Blog > Net 30: What Is It and How Does It Work?
Net 30: What Is It and How Does It Work?
In the fast-paced business world, payment terms can make or break a deal. Understanding the implications of Net 30 can help companies streamline their transactions and manage cash flow more effectively.
Whether you’re a vendor setting terms or a buyer negotiating payment, knowing how Net 30 impacts invoicing, payment cycles, and financial planning is crucial. By mastering these terms, businesses can foster better relationships with partners and ensure smoother financial operations, ultimately contributing to long-term success.
What does Net 30 mean on invoices?
Net 30, or n30, is a common invoice payment term that indicates that a client or customer has 30 calendar days to pay the total amount due on an invoice.
When a business issues an invoice with the term Net 30, it states that the total amount of the invoice is expected to be paid in full, without any deductions, within 30 days from the invoice date. Net 30 is essential for managing cash flow and payment schedules for a business’s accounts receivable (AR) and accounts payable (AP) sectors.

It’s important to note the distinction between business and calendar days; unless otherwise specified, Net 30 refers to the latter, including weekends and holidays.
Businesses should clearly understand Net 30, which directly affects their financial operations and planning. Late payments beyond these 30 days may incur additional charges or penalties, impacting business relationships and credit scores.
Why do businesses use Net 30?
By offering Net 30 terms, companies can encourage prompt payments while giving customers flexibility. This practice can improve client relationships, maintain a steady income stream, and provide a competitive edge in the market.
Businesses choose Net 30 because it balances the need for timely payments with customer convenience, creating a win-win situation for both parties. Other reasons to use this payment term include:
- Cash flow management: Net 30 allows businesses to manage their cash flow by providing extra time to collect and allocate funds before settling a bill.
- Building business relationships: Offering Net 30 can strengthen business relationships by showing trust in a client’s ability to pay, facilitating smoother transactions, and potentially fostering long-term partnerships.
- Competitive advantage: Companies can gain a competitive edge with Net 30 by offering clients more flexible payment options than competitors.
- Financial health: Net 30 terms can contribute to a company’s financial health by allowing time to earn interest on cash reserves or to use them for other investments before payment is due.
- Business credit scores: Consistent use and adherence to Net 30 terms can positively impact both parties’ business credit scores, as prompt payments are often reported to credit bureaus.

