Blog > What Are Merchant Service Providers? Finding the Right One for You
What Are Merchant Service Providers? Finding the Right One for You
In today’s digitally-driven economy, more and more businesses are embracing electronic payment solutions to meet growing demand. However, navigating the complex payment processing landscape can be daunting.
Thankfully, merchant service providers offer various services and tools that enable businesses to accept electronic payments securely and efficiently. This article will give you an in-depth look into these providers and factors to consider when determining the best fit for your business.
What is a merchant service provider?
Merchant service providers (MSPs) offer payment processing services that allow businesses to accept various types of digital payments.
From credit and debit card processing to providing point-of-sale systems and payment gateways, MSPs offer the tools and infrastructure that give businesses the ability to securely and efficiently process customer payments. So, who qualifies for these services?

What types of businesses qualify as merchants?
Payment processors refer to their customers as merchants, a blanket term for businesses that sell goods and services to a customer base through commercial activities. In other words, a merchant is a business or individual that intends to profit by selling goods and services.
Payment processors are a valuable tool for merchants as they facilitate the transaction process between the merchant, the customer, and the financial institution involved, allowing merchants to accept debit and credit cards as payment methods.
Merchants come in all shapes and sizes. Some examples of merchants include:
- Online and brick-and-mortar retailers
- Wholesale and distribution companies
- Restaurants
- Hair salons
- And many more
Regardless of the industry, merchants must open a merchant services account to process payments from their customers.
What is a merchant services account
A merchant services account is a bank account that allows merchants to accept payments, such as credit and debit card transactions and online payment methods.
Unlike other bank accounts, merchant services accounts are typically accompanied by payment processing technology such as point-of-sale (POS) terminals, card readers, virtual payment gateways, and software integrations.
Merchant service accounts also provide valuable tools, including reporting and analytics, real-time transaction authorization and verification, customer support, and PCI-compliant security. These accounts use security measures such as encryption and tokenization to protect your funds.
Businesses can open a merchant services account by following a few simple steps.
How to open a merchant account
When choosing a merchant account provider to open a merchant account, be sure to research different payment processors or acquiring banks to find one that’s most compatible with your business model and needs.
After determining the right provider for your business, you must follow six steps to open a merchant account:
- Gather the required documents: Merchant account providers need specific information during the application process, such as business licenses or tax IDs, proof of the business’s address, and financial statements. Providers may also request personal identification from business owners.
- Fill out the application: Once you’ve acquired all the necessary information, you can complete the application. Double-check all your information is accurate and all the required boxes are checked — any deviation or inaccuracy can prolong the process of opening your merchant account.
- Risk Assessment: The risk assessment allows payment processors to assess any risks a business poses — your financial stability, credit history, and projected volume of transactions determine this. Occasionally, the processor will conduct background checks or credit checks on the business owner.
- Reviewing the terms of use: Once your application has been processed and approved, you’ll be provided with the merchant agreement outlining the terms and conditions associated with the merchant account. When reviewing this contract, read everything carefully and be cautious of associated fees, processing rates, and termination clauses.
- Setting up payment processing equipment: Merchant accounts will require software installation or, in some cases, setting up physical equipment. This equipment and software can include POS terminals, card readers, payment gateways, or integrations.
- Testing the product: Lastly, you can test your payment processing system to ensure all the software and equipment are set up correctly. Once you verify everything works, your processor will activate the merchant account for you to start accepting electronic payments.
Opening a merchant account is a relatively straightforward process, but it’s only the first step to understanding merchant services.
How do merchant services work?
If you’re a new merchant, you may not be familiar with how merchant services work.
