Blog > Cash Disbursement: What is it and How Does it Work?
Cash Disbursement: What is it and How Does it Work?
Healthy cash flow is essential for maintaining a business’s financial stability. Excessive outflows of capital from any organization, if left unchecked, can lead to problems involving slow growth rates, inability to meet financial obligations, and, in extreme cases, bankruptcy.
In the world of finance, cash disbursements are pivotal in maintaining a financial balance between businesses and other organizations. Therefore, business leaders must understand cash disbursements, how they work, and best practices to organize and streamline the process.
What is cash disbursement?
Cash disbursements lie at the heart of every business transaction since they involve using funds from a company’s accounts to make payments for various expenses and financial commitments.
Some of these commitments include payments to suppliers and vendors for goods and services, compensation to employees through salaries and benefits, repayments of loans and any accrued interest, covering day-to-day operating costs like rent and utilities, tax obligations, and investing in growth initiatives.
Examples of cash disbursements
To better understand how these payments work, you can examine and apply real-world cash disbursement examples.
Three examples of cash disbursements include supplier payments for raw materials, employee compensation, and acquiring essential assets.
Examples of cash disbursements
To better understand how these payments work, you can examine and apply real-world cash disbursement examples.
Three examples of cash disbursements include supplier payments for raw materials, employee compensation, and acquiring essential assets.
Supplier payments for raw materials
Imagine a manufacturing company specializing in crafting artisanal furniture. In order to create their exquisite pieces, they rely on a consistent supply of high-quality raw materials.
To achieve this consistency, the manufacturing company initiates a cash disbursement when settling their dues with suppliers for the timber, upholstery, and hardware. This payment is disbursed and paid to the respective organizations and material providers, settling the company’s debts and promoting future transactions.
Employee compensation
Consider a rapidly growing software development startup with a dedicated team of programmers, designers, and project managers who contribute their expertise to bring innovative digital solutions to life.
As compensation for their contributions, the company issues recurring cash disbursements to the employees to satisfy the payroll.
Acquiring essential assets
In an attempt to increase operational efficiency while promoting sustainability, a transportation company purchases a fleet of eco-friendly vehicles with lower emission rates than standard transport vehicles. Acquiring these vehicles requires payment to the supplier and the shipping company responsible for the delivery.
The total amount paid by the transportation company is separated into a cash disbursement, disbursing the funds to the respective entities.
These cash disbursement examples outline how funds are distributed to separate entities within a given transaction.
Drawdowns are another critical component to factor before utilizing cash disbursements in your business.
What are drawdowns?
Drawdowns typically refer to reducing available funds from a larger sum. In cash disbursements, drawdowns often occur when a business accesses a pre-approved line of credit or utilizes a fund for specific purposes.
For example, a construction project might have a designated fund from which disbursements are drawn as various project milestones are achieved.
Drawdowns are important to track as they give the accounting team and company leadership visibility into how much actual cash is still available for future disbursements.
For example, if the company has a $100,000 fund for new manufacturing equipment and has spent $20,000, a $20,000 drawdown is applied to the fund total, letting all stakeholders know that there is only $80,000 remaining in the budget for this type of purchase.
Since various expenses and factors are involved in cash disbursements, keeping accurate records of these payments is imperative.
What is a cash disbursement journal?
A cash disbursement journal is a dedicated journal that records all disbursement transactions, providing a clear and organized overview of cash outflows.
Not only does a cash disbursement journal aid in tracking expenses, but it also ensures accurate bookkeeping, offering a detailed historical record for audits and financial analysis. It also helps organizations keep track of the remaining funds available in their budget.
Before using and recording cash disbursements in a journal, it’s essential to understand the different forms these transactions can come in.
8 types of cash disbursement
Cash disbursements can take many forms, each with its own characteristics, benefits, limitations, and implications.
