Blog > What is EMV Payment Processing and How Can My Business Use It?
What is EMV Payment Processing and How Can My Business Use It?
As industries shift toward digital payments, payment security has never been more essential. Thankfully, businesses can look to reliable security sources like EMV technology to revolutionize how they process transactions.
This article will explore the world of EMV payments, how they work, their costs, and the benefits they can yield for your company.
What is an EMV payment?
You may wonder, what is EMV technology? EMV stands for Europay, Mastercard, and Visa, the three companies that initially developed this technology in the 1990s. Therefore, EMV payments are transactions that use EMV chip-enabled technology in credit and debit cards to process payments securely.
EMV payments aim to increase security for consumers and merchants by utilizing a more secure chip-based card technology than the traditional magnetic stripe. The technology behind EMV transactions may seem complicated, but it’s easier to understand than it looks.
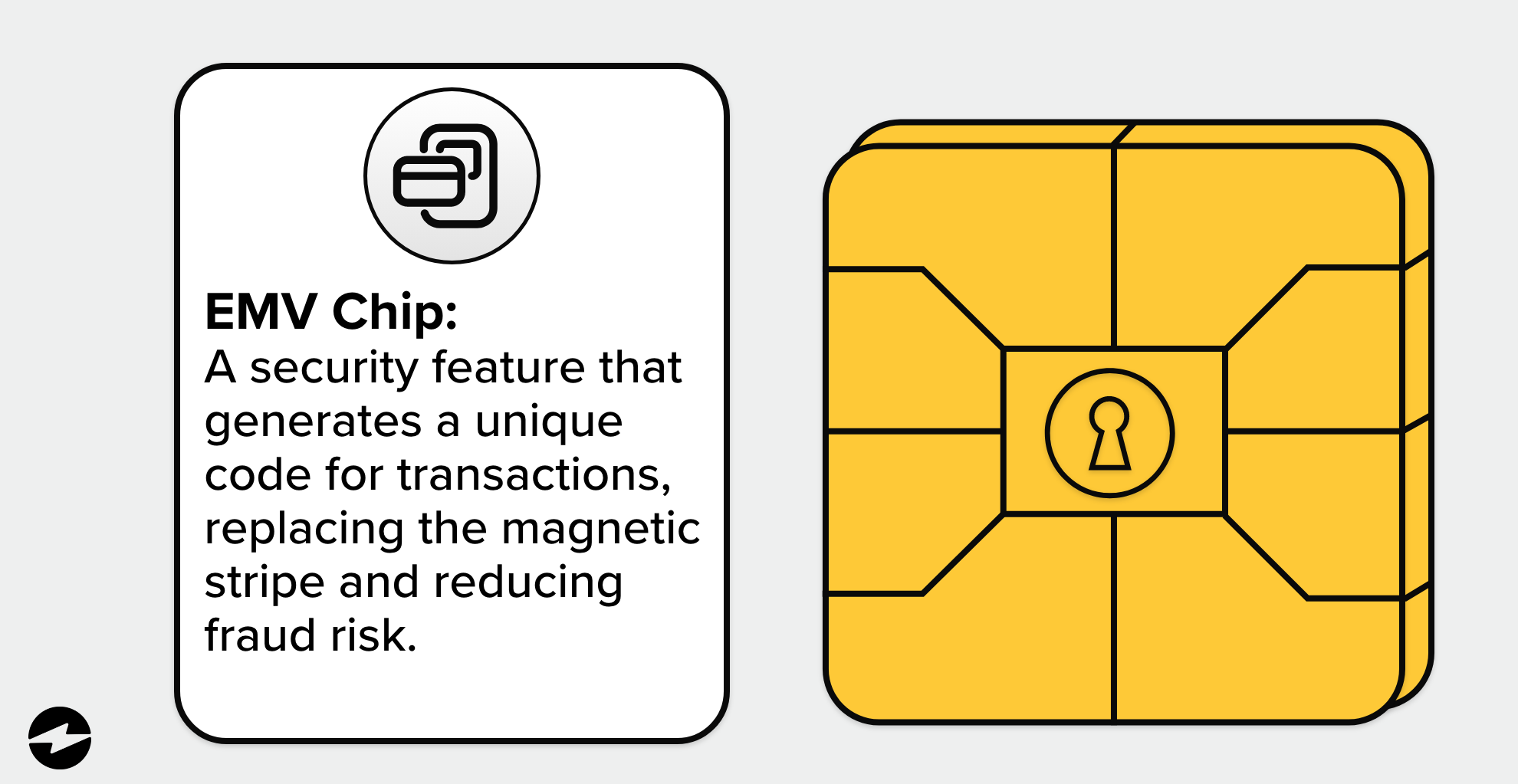
EMV technology uses a chip embedded in the card that generates a unique code for each transaction, making it much more difficult for criminals to copy or steal the user’s account information. The chip creates a unique code only valid for a single transaction. Therefore, it can’t be used again even if it’s intercepted. This process is called dynamic authentication, providing a higher level of security than traditional magnetic stripe payments.
