Blog > Understanding B2B Payments: Exploring Payment Methods and Key Terms
Understanding B2B Payments: Exploring Payment Methods and Key Terms
Business-to-business payments play a crucial role in commerce by allowing companies to process payments with each other using specific payment methods and key players to facilitate these transactions. To better understand what and who is involved in these transactions, this article will dive into common business-to-business (B2B) terminology and payment methods.
What are B2B payments?
Unlike business-to-consumer (B2C) payments, where customers pay businesses for goods and services, B2B payments involve one company making payments to another. These payments occur for various reasons, including purchasing raw materials, settling invoices, and procuring services. A reliable B2B payment system plays a pivotal role in the smooth operation of businesses across industries. It’s important to familiarize yourself with some essential terms of the B2B payment landscape to ensure your business can best optimize its payments.
How do B2B payments work?
Compared to B2C payments, B2B payments have a more tedious and complex process to go through. Below is the eight step process B2B payments need to go through to be processed.

- Invoice Generation: The process begins with one business providing goods or services to another. The seller generates an invoice detailing the products or services provided, along with their prices and any applicable taxes or fees. This invoice serves as a request for payment.
- Payment Terms: Before the transaction occurs, both parties agree on payment terms, including the payment due date, acceptable payment methods, and any discounts or penalties for early or late payment.
- Payment Initiation: Once the buyer receives the invoice, they initiate the payment process. Payment methods commonly used in B2B transactions include bank transfers, checks, electronic funds transfers (EFT), credit cards, and increasingly digital payment platforms.
- Payment Authorization: Before the funds are transferred, the payment may undergo authorization processes to ensure security and legitimacy. This step can involve verification of the payer’s identity and authorization of the transaction by relevant stakeholders within the buying organization.
- Funds Transfer: After authorization, the funds are transferred from the buyer’s account to the seller’s account through the chosen payment method. The time it takes for the funds to reach the seller varies depending on the payment method used.
- Reconciliation: Both parties reconcile their financial records to ensure that the payment matches the invoiced amount. This step helps identify any discrepancies or errors that need to be resolved.
- Confirmation and Settlement: Once reconciliation is complete and both parties agree on the transaction details, the payment is considered settled. A confirmation may be sent to acknowledge the successful completion of the payment process.
- Record Keeping: Finally, both parties maintain records of the transaction for accounting and auditing purposes. These records include invoices, payment receipts, and any communication related to the transaction.
