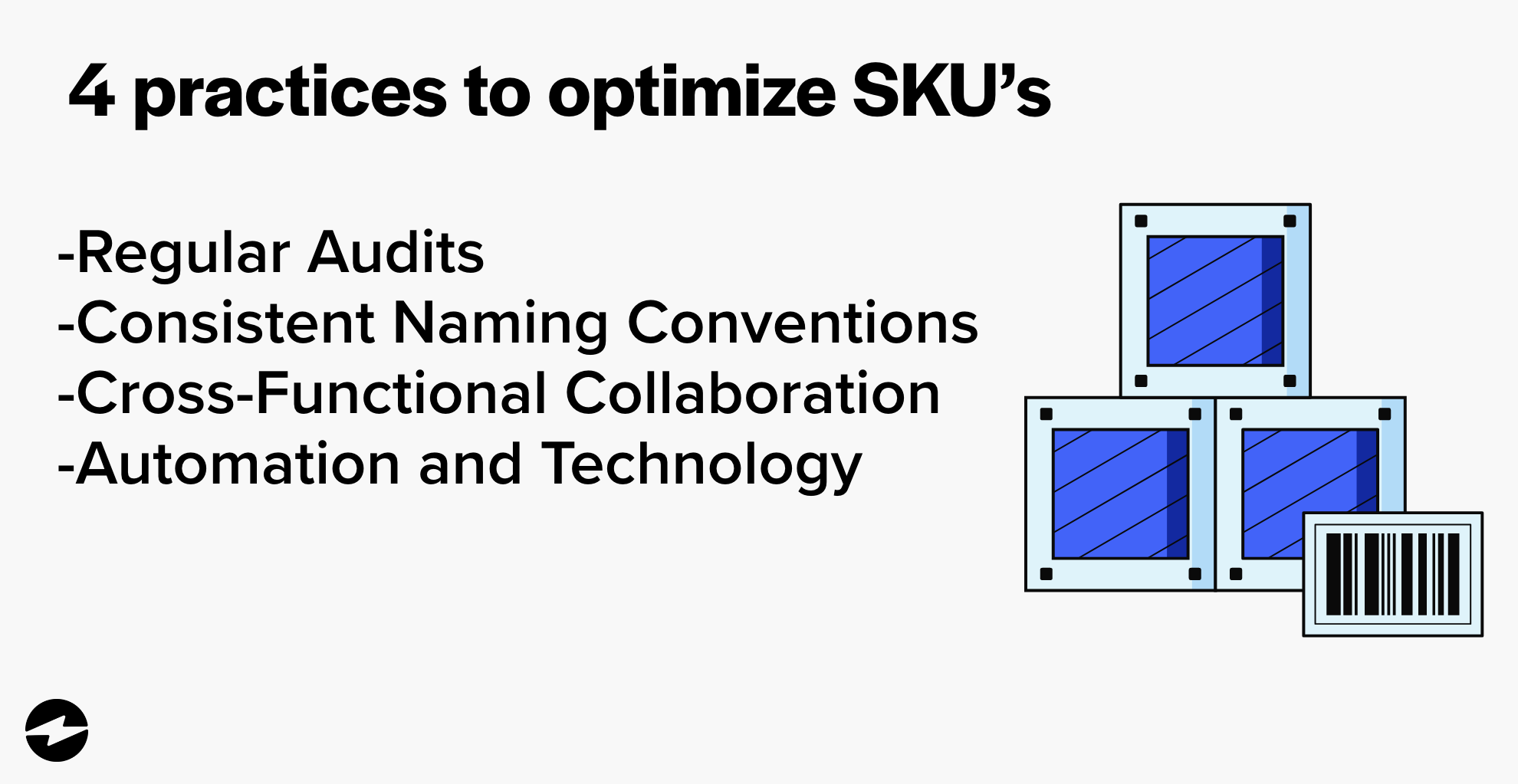
4 best practices to optimize your SKU management
SKU management should be regularly analyzed and tweaked to maximize your company’s efficiency.
Regular analysis of SKU performance, inventory turnover, and customer demand patterns allows businesses to make informed adjustments and streamline operations for improved productivity and profitability.
Best practices for managing SKUs
Effective SKU management requires adopting helpful protocols and measures. Here are some best practices to better manage these operations:
- Regular audits: Conduct routine audits to ensure accuracy and identify discrepancies between physical inventory and digital records.
- Consistent naming conventions: Establish consistent naming conventions for SKUs, making them easily understandable and the same across all products.
- Cross-functional collaboration: Foster collaboration between different teams, such as marketing, sales, and operations, for more consistent SKU management practices.
- Automation and technology: Like AR automation, you can leverage inventory management software and tools to automate SKU creation, tracking, and reporting, reducing manual errors and improving efficiency.
Alongside these practices, your business can use specific tools to enhance its SKU management strategy and stay more organized.
3 effective tools to simplify SKUs
Businesses can leverage specialized tools and software solutions to streamline and optimize SKU management processes.
Inventory management systems, such as cloud-based platforms and ERP software, offer comprehensive features for SKU generation, tracking, reporting, and integration with other business systems.
Some software solutions are also dedicated to organizational efforts, inventory control, and data synchronization, empowering businesses to enhance their SKU management capabilities and operational efficiency.
Here are three SKU management tools your business can look into:
- Zoho Inventory: Zoho Inventory is an inventory management software that enables you to create and manage SKUs, track stock levels, set reorder points, and handle multi-channel sales.
- NetSuite: Netsuite, a popular ERP software, has exceptional inventory management functions. NetSuite is geared more toward businesses that want to scale quickly and larger companies requiring heavy inventory management.
- SkuVault: SkuVault is a cloud-based inventory and warehouse management system with SKU management features. It provides tools for creating and managing SKUs, tracking inventory levels across multiple locations, and optimizing order fulfillment.
In addition to the various SKU tools and management strategies, your business should be aware of upcoming trends.
Future SKU management trends to look out for
The future of SKU management holds promising advancements driven by technological innovations and evolving industry practices.
Here are a few key trends to anticipate:
- The integration of automation and AI technologies will revolutionize SKU. Machine learning algorithms will enable intelligent demand forecasting, automated replenishment, and SKU optimization, leading to more accurate inventory control and reduced manual intervention.
- Adoption of cloud-based inventory management systems, enabling real-time access to SKU data across multiple locations or sales channels.
- Continued development of mobile applications for SKU management, allowing businesses to track and manage inventory on the go.
- SKU management will continue to align with eCommerce platforms. Integration of SKU systems with online marketplaces, fulfillment centers, and digital platforms will ensure accurate inventory synchronization, streamlined order processing, and seamless customer experiences.
Businesses should keep up with the latest trends in SKU management to update their business systems with the latest technology and best practices.
Enhance your inventory control and overall success with effective SKU
SKUs are critical to inventory management, providing numerous benefits for businesses to enhance their operations.
Businesses that embrace efficient SKU management measures and valuable software and take advantage of evolving trends can optimize their inventory control to meet customer demands and add to their overall success.
 Get a free cost-comparison of your current payment processing costs vs. EBizCharge
Get a free cost-comparison of your current payment processing costs vs. EBizCharge 