EMV technology has become the standard for global credit and debit card payments, with many countries mandating its use. It has helped reduce fraud and increase security for both merchants and consumers. In addition, EMV payments can also include additional security features, such as requiring a PIN or biometric authentication, adding another layer of security to the payment process.
The following section will discuss the technology behind EMV payments and how it offers more security than traditional methods.
The technology behind EMV payments
You may wonder how EMV transactions are processed more securely and efficiently than other payments. The answer lies in its sophisticated EMV technology, a multi-layered system with three essential components.
The three components of EMV transactions include:
- Physical EMV chip readers on credit and debit cards
- EMV terminals that read the chip
- Processing systems that authorize EMV payments and transfer funds
EMV technology works together to provide a more secure and efficient payment experience by reducing the risk of fraud and chargebacks, which results in significant cost savings for merchants. Moreover, this technology provides increased protection for customers, making them feel more confident and secure when purchasing.
How to accept EMV transactions
To accept EMV transactions, your business must have compatible payment processing software and an EMV-compliant terminal capable of reading chip-based cards.
Once an EMV terminal is installed, businesses can sync their point-of-sale (POS) system to their terminal to accept EMV transactions.
It’s important to note that businesses that fail to upgrade to an EMV system may be held liable for fraudulent transactions. Therefore, it’s essential to stay ahead with the latest payment acceptance technology, such as EMV terminals and payment processing software.
EMV terminals
So, what is an EMV terminal? An EMV terminal is a payment processing device that accepts payments from chip-enabled credit and debit cards.
With various EMV terminals on the market, conducting thorough research is essential to find one that best suits your business’s needs. When evaluating different terminals, your company should consider costs, compatibility with existing systems, and ease of use for customers and employees.
Many payment processors and merchant service providers will include EMV terminals within their services, often with the option to purchase or lease the equipment. Leasing may be a more cost-effective option for businesses with limited capital or requiring frequent upgrades to their payment processing systems.
Payment processing software
In addition to upgrading your hardware, it’s crucial to ensure your payment processing software is EMV-compatible. Upgrading your hardware will allow the terminal to communicate with the processing system to complete the transaction.
Your payment processor or merchant service provider can assist with this step and provide any necessary updates or integrations to your existing systems. Upgrading your payment processing systems to EMV technology can provide a more secure and reliable customer payment experience while protecting your business from fraud.
Once your business purchases the EMV terminals and payment processing software, it can start accepting EMV payments. Before accepting these payments, you should know the costs of an EMV device and its associated transactions.
What are the costs of EMV terminals?
When considering EMV terminals for your business, it’s essential to understand the costs involved. From initial purchase or leasing charges to ongoing maintenance and fees, the price of EMV technology can vary depending on multiple factors.
The main costs associated with EMV transactions are the initial hardware charges and payment processing fees.
Hardware costs
Typically, businesses can expect to pay a few hundred to several thousand dollars for an EMV terminal. The price of EMV terminals varies significantly depending on a few different factors:
- Type of terminal: There are several EMV terminal options available on the market, which vary in price. EMV hardware can include countertop terminals, mobile card readers, and wireless terminals.
- Brand: The brand of the EMV terminal is another factor that can impact pricing. Brands like Verifone and Ingenico are leaders in the industry and charge a higher price than lesser-known brands.
- Features: Terminals with more advanced features will generally be more expensive. More advanced terminals may include features and capabilities such as contactless payments, encryption capabilities, and NFC mobile payments.
In addition to the initial hardware costs of EMV devices, there may be ongoing fees for leasing, maintenance, and software updates.
Despite hardware costs generally being more upfront, EMV terminals can accrue fees each time a customer uses this system.
Transaction costs
There are several costs to consider when processing an EMV transaction, such as transaction and chargeback fees, monthly statements, and more.