While longer payment terms provide buyers more flexibility, they can impact the seller’s cash flow if not managed properly. Some businesses opt for a shorter payment window to encourage quicker payments. Offering Net 30 can signify financial health and stability, fostering trust between trading partners.
How does Net 30 work?
Net 30 is a relatively simple concept, but there are a few things that businesses need to understand about the process.
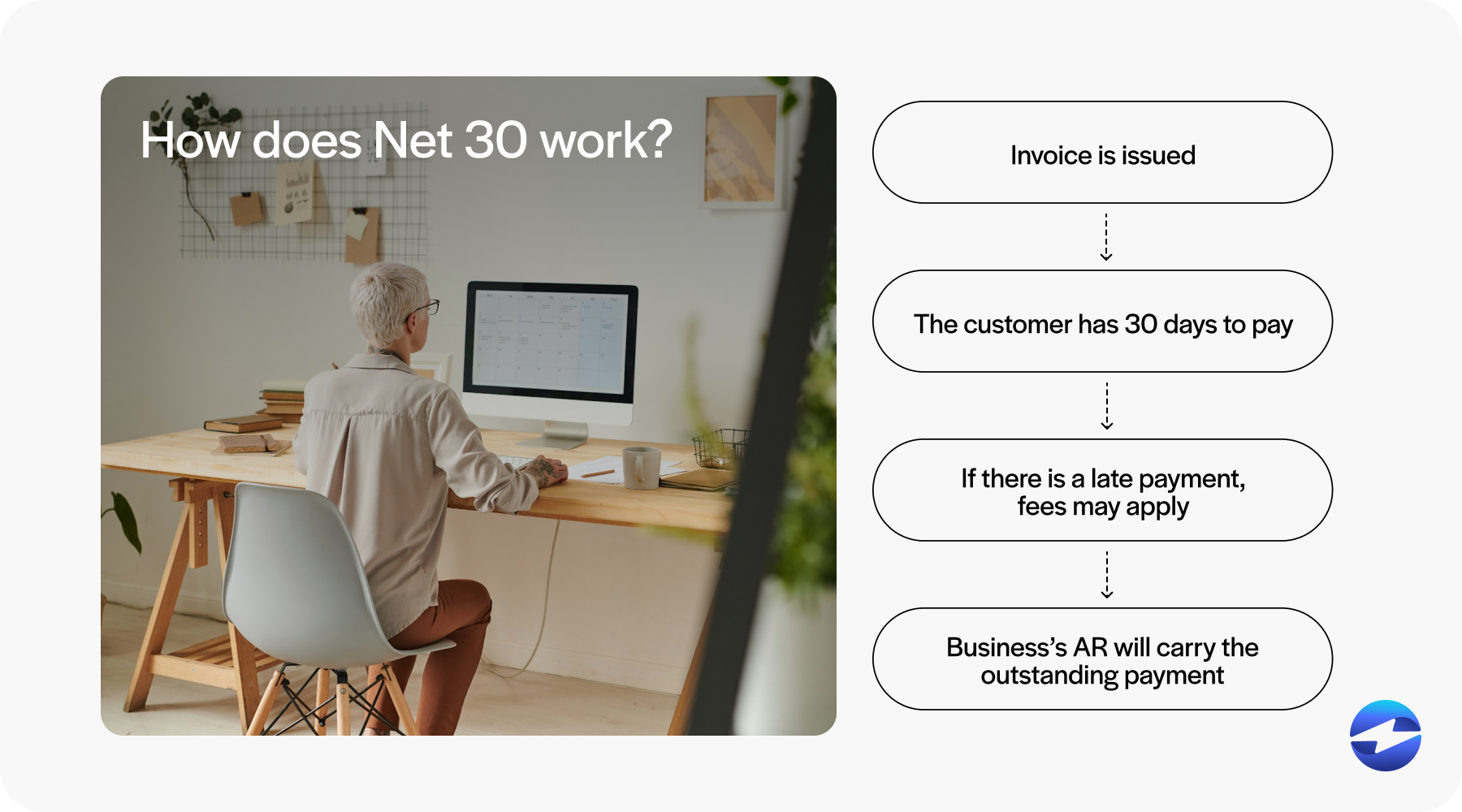
Net 30 can be understood using the following structure:
- Invoice issued: A business provides a product or service and sends an invoice to the customer stating Net 30 as the payment term
- Payment period: The customer has 30 consecutive calendar days to make the payment.
- Late payments: If payment occurs after 30 days, late fees may apply, impacting the buyer’s business credit score.
- Accounts receivable: The business’s AR will carry the outstanding payment as a receivable until it’s paid.
Net 30 terms can give buyers extra time to make payments and improve cash flow for your company. Still, it can also affect liquidity if this cash flow and your business credit score depend on these timely payments. Therefore, it’s important to evaluate the pros and cons of these terms to see if they’re a good match for your business infrastructure.
Is Net 30 right for your business?
Determining whether Net 30 payment terms suit your business requires careful consideration of your financial health and cash flow needs.
Offering Net 30 can boost competitiveness for business owners by providing clients with extra time to pay, improving business relationships. It can also reflect a company’s financial stability. Receiving payments on time can enhance your business credit score by generating favorable reports to credit bureaus. This practice not only reflects responsible financial management but also strengthens your credibility with lenders and suppliers.
Extending Net 30 payment periods can strain cash flow if not appropriately managed, particularly for businesses with tighter margins or those that rely on faster payments for operational expenses.
When deciding if Net 30 is suitable for your business, you can assess several areas of your infrastructure to see if these terms will enable you to maintain a healthy cash cycle.
Before implementing Net 30, companies should assess their financial health to ensure they can handle longer payment cycles without disrupting operations. They should also review client payment history to identify any customer payment trends related to on-time or late payments. Lastly, you should determine if Net 30 will yield competitive advantages for your business and industry.
Ultimately, shorter payment terms offer a shorter payment window, improving cash flow, but may only sometimes cater to client needs. Balancing client relations with financial stability is critical when choosing payment terms like Net 30.
Where does Net 30 go on the invoice?
When creating an invoice with Net 30, these terms should be prominently displayed so the customer is fully aware of payment expectations.