Efficient B2B payment processes are crucial for maintaining healthy business relationships and ensuring smooth financial operations. As technology advances, digital payment solutions and automation tools are increasingly adopted to streamline B2B payment workflows and improve efficiency and transparency in transactions.
5 B2B payment terms your business should know
Just like learning the basics before tackling a new challenge, knowing these terms will help give you a head start when you explore the details of B2B payments and B2B payment solutions.
Here are some fundamental terms to understand:
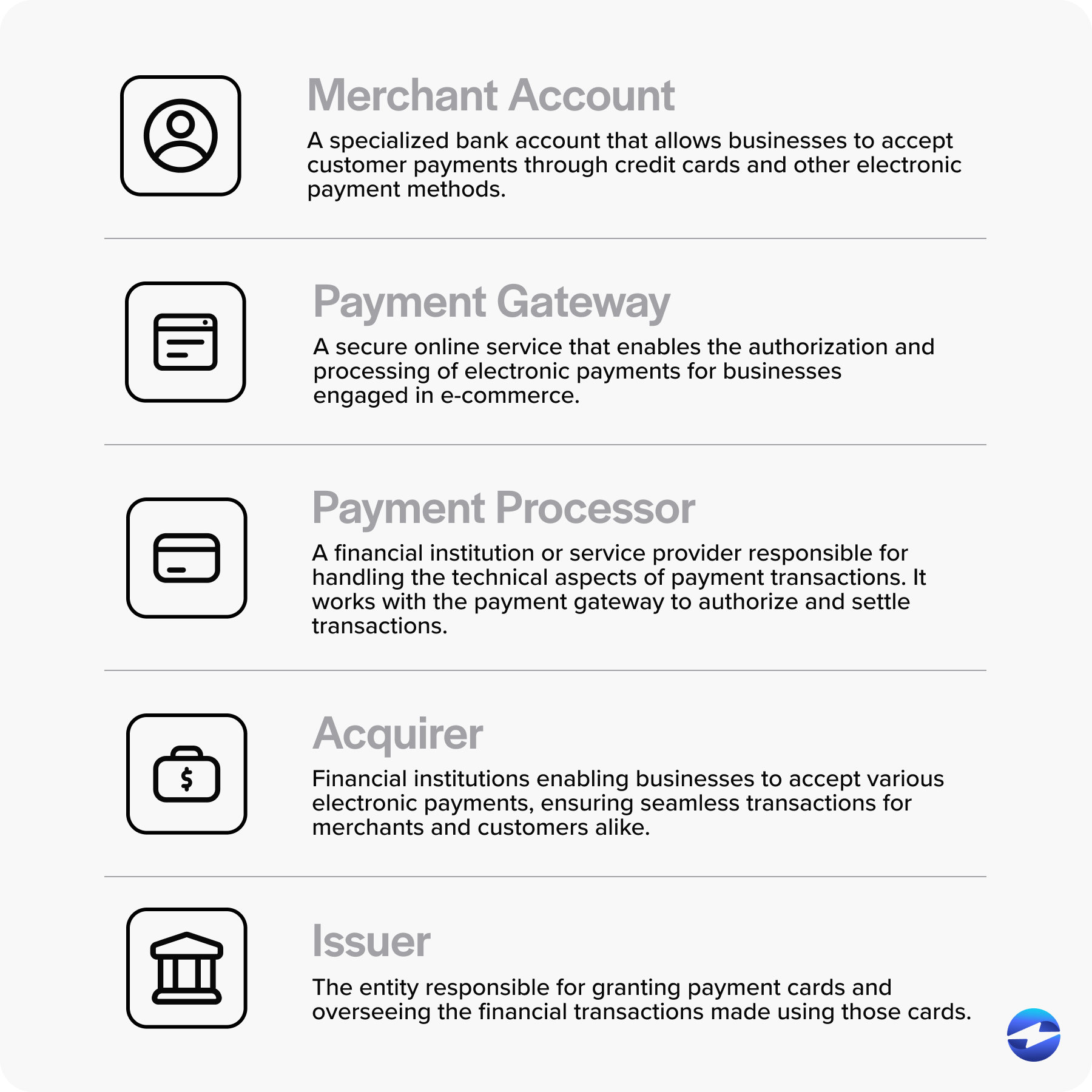
- Merchant account
- Payment gateway
- Payment processor
- Acquirer
- Issuer
Merchant account
A merchant account is a specialized bank account that allows businesses to accept customer payments through credit cards and other electronic payment methods. It acts as an intermediary for transferring funds from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account after a successful transaction.
Merchant accounts are essential for businesses in online commerce or retail environments where card payments are prevalent.
Setting up a merchant account typically involves a partnership between the business, the acquiring bank, and a payment processor. Some merchant accounts may also support additional payment options, such as mobile wallets and digital payment platforms, ensuring a seamless customer payment experience and broadening the business’s reach.
Payment gateway
A payment gateway is a secure online service that enables the authorization and processing of electronic payments for businesses engaged in eCommerce. It acts as an intermediary between customers, merchants, and financial institutions, ensuring that sensitive payment information is transmitted securely and efficiently.
Payment gateways encrypt sensitive payment data, such as credit card details, ensuring secure transmission. The encrypted data is forwarded to the acquiring bank for processing, and upon approval, the payment gateway confirms the transaction to the customer and merchant. Payment gateways are also responsible for facilitating various payment methods, providing transaction reports, and supporting businesses in any online transactions.
Choosing the right payment gateway is essential for ensuring a seamless payment process, customer trust, and success in the digital economy.
Payment processor
A payment processor is a financial institution or service provider responsible for handling the technical aspects of payment transactions. It works with the payment gateway to authorize and settle transactions. It also ensures the secure funds transfer between the customer’s bank and the merchant’s bank account. While the payment gateway focuses on securely transmitting payment data, the payment processor handles the behind-the-scenes operations, including verifying the customer’s payment information, confirming available funds, and coordinating with the acquiring bank to finalize the transaction.