Transaction fees are one of the main costs of EMV transactions charged by payment processors or merchant service providers. These fees vary depending on the provider and the type of transaction. Additional EMV processing costs can include chargeback or monthly statement fees.
It’s essential to carefully review and understand these costs before selecting a payment processor or merchant service provider for your EMV transactions. Some providers may offer lower fees but charge for equipment or software, while others may include these costs in their pricing structure. Ultimately, the total cost of processing EMV transactions will depend on the provider you choose and the specific needs of your business.
While EMV technology has some initial hardware and transaction costs, it can enhance your business’s payment processing.
How EMV enhances your business’s payment processing
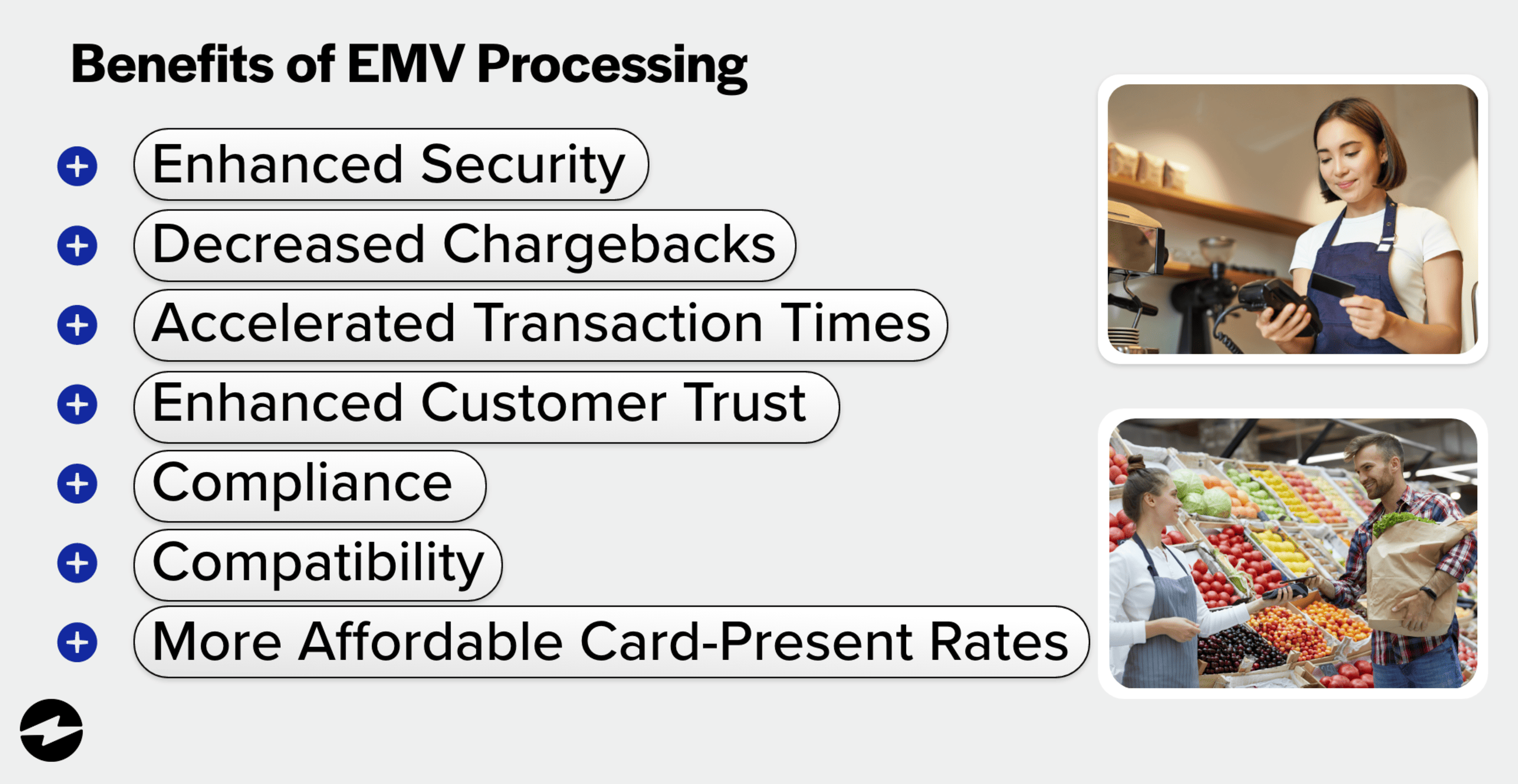
EMV transactions offer numerous benefits that significantly impact your business’s bottom line. Here are the main advantages of incorporating EMV payments into your company:
- Increased security: EMV technology provides increased protection and reduces the risk of fraud by generating a unique code for each transaction that makes it significantly more difficult to counterfeit or use stolen card information.