Here are eight common forms of cash disbursements:
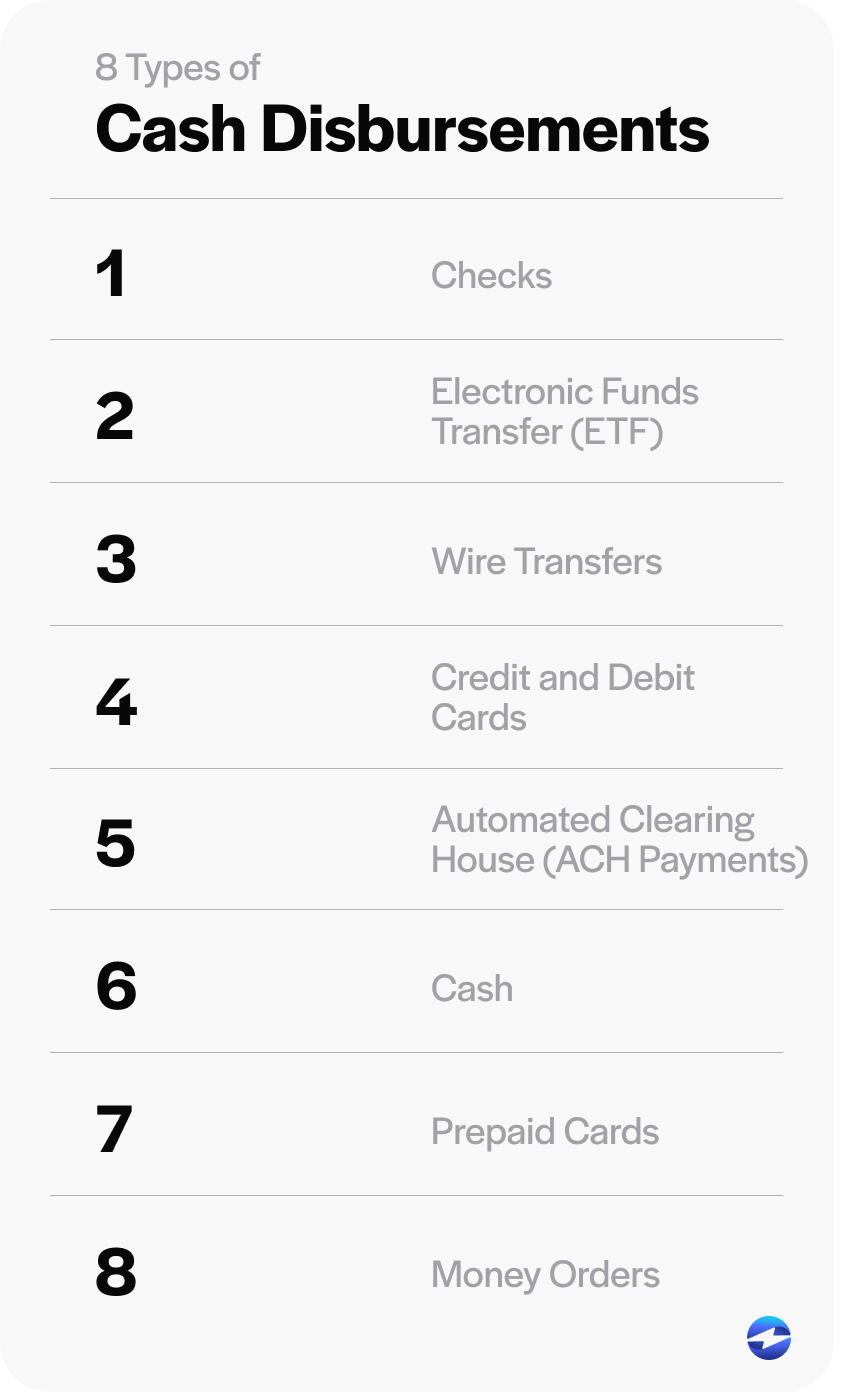
- Checks: While personal checks are losing popularity due to the rise of debit cards, physical checks are often used for routine business-to-business (B2B) payments. Checks are a reliable payment method that provide a tangible paper trail of transactions.
- Electronic funds transfer (EFT): EFT payments involve electronically transferring funds from one account to another and are popular due to their speed and efficiency.
- Wire transfers: Wire transfers electronically move funds from one bank account to another. These transfers typically involve senders instructing their banks to transfer specific amounts of money to recipients’ bank accounts, whether it’s within the same bank or across different financial institutions.
- Credit and debit cards: Card payments are a prevalent option in today’s commerce environment, making up roughly 77% of all noncash payments. Credit and debit cards are extremely versatile, as businesses can accept these payments in person or online.
- Automated Clearing House (ACH) payments: ACH payments are electronic transactions allowing direct transfers between bank accounts and are commonly used for payroll and bill payments.
- Cash: Cash payments still make up about 18 percent of all U.S. transactions. While these transactions are becoming less common with the rise of digital advancements, they still hold significance, particularly in small-scale and in-person transactions.