Payment processors are essential for businesses to receive timely and accurate payments, as they play a crucial role in streamlining the payment flow and reducing the risk of fraudulent activities. By integrating multiple payment methods and supporting various currencies, payment processors enable merchants to expand their reach and cater to a global customer base. Additionally, payment processors handle issues such as chargebacks and refunds, ensuring a smooth and reliable payment experience for customers and merchants.
Acquirer
Credit card acquirers, also known as payment acquirers, are financial institutions that enable businesses to accept various electronic payments, ensuring seamless transactions for merchants and customers alike.
Acquirers play a vital role by collaborating closely with businesses to establish merchant accounts, which are the foundation for enabling electronic payment acceptance. Acting as intermediaries, they seamlessly process transactions, ensuring the secure transmission of payment data, verifying transaction authenticity, and initiating fund movement. Acquirers are pivotal in acquiring authorization from the customer’s issuing bank, thus greenlighting the transaction. Subsequently, they facilitate the settlement process, overseeing the smooth transfer of funds from the customer’s account into the merchant’s. Acquirers also manage risk by scrutinizing transaction activity to detect fraud or suspicious behavior to safeguard merchants and customers.
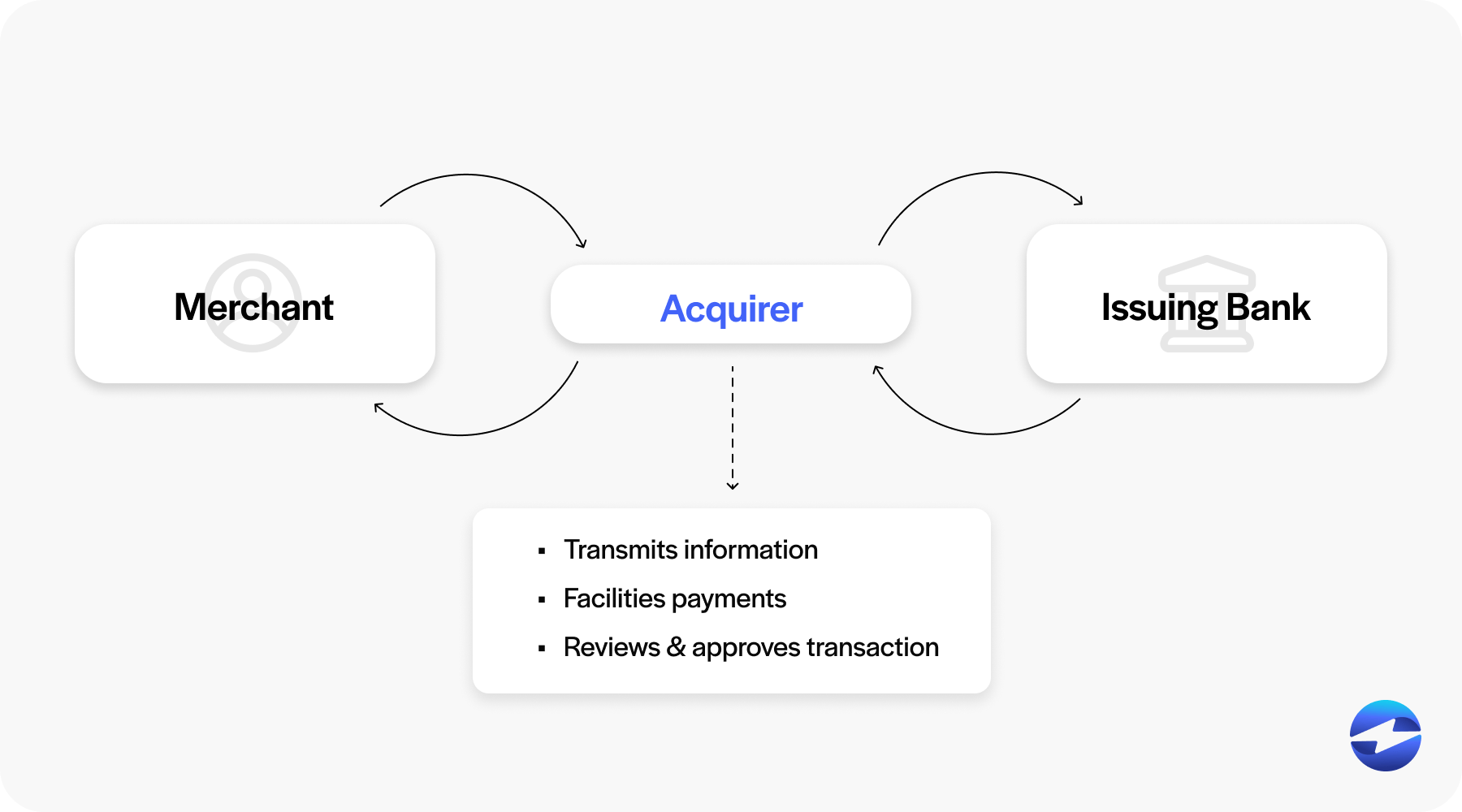
Additionally, acquirers facilitate the collection of various fees, encompassing interchange fees dictated by card networks, processing fees, and an array of service charges. These fees cover the essential costs of maintaining a payment processing infrastructure and delivering various necessary services. Recognizing the multifaceted nature of their role, acquirers extend their support beyond the transactional realm, offering dedicated customer assistance. This encompasses addressing inquiries, resolving technical challenges, and ensuring the seamless facilitation of payment processing operations, empowering merchants to focus on their core business objectives.