- Reduced chargebacks: When a fraudulent transaction occurs, the code generated by the EMV chip becomes invalid, and the transaction is denied. As a result, there’s a reduced risk of chargebacks, which are costly and time-consuming for businesses.
- Faster transaction times: EMV transactions are processed faster than traditional magnetic stripe transactions, reducing customer and business wait times.
Improved customer trust: EMV technology is more secure and reliable, which can enhance customer trust and loyalty. - Compliance: EMV technology is required by law in some countries, meaning businesses that offer these payments can achieve compliance.
- Compatibility: Since EMV payments are becoming increasingly popular worldwide, businesses can adopt this technology to ensure compatibility with other payment systems and providers.
- Cheaper card-present rates: EMV technology can lead to more affordable card-present rates because it increases security by encrypting and protecting sensitive payment data, making it more difficult for fraudsters to clone or steal the information.
Despite the many security benefits EMV transactions provide, it’s still important to know how they stack up against other payment methods to choose the right one for your business.
Are EMV transactions more secure than non-EMV transactions?
EMV technology is proven to enhance the security of transactions, and credit card chips have been shown to reduce fraud significantly.
For example, EMV technology has dramatically reduced card-present fraud in Australia. The Australian Payments Network reported a 45% decrease in counterfeit fraud losses between 2014 and 2019. This example shows how EMV technology can prevent fraudulent transactions and protect businesses and customers from financial losses.
EMV transactions use a secure technology known as point-to-point encryption to ensure hackers can’t use illegally obtained data, as it becomes unusable after each point-of-sale transaction.
With non-EMV transactions, cardholders typically rely solely on magnetic strip technology to process payments. These magnetic strip-based cards contain static data that can be easily stolen and copied, making it easy to create counterfeit cards or make fraudulent transactions.
It’s worth noting that EMV transactions aren’t foolproof, and fraud can still occur, particularly in cases where a chip fails to register or during card-not-present transactions.
Nevertheless, EMV technology has significantly reduced fraud in card-present transactions and has become a standard payment method worldwide.
Has EMV made it to online transactions?
Despite online payments growing in popularity, the EMV payment system has yet to be adopted. Therefore, digital transactions aren’t typically considered EMV-enabled and accrue higher interchange rates.
One reason for this slow adoption is the lack of compatibility traditional EMV chips offer for online transactions. Instead, online transactions rely on the card’s magnetic stripe, which can be easily transferred and copied online.
As technology evolves, new security measures for online payments are expected to emerge. Businesses should stay informed about these developments and implement the proper security measures to protect their customers’ payment information.
Is EMV technology required by law?
While no federal law requires businesses to use EMV technology, some states have passed laws that hold merchants responsible for fraudulent charges if they don’t use EMV technology.
In states with these laws, if a business accepts a card with a chip reader but processes it using the magnetic stripe instead of the chip, and a fraudulent transaction occurs, the company may be held liable for the cost of the fraudulent charge — also known as a liability shift. This can be a significant financial burden for businesses that neglect EMV technology.
Businesses in states without these laws may still face reputational damage and a decline in customer trust if they experience a data breach or other security incident. Therefore, companies need to consider the benefits of EMV technology and take steps to adopt it to protect their customers and revenue.
Securing your payments with EMV payment processing
EMV technology is becoming increasingly important in the payment processing industry to provide enhanced security and protection against fraud.
As digital payments become more prevalent, prioritizing payment security is essential. EMV technology is a leading solution in this regard, and with the proper hardware and payment processing software, your business can start accepting EMV payments securely and efficiently.
Businesses can look to a compatible EMV payment gateway like EBizCharge to ensure a reliable, secure, and cost-effective option for payment processing. With EBizCharge, you can provide a secure payment experience for your customers while protecting your business from fraudulent activities.
Frequently asked questions about EMV payments
Frequently asked questions about EMV payments
- What is an EMV payment?
- How to accept EMV transactions
- What are the costs of EMV terminals?
- How EMV enhances your business’s payment processing
- Are EMV transactions more secure than non-EMV transactions?
- Has EMV made it to online transactions?
- Is EMV technology required by law?
- Securing your payments with EMV payment processing
- Frequently asked questions about EMV payments