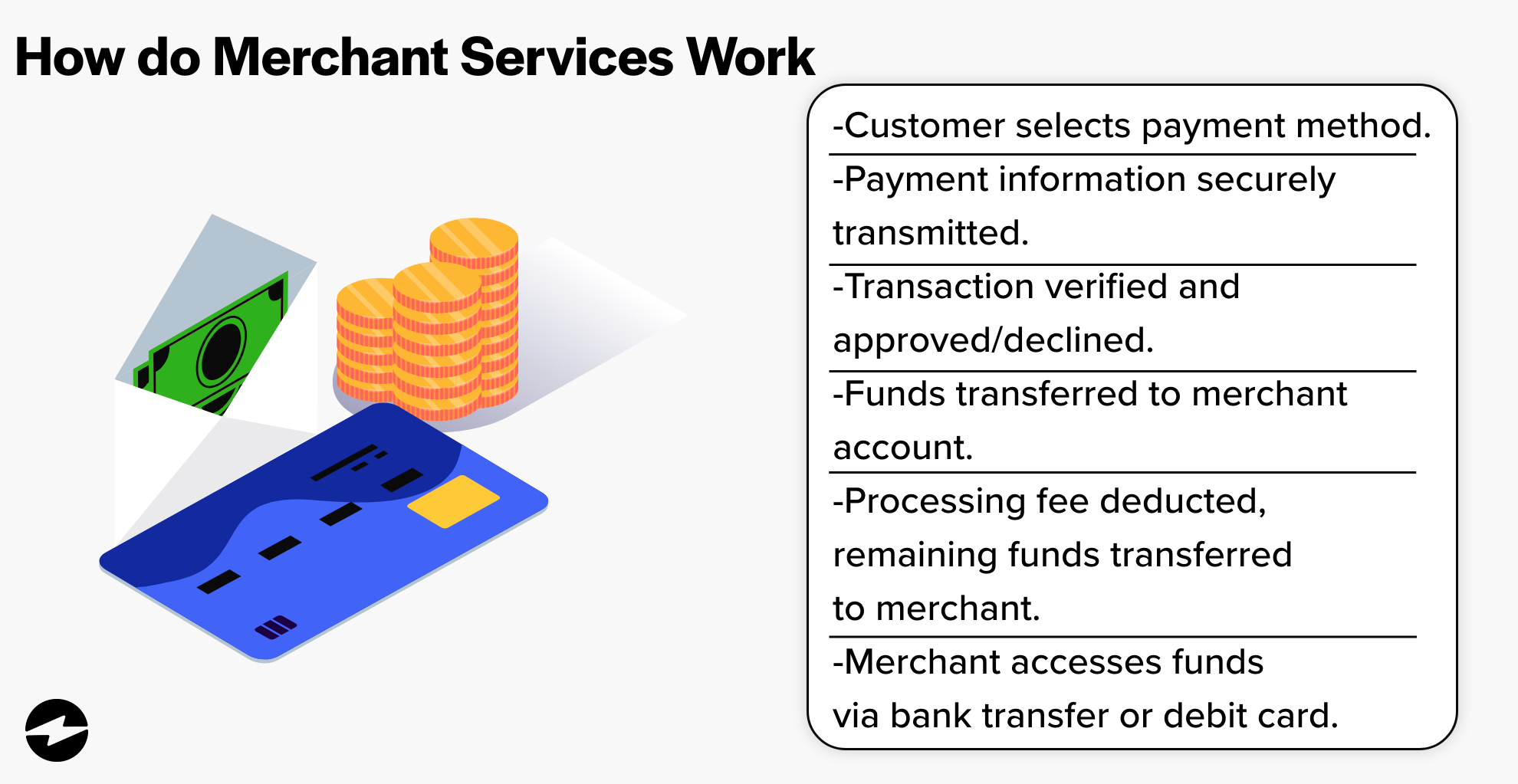
Here’s a quick breakdown of the merchant services process:
- A customer makes a purchase from a business using their preferred payment method.
- The payment information is then transmitted securely to the payment processor or acquiring bank.
- Once transmitted, the payment processor or acquiring bank verifies the payment information and approves or declines the transaction based on the availability of funds and other factors.
- If the transaction is approved, the funds are transferred from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account.
- The payment processor or acquiring bank will charge a fee for processing the transaction and transfer the remaining funds to the merchant’s account.
- Finally, the merchant can access the funds in their account by transferring them to their business’s bank account or using a merchant account debit card.