Issuer
The issuer refers to the bank or financial institution issuing the customer’s credit card. An issuer plays a crucial role as the entity responsible for granting payment cards and overseeing the financial transactions made using those cards.
Issuers initiate payment card issuance for eligible entities, such as credit and debit cards, and maintain cardholder relationships by managing accounts and providing dedicated customer support. During transaction authorization, issuers evaluate fund availability to ensure seamless payment progression. Their security measures and fraud detection systems actively safeguard cardholder accounts, and they facilitate billing by creating statements while also initiating fund transfers. Moreover, issuers manage credit limits and oversee credit card billing cycles while serving as crucial mediators in dispute resolution. They administer rewards and benefits tied to payment cards, enhancing cardholder experiences.
In essence, issuers play a pivotal role in the B2B payment landscape by issuing cards, ensuring secure transactions, managing financial matters, and delivering essential support services.
Understanding these fundamental terms is just the first step. It’s just as important to be aware of the various popular payment methods that customers or businesses commonly use for their purchases.
5 common B2B payment methods to understand
In the B2B realm, various payment methods cater to the diverse needs of businesses. Each method is tailored to suit a company and cater to its operations. Each option has its advantages and drawbacks to consider. Here we will dive into the prevalent B2B payment methods in today’s modern commerce.
Some standard B2B payment options include:
- Credit Card
- Check
- ACH
- Wire Transfer
- EMV

Credit card
Credit cards are a standard and versatile payment method in the B2B landscape. By accepting credit cards, businesses can conveniently make purchases and pay for services, even when immediate cash flow might be challenging. Credit cards offer the added advantage of flexible credit terms, providing enterprises with a temporary financing option that aligns with their operational needs. Credit card issuers can also provide expense-tracking features to help a company’s financial management.
Check
Despite the digital revolution in payment technologies, traditional paper checks remain significant in B2B transactions. The enduring nature of checks is particularly evident when businesses settle invoices and payments with other companies. Checks offer a sense of familiarity and simplicity, allowing for a tangible record of the payment process. Moreover, checks retain their value in specific industries and relationships as a trusted and well-established payment method.
ACH transfers
Automated Clearing House (ACH) transfers have emerged as a preferred B2B payment option for electronic bank-to-bank transactions. ACH transfers streamline fund transfers securely and cost-effectively, making them an ideal choice for businesses conducting recurring payments, such as regular subscriptions or vendor remittances. Getting your company set up to seamlessly integrate B2B ACH payments with their accounting systems will help enhance operational efficiency, and enable companies to allocate resources more strategically.
Another notable method of ACH payments is the electronic check or eCheck. EChecks offer a digital alternative for transferring funds directly from one bank account to another. EChecks provide the convenience of paperless transactions while retaining the familiarity of the check format. They are particularly advantageous for businesses that need to manage high volumes of payments efficiently and securely. Incorporating eChecks alongside standard ACH transfers can offer businesses greater flexibility and choice in electronic payment strategies.