- Prepaid cards: Prepaid cards, often used for employee expenses or travel, allow controlled spending within predetermined limits.
- Money orders: Similar to physical checks, money orders are secure paper documents usually issued by a government or banking institution with prepaid amounts.
Now that you know the various types of cash disbursements, you can look into why these disbursements are important for companies.
Why are cash disbursements important?
Cash disbursements are important because they serve as a financial compass guiding businesses toward sustainable growth and fiscal responsibility.
Businesses can significantly benefit from systematically recording and managing cash disbursements. Four benefits of cash disbursements include:
- Accurate financial records: By tracking the outflow of funds from an organization, cash disbursements provide a detailed record of all financial transactions, ensuring each expense is accurately documented. This level of transparency is indispensable for audits, financial analytics, and compliance.
- Compliance and reporting: In regulated industries, maintaining accurate records of cash disbursements is not just recommended, it’s mandatory. Failure to comply with legal standards can result in fines, additional taxes and interests, and a heavy hit to your reputation. By adhering to legal and financial reporting requirements, businesses can avoid penalties and legal discrepancies.
- Strategic planning: Cash disbursement data provides a wealth of information for strategic planning. Businesses can identify trends, assess spending patterns, and make informed decisions about resource allocation.
- Vendor and creditor relationships: Timely and consistent cash disbursements are pivotal in nurturing healthy relationships with vendors, suppliers, and creditors. Companies can build trust and strengthen these business relationships by ensuring vendors and creditors can rely on predictable cash flow.
In addition to knowing the importance of cash disbursements, businesses must also understand how these transactions are conducted.
How do cash disbursements work?
Initiating a cash disbursement involves a series of carefully orchestrated steps. So, businesses shouldn’t take shortcuts when processing corporate disbursements, as failure to properly authorize, process, and record disbursements can lead to poor financial decisions.
The nine steps of cash disbursement transactions include:
- Authorization and verification
- Invoice or payment request
- Documentation and recording
- Selection of payment method
- Approval
- Payment execution
- Recording the transaction
- Reconciliation
- Notification
Step 1: Authorization and verification
Each organization has a financial plan to guide its actions throughout the fiscal year. Before the cash disbursement process can begin, there’s typically an authorization decision to complete a purchase, commit to a new expense, or make other financial decisions.
For example, when a company decides to expand its manufacturing department, it must ensure that hiring additional staff or acquiring supplementary warehouse space aligns with the company’s financial interests and carries the approval of the necessary authorized representatives. These financial commitments are often locked in via a legal document such as a contract or purchase order.
Step 2: Invoice or payment request
Once a cash disbursement has been authorized and verified, the disbursement process officially begins when a request is made for payment from a vendor, supplier, or other outside party.
A cash disbursement request usually comes as an invoice or verified document that outlines the transaction details, the requested amount, the recipient’s contact information, and the required payment method.
Step 3: Documentation and recording
Next comes the documentation and recording process, as it’s essential to accurately document each part of the payment request process.
Accessing copies of the invoices or purchase orders and tracking the payment due dates will help ensure your financial obligations are completed on time. You may also require this documentation for future reference to complete your annual tax return or in the event of an audit.
Step 4: Selection of payment method
Your company must also decide which payment method to use for this cash disbursement. Different transactions may require specific payment methods, including checks, EFT payments, wire transfers, or credit cards.
For example, it’s not recommended for companies to pay their employees with cash or prepaid credit cards. Some payment methods are seen as more secure than others, so they’re used when transferring large sums of money.
Step 5: Approval
Before cash disbursements are executed, they must receive proper authorization from designated individuals or departments to ensure these payments align with company policies.
The person authorized to approve cash disbursements may vary depending on the size and type of the organization. For small businesses, an owner may have sole control over cash disbursements, possibly handled by an accountant or bookkeeper at their direction. For larger organizations, multiple people may be authorized to execute cash disbursements.
Many companies also have limits on how much can be approved by specific individuals. For example, a staff accountant may be authorized to approve cash disbursements of up to $200, but the CFO would have to sign off on a cash disbursement of $200,000.
Step 6: Payment execution
Once these previous steps have been met and the payment is approved, the cash disbursement can be executed using the chosen payment method.
Executing a cash disbursement can involve generating a physical check, initiating an electronic transfer, or processing a credit card payment.