Merchant service providers can provide valuable tools to help streamline the payment process and improve cash flow. These tools consist of products and services for merchants to diversify their methods of receiving payments, providing flexibility for their customers and improving the overall customer experience.
What products and services are included in merchant services?
Merchant services typically include financial products and services that help businesses accept and manage customer payments.
These products and services include:
- Payment gateways
- Virtual terminals
- Point-of-sale systems
- Contactless payments
- Mobile payments
- eCommerce solutions
- Fraud prevention and security tools
Payment gateways
Payment gateways facilitate the secure transmission of payment information between an online merchant and the payment processor or acquiring bank.
Payment gateways act as middlemen between a merchant’s website or application and the financial institution to quickly and securely process electronic payments.
By handling the complex payment flow and protecting sensitive data, payment gateways enable businesses to accept various electronic payment methods, enhance customer trust, and streamline their accounts receivable.
Virtual terminals
Virtual terminals are software applications merchants can use to process payments from any secure web browser.
As a digital version of a physical point-of-sale (POS) terminal, virtual terminals allow merchants to accept payments over the phone, in person, via email, and other remote channels.
The best virtual terminals have diverse payment options, enhanced security, robust integration capabilities, and high-quality customer service.
POS systems
POS systems include hardware and software to complete sales transactions at the point of purchase. These systems serve as a central hub where customers make payments and businesses record and process sales.
Point-of-sale systems are used in various industries, including retail stores, restaurants, hospitality, and service-based businesses.
Contactless payments
Contactless payments allow customers to make purchases without physically swiping or inserting a card, or handling cash.
Contactless payment terminals use radio frequency identification (RFID) technology or near field communication (NFC) to communicate between the customer’s payment card or mobile wallet and the payment terminal.
RFID technology uses radio waves to identify and track objects or individuals wirelessly. This technology offers numerous benefits, including automated identification and data capturing, increased security, and a seamless customer experience.
On the other hand, NFC technology is a short-range wireless communication technology that allows the exchange of contactless data between two NFC-enabled devices for customers to make payments simply by tapping their mobile device or card to a compatible payment terminal.
Mobile payments
Mobile payment methods have gained popularity since they allow customers to purchase using mobile devices.
Mobile payments consist of multiple options, including mobile wallets, mobile apps, and peer-to-peer (P2P) payment platforms. These payments offer a convenient way to make purchases because they eliminate the need to carry credit or debit cards and cash.
eCommerce solutions
Merchant service providers use eCommerce to facilitate digital transactions and enable merchants to sell their products and services online. MSPs typically provide a range of payment processing software as well as the necessary tools to allow merchants to engage in eCommerce transactions.
ECommerce tools and software often include payment gateway integrations, order and inventory management tools, shopping cart functionality, and more.
MSPs are a great way to facilitate eCommerce for merchants as they establish a robust online presence, streamline operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive growth within the world of eCommerce.
Fraud prevention and security tools
The merchant services industry takes security seriously and implements measures to protect its merchants and customers from threats.
Merchant service providers invest significant resources in securing their payment processing systems and ensuring they comply with regulations such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Encryption, tokenization, and Secure Socket Layer (SSL) Certificates are only some of the security features MSPs utilize.
MSPs also employ security professionals trained to identify and respond to security threats. These professionals monitor systems to detect and respond to any suspicious activity and have protocols to notify merchants and customers in the event of a data breach.
By prioritizing security, businesses can create a safe and trustworthy environment to instill customer confidence and ensure long-term success when processing payments.
Now that you know the tools and services MSPs offer, you should take a moment to learn the difference between merchant service providers and merchant accounts since they’re often confused as the same entity.
Merchant account vs. merchant service provider
Despite merchant accounts and merchant services providers sharing commonalities, there are a few important distinctions between the two.
A merchant account is a bank account that stores the funds from customer transactions. Whereas a merchant service provider is a company that provides the tools, services, and infrastructure for businesses to accept and process these payments.
Merchants typically need a merchant account and a merchant service provider to effectively manage their payment processing needs.
4 questions to ask your merchant service provider
When choosing a merchant services provider, asking the right questions will help your business ensure it receives the best service.