While eChecks and ACH transfers involve electronic fund transfers, eChecks specifically refer to digital versions of traditional paper checks. In contrast, ACH transfers encompass a broader range of electronic bank-to-bank transactions
Wire transfer
Wire transfers reign as a reliable option in the B2B payment arsenal for high-value transactions and international payments. Wire transfers give businesses the confidence to engage in global commerce due to their efficiency and multi-currency capabilities. Wire transfers expedite fund transfers between banks with speed and security, making them suitable for time-sensitive deals or cross-border partnerships.
Benefits of digital B2B payment solutions
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, embracing digital B2B payment solutions offers numerous advantages for companies looking to streamline their financial operations and enhance efficiency.
Here are four key benefits of adopting digital B2B payment solutions:
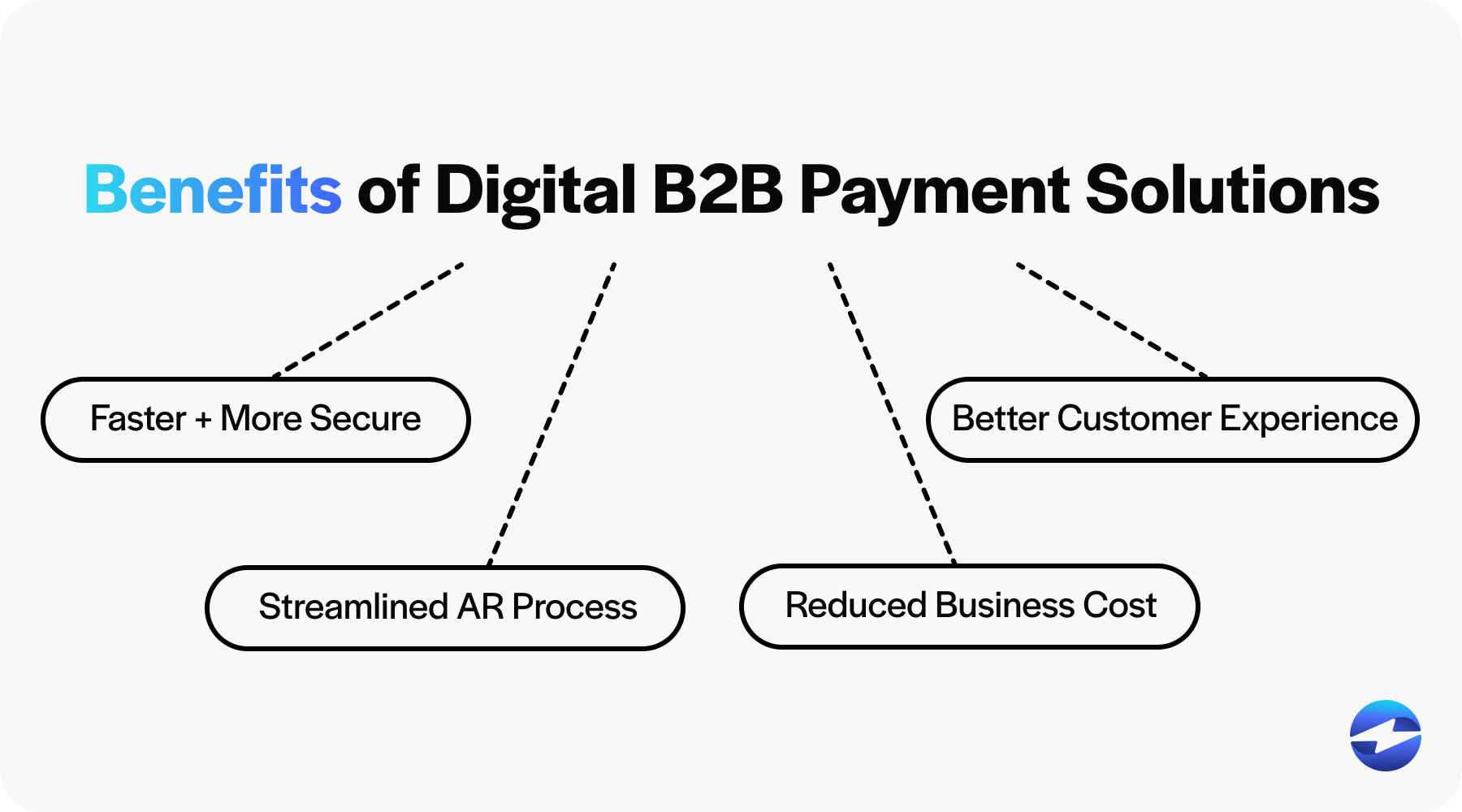
1. Faster and more secure payments
Unlike traditional methods such as paper checks or manual bank transfers, digital payments can be completed swiftly, often within minutes or even seconds. This speed not only accelerates cash flow but also enhances liquidity, allowing businesses to access funds more quickly to support their operations.