Step 7: Recording the transaction
When the payment is executed, the transaction should be simultaneously recorded in the organization’s cash disbursement journal.
Cash disbursement journals allow companies to maintain a more precise transaction history log for more accurate expense tracking, bookkeeping, budgeting, and financial forecasting.
Step 8: Reconciliation
Recording cash disbursements is often a tedious and manual process handled by a company’s accounting team. With any manual process, mistakes and human errors are likely to occur.
For this reason, businesses should conduct regular reconciliations to ensure disbursement records align with bank statements and other financial records. Any discrepancies should be promptly addressed.
Step 9: Notification
Upon successful execution of the payment, all relevant stakeholders should be notified of the completed cash disbursement.
Cash disbursement notifications should include internal teams and external parties for the most accurate reporting and financial tracking.
While these nine steps can help you maintain more efficient cash disbursements, your business can also take advantage of automation tools.
6 ways to automate your cash disbursement process
Cash disbursements are rapidly evolving with technology, and automation is at the forefront of this evolution. Automated cash disbursement can improve the speed of processing payments, reducing human error and saving valuable time for finance teams.
Here are six ways to help you start automating your cash disbursement system:
- Select a robust accounting or ERP software. Not all accounting and ERP software are created equal. It’s important to carefully select a reliable software that can handle the volume of your financial operations, offers integrated automation tools, and can be customized to your needs. Payment solutions like EBizCharge complement your existing software by offering a QuickBooks payment gateway and NetSuite payment processing, so every cash disbursement and incoming payment posts to your books automatically without manual entry.
- Set up automated approval. Next, design an automated approval workflow that aligns with your organization’s hierarchy and policies. This will ensure all cash disbursements are approved on time and can be tracked electronically.
- Integrate your software with various payment methods. A well-integrated system can seamlessly connect with multiple payment methods, streamlining the payment execution process.
Schedule recurring payments for regular expenses. For routine or predictable payments, such as lease payments on company vehicles, offering automated cash disbursement schedules can ensure timely disbursements without the need for manual intervention. - Utilize strong security measures. Although, automation is typically more efficient, it demands stringent security measures to protect sensitive financial data. As technology advances, so do the methods of potential financial fraud. Companies should look for ways to implement robust internal controls to safeguard against fraudulent activities, such as duplicate payments or unauthorized disbursements.
- Regularly test and monitor your automated process. Businesses should periodically review and test their automated disbursement process to identify any glitches or areas for improvement. Consistent monitoring can guarantee more efficient automation and alignment with your company’s needs.
If properly implemented and managed, automation can enhance your cash disbursement system and your overall financial performance.
Optimize your cash disbursement process to adapt to evolving technology and trends
Cash disbursements form the backbone of financial transactions, fueling the economic engines that power businesses.
Since corporate disbursements continue to evolve with emerging technologies and trends, businesses must adapt their strategies and software to meet new demands. From meticulous documentation to embracing innovative automation and payment software, mastering the art of cash disbursements empowers companies to easily navigate the complex financial landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are cash disbursements?
Cash disbursements are the amount of cash that flows out of a business or organization. These payments are usually made to suppliers, employees, lenders, and other entities for goods, services, or obligations. Cash disbursements can include various expenses such as payroll, rent, utilities, purchasing inventory or equipment, repaying loans, and other operating expenses. Keeping track of cash disbursements is crucial to managing cash flow effectively and ensuring that a business can meet its financial obligations on time.
What is a disbursement check?
A disbursement check is a document a business issues to transfer funds to another party for goods, services, or obligations. It contains information such as payee name, amount, date, and reference numbers. It can be issued manually or electronically.
What is a cash disbursement journal a summary of?
A disbursement journal is a log that tracks all cash disbursements made by a business or organization within a specific period. It contains information about each disbursement, such as the date, payee, purpose of payment, the amount disbursed, and account codes or references.
The disbursement journal is essential for managing cash flow, tracking expenses, and maintaining accurate financial records. It is also used for financial reporting, budgeting, planning, auditing, and compliance purposes.
- What is cash disbursement?
- What are drawdowns?
- What is a cash disbursement journal?
- 8 types of cash disbursement
- Why are cash disbursements important?
- How do cash disbursements work?
- 6 ways to automate your cash disbursement process
- Optimize your cash disbursement process to adapt to evolving technology and trends
- Frequently Asked Questions