Here are four questions to ask your MSP:
- What kind of technology do you offer? The best MSPs should provide payment processing options, fraud detection, and reporting capabilities.
- How does your technology integrate with my existing systems? Merchants already use inventory management systems or accounting software, so it’s best to ask if and how providers can integrate with their current systems.
- What’s the cost of your technology? Knowing the costs associated with your payment processing products and services is essential — you should also look out for additional charges or hidden fees.
- What kind of training and onboarding do you provide? Many MSPs provide training and onboarding services, so it’s important to know what this entails and the length of this training.
It’s imperative to ask these questions before choosing an MSP to ensure you don’t run into technical problems down the road. In addition to these questions, there are three important factors to research when looking for the right provider for your business.
3 factors to consider when choosing an MSP
Selecting the best merchant services provider for your business can be daunting, but doing your due diligence to find the right fit will be well worth it in the long run.
In addition to reviewing the quality of products and compatibility with your existing systems, your business should assess three key areas when comparing providers: pricing structures, processing fees, and support.

Pricing structures
Pricing is one of the most crucial components in looking for a quality MSP, so be sure to look at the provider’s pricing structure and fees associated with their services.
Merchant service providers will typically offer three pricing structures. These structures include flat rate pricing, interchange-plus pricing, and tiered pricing:
- Flat rate pricing: Flat rate pricing includes a fixed percentage and a flat fee for each transaction, regardless of the card type or transaction category. It’s particularly beneficial when most transactions fall within the “qualified” category, as there are no tiered rates to consider.
- Interchange-plus pricing: Interchange-plus pricing (or cost-plus pricing) consists of interchange fees set by the card networks plus a predetermined markup or fee. In this pricing structure, the MSP transparently passes on the interchange fees, making it easier to understand the actual cost of processing each transaction. Interchange-plus pricing is widely seen as the cheapest processing option.
- Tiered pricing: Unlike flat rate pricing, tiered pricing categorizes transactions into different tiers or categories, each with its own associated rate. These tiers include debit, qualified, mid-qualified, and non-qualified rates. Although tiered pricing offers ease of use for novice merchants, it’s not the cheapest of the options.
When comparing merchant service providers, you should look for transparency and clarity in their pricing models and the most flexible and affordable options to get the best bang for your buck.
Processing fees
When signing up with a merchant services provider, you should carefully review the fees associated with their products and services.
Standard merchant services fees may include:
- Setup fees
- Transaction fees
- Monthly statement fees
- Chargeback fees
- Termination or cancellation fees
- PCI compliance fees
Standard fees will always be attached to merchant services, but you should still look for MSPs that are transparent about what they intend to charge you. Some providers hide fees in pricing structures that may not be explicitly or clearly outlined. Therefore, reviewing terms and conditions before committing to a provider is imperative.
Customer support
Whether it’s troubleshooting or product training, customer support is essential to merchant services, but not all MSPs are created equal.
Some areas to look for when evaluating support departments include responsiveness, knowledge and expertise, training and onboarding resources, account management, and more. Researching current and previous client testimonials and reviews is one of the best ways to ensure your business finds a provider with high-quality support.
Finding a merchant service provider with excellent customer support can ensure a smooth payment experience for your customers and provide your business with peace of mind knowing assistance is readily available.
The best merchant services providers will provide affordable and customizable pricing structures, minimal processing fees, and direct, high-quality support.
Optimize your accounts receivable with a top-rated merchant service provider
From online transactions to point-of-sale systems, finding a reliable merchant service provider with robust features and functionality is pivotal in streamlining payment processing operations.
With a comprehensive suite of payment processing solutions, businesses can use MSPs to accept and manage in-person and online electronic payments seamlessly.
Summary
- What is a merchant service provider?
- What types of businesses qualify as merchants?
- What is a merchant services account
- How do merchant services work?
- What products and services are included in merchant services?
- Merchant account vs. merchant service provider
- 4 questions to ask your merchant service provider
- 3 factors to consider when choosing an MSP
- Optimize your accounts receivable with a top-rated merchant service provider