2. Streamline the AR process
Digital B2B payment solutions offer advanced features that streamline AR processes, such as automated invoicing, recurring billing, and real-time payment tracking. These capabilities help businesses optimize cash flow by minimizing the time and effort required to manage outstanding invoices and track payment statuses. Furthermore, digital payment platforms often integrate seamlessly with accounting software and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, facilitating seamless data synchronization and enhancing overall financial visibility and control.
3. Reduced business cost
By transitioning to digital B2B payment solutions, businesses can reduce these overhead expenses and achieve cost savings over time. Moreover, digital payments eliminate the need for paper-based documentation and manual reconciliation, reducing administrative burdens and freeing up resources for more strategic initiatives. The automation and efficiency offered by digital B2B payment solutions enable businesses to operate leaner and more cost-effectively, ultimately contributing to improved profitability and competitiveness in the marketplace.
4. Enhances the customer experience
By providing multiple payment channels and streamlined checkout processes, businesses can enhance the overall customer experience and build stronger relationships with their clients. Additionally, digital payment solutions enable businesses to offer personalized invoicing and billing options tailored to each customer’s preferences, further enhancing satisfaction and loyalty.
While B2B payments have many benefits for your company, there are some difficulties associated with B2B payments as well.
Difficulties of traditional B2B payments
Traditional B2B payment methods, while once the standard, come with many challenges that can hinder efficiency and create headaches for businesses.
Here are some difficulties associated with traditional B2B payments:

1. High transaction fees
Traditional B2B payment methods frequently come with high transaction fees, particularly for cross-border transactions or payments processed through intermediary banks. These fees can eat into profit margins and increase the overall cost of doing business, particularly for companies that engage in frequent or large-value transactions.
2. Slow processing times
One of the most significant drawbacks of traditional B2B payments is the slow processing times involved. Methods such as paper checks or manual bank transfers often require several days, if not longer, to complete. This delay can impact cash flow, hinder working capital management, and prolong the time it takes for businesses to receive payments from their customers.
3. Late payments
Late payments are another common challenge in B2B payment systems, contributing to cash flow issues and operational disruptions for businesses. B2B payments sometimes offer limited visibility into payment statuses and lack of automated reminders make it difficult for businesses to track and manage payments effectively causing late payments. Without real-time insights into outstanding invoices or automated alerts for approaching due dates, businesses may inadvertently overlook or delay payments, causing frustration and uncertainty for their trading partners.
4. Security concerns
Traditional B2B payment methods are susceptible to security risks, including fraud, data breaches, and unauthorized access. Paper checks, for example, can be easily intercepted or altered, while manual bank transfers may lack the encryption and authentication measures necessary to protect sensitive financial information. As cyber threats continue to evolve, businesses must remain vigilant to safeguard their payment processes and mitigate the risk of financial loss or reputational damage.
5. Lack of collaboration
B2B payment methods often lack the collaborative features necessary for effective communication and dispute resolution between trading partners. Without real-time visibility into payment statuses or automated reconciliation capabilities, businesses may struggle to resolve discrepancies or address payment-related issues in a timely manner, leading to inefficiencies and frustrations for all parties involved.
While there are some apparent difficulties with B2B payments, they still offer an excellent solution for businesses who need to get paid by their customers.
Use EBizCharge for your B2B payments
Understanding the intricacies of B2B payments, including payment, the typical methods, and critical terms, is crucial for businesses engaging in commercial transactions. By familiarizing yourself with the fundamentals of B2B payments, you can make informed decisions and facilitate seamless financial transactions for your business. Optimize your B2B payment processing by using an award-winning merchant service provider. EBizCharge helps your business get paid on time by providing customers with an abundance of features like email payment links, recurring billing, and a personally branded portal for customers to make multiple payments to help speed up the invoicing process.