Typically, Net 30 terms are included near the top of the invoice, right under the invoice date, or they may be placed near the bottom, close to the total amount due. This placement ensures that the payment terms are immediately noticeable and associated with the financial summary of the transaction.
Here is an example outline of where Net 30 may be positioned on an invoice:
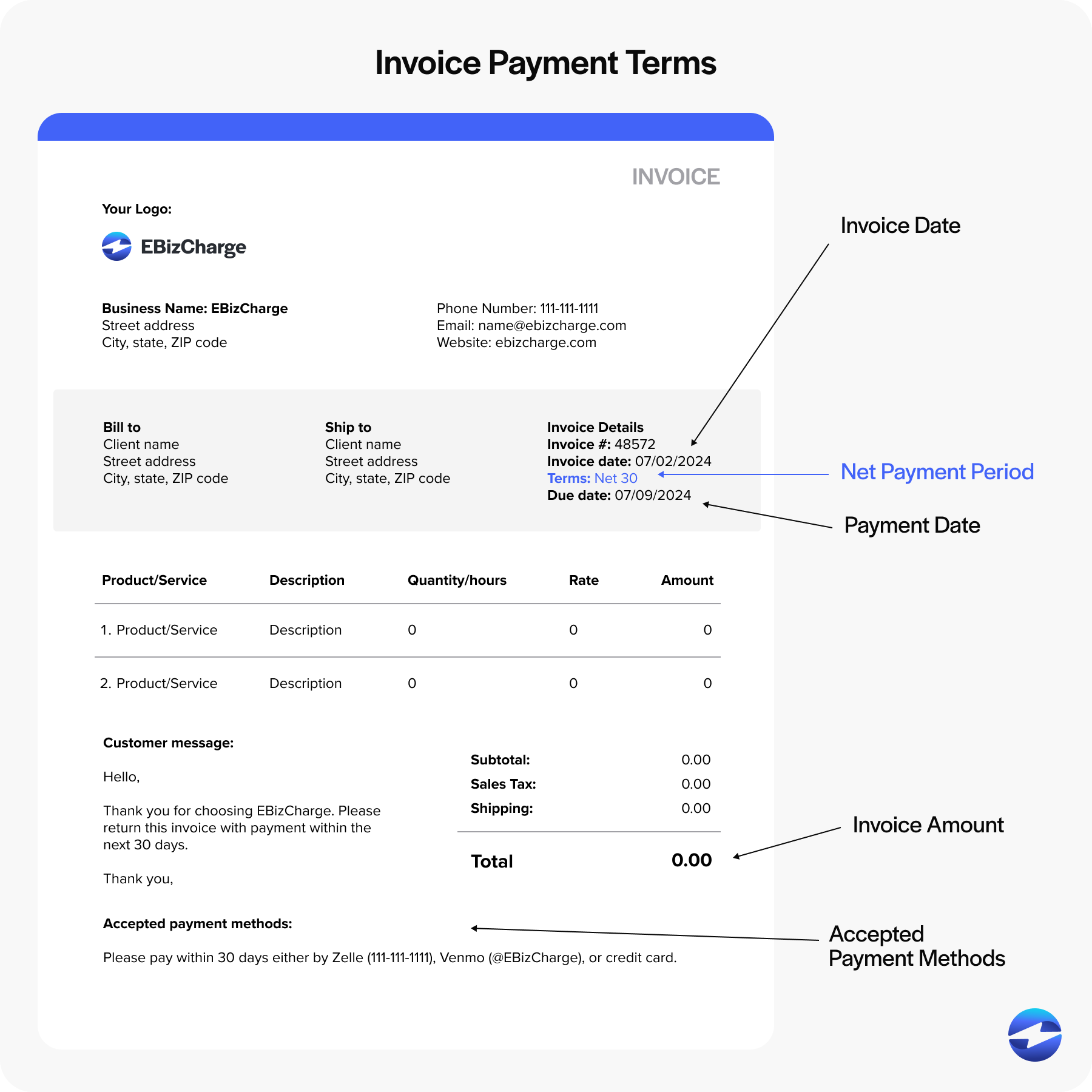
Placing Net 30 in these strategic positions directly ties the payment terms to the essential invoice details, ensuring clarity and reducing the likelihood of late payments.
6 benefits of implementing Net 30 in your customer payments
Net 30 payment terms can offer significant advantages for your company, yielding more long-term revenue and long-lasting business relationships.
Here are six key benefits of incorporating Net 30 into your customer payment strategy:
- Improved cash flow: Business owners can leverage trade credit to acquire inventory or services immediately, allowing them to generate revenue from sales before the payment for these resources becomes due. This timing advantage creates a positive cash flow cycle, enabling businesses to reinvest profits and expand operations more efficiently.
- Enhanced business credit scores: Timely Net 30 payments can contribute to building a positive credit history, which is critical for future financing needs.
- Vendor relationships: Net 30 payment terms can encourage timely payments that promote good supplier relationships, which is advantageous for long-term business dealings.
- Competitive advantage: Extending Net 30 payment terms to clients can significantly bolster a company’s competitive position in the market. By offering this 30-day payment window, businesses demonstrate financial robustness and operational confidence, which can attract more customers and larger accounts.
- Financial flexibility: Net 30 terms allot extra time for companies to manage their funds, enabling better budgeting and less reliance on costly short-term credit.
- Prompt payment discounts: Net 30 allows vendors to offer payment discounts for early settlement, saving businesses money.
While Net 30 can promote early or on-time payments without compromising a business’s financial health, these terms still have some limitations.
Net 30 limitations
While Net 30 is an excellent method to get your customers to pay their invoices on time, it carries certain limitations.
One of the most significant limitations is that Net 30 terms can strain the seller’s cash flow, especially for those with less capital, as they wait for payment.
Furthermore, offering several Net 30 payment terms can complicate AR management and increase the administrative burden. There’s also the risk of late invoices, as payments made after 30 days can disrupt a company’s financial planning and operations.
Frequent late payments may impact the buyer’s business credit scores. Credit bureau agencies such as Dun & Bradstreet and Equifax monitor this and can influence the company’s ability to secure future trade credit.

Despite its advantages, the limitations of Net 30 terms have led businesses to explore alternative payment structures that better meet their customers’ needs, as well as their own needs. These alternatives aim to address the challenges associated with Net 30 while still providing flexibility and maintaining competitive appeal.
What are the alternatives to Net 30 terms?
Businesses may consider alternative payment terms to Net 30 for various reasons, such as cash flow management, customer relationships, or incentives for faster payments.
Here are five alternatives to Net 30 that merchants may consider:
- Net 60 or Net 90: Net 60 or Net 90 extends the payment window, giving consumers 60 or 90 days to make payment.
- Net 10 or Net 15: Net 10 or Net 15 shortens the payment period to 10 or 15 days. They can accelerate the supplier’s cash flow and lead to consumer discounts.
- 2/10 Net 30: 2/10 Net 30 offers a 2% discount if payment is made within 10 days encouraging timely payments and benefits for both parties. If consumers can’t pay within 10 days, the terms will revert to the original 30-day payment window.
- Cash on Delivery (COD): COD payments are made at the time of delivery rather than being deferred to dramatically reduce the risk of late payments for businesses.
- Prepayment or advance payments: Prepayment or advance payments require consumers to make partial payments or pay in full before receiving products or services. This provides immediate cash flow and eliminates default risk for merchants.

As businesses explore these alternatives, it’s essential to assess how they will affect operations, relationships, and overall finances.
Leverage Net 30 terms to optimize your customer payments
Despite the many benefits that Net 30 offers, these terms demand diligent accounting practices and effective cash flow management to ensure on-time payments and maintain financial health. Net 30 is a vital component of the payment cycles that can enhance your company’s day-to-day operations and strategic financial planning for more long-term success.
The EBizCharge payment processing solution helps you collect on those Net 30 invoices faster with accounts receivable automation and payment integrations for ERP and accounting software that automatically post payments the moment they come in.
- What does Net 30 mean on invoices?
- How does Net 30 work?
- Is Net 30 right for your business?
- Where does Net 30 go on the invoice?
- 6 benefits of implementing Net 30 in your customer payments
- Net 30 limitations
- What are the alternatives to Net 30 terms?
- Leverage Net 30 terms to optimize your customer payments

