Blog > What is Credit Card Tokenization?
What is Credit Card Tokenization?
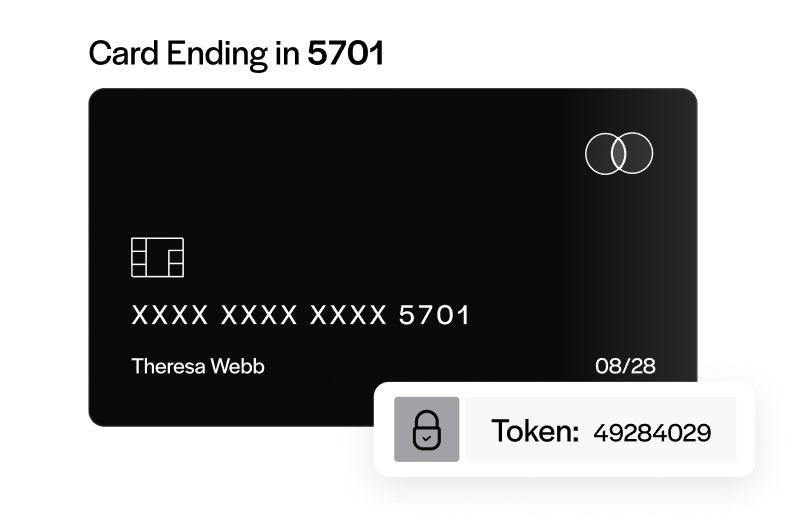
What does tokenization mean?
With regard to data security, tokenization refers to the process of securing sensitive data by substituting valuable elements with nonvaluable equivalents known as tokens. Tokens serve merely as a reference to the original item or currency and provide value only within an authorized, isolated ecosystem that validates its purpose.
Watch the video below to learn more about tokenization.
Outside of computers and data networks, common everyday examples of tokenization include casino chips and bus tokens. A bus token from a Chicago bus line is unusable on a bus in New York City unless the NYC transit authority were to authorize and recognize Chicago tokens as valid bus fare.
The parameters of an authorized ecosystem can be as narrow or as wide as the tokenizing entity chooses. Thus, the narrower the ecosystem scope is, the more limited a token’s acceptance becomes which consequently reduces exposure to unauthorized users.
Data Tokenization
The constant threat of cyber attacks and fraud has made both personal and financial data extremely susceptible to exploitation. Thankfully, tokenization converts sensitive data to digital tokens that have little or no value outside a specific digital ecosystem.
Once a data element has been tokenized, the data in its original form no longer plays a role within the designated system and is, therefore, protected. Thus, in the event of a data breach, hackers are left with tokens of no monetary value with very limited ways to be used.
Surprisingly, it’s the actual tokenization process that presents the only vulnerability, since it creates the only point of exposure for the original data within the ecosystem. This is why it’s extremely important for this process to be secure and reliable.
Once all elements have been tokenized, there’s no distinguishable relationship between the original information and its tokenized results which provides excellent security to data that’s stored or “at rest.”
Common forms of payment tokenization
eCommerce:
Token payment systems are a handy tool that replaces card data with a token in a mobile wallet, allowing customers to purchase products or services from a particular site without exposing their credit card information. Replacing card information with a token decreases the chances of a data breach.
Different payment tokens are generated for each customer’s card data which eliminates the chance of a widespread leak and minimizes the risk of credit card fraud.
In-app:
More and more companies are offering an online shopping experience for their customers. Since shoppers typically prefer an easy payment process that requires fewer steps to make a purchase, payment methods such as shopping apps are an enticing option.
Shopping apps integrate directly with mobile wallets to eliminate the need for manual card entry when a customer makes a purchase, creating a quicker and more efficient payment process without sacrificing payment security. This payment gateway tokenization ensures that credit card data is safe from potential hackers looking to get their hands on your information.
PCI Compliance:
With the rate of data breaches rising in the past years, PCI compliance is an essential component of any payment process. By replacing the primary account number (PAN) with randomly generated tokens, hackers won’t have any data to steal in the event of a data breach.
PAN tokenization is a popular component of PCI compliance because it keeps your payment information off the initial server and away from potential data breaches. These breaches can be a costly problem for companies to recover from, making card tokenization a cost-effective method.
Payment solutions protection:
Online shopping has become the standard for many industries and contactless payment methods like Apple Pay, Google Pay, Android Pay, and others are quickly gaining popularity.
With many different forms of payment, customers want to ensure their card information is secure. Tokenized data offers this security for many payment options including the ones listed above, as well newer methods like cryptocurrency.
When people define tokenization, they often relate it to encryption. While encrypted data can be decrypted by a key, PAN tokens can’t be reverted to their original form. This makes tokenization a much safer solution. EMV tokenization takes it a step further by creating unique tokens for each device, further exemplifying why token payments are more secure than encrypted payments.
What roles do tokenization and encryption play in credit card processing?
As high-profile data breaches continue to occur, the need to block external threats and shield digital assets has led to the implementation of various security techniques like tokenization and encryption.
Integrating tokenization into credit card processing provides substantial protection to consumers and businesses alike, by yielding only unusable tokens to hackers. This forces fraudsters to go elsewhere to seek valuable digital assets like credit card numbers and social security numbers.
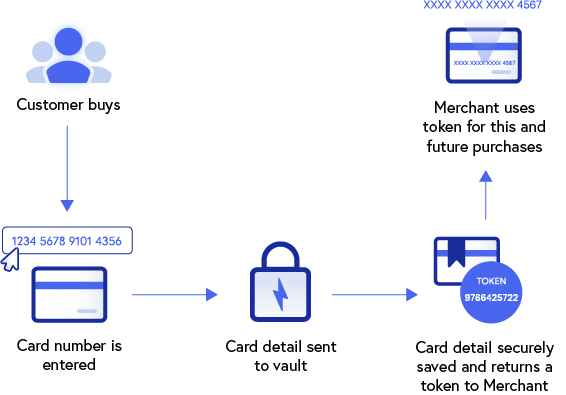
To enhance credit card processing, tokenization and encryption can be paired together for better data security.
Encryption serves an important role in credit card processing where data is transmitted across digital networks. Since tokens exist and operate strictly within their designated ecosystems, encryption provides both a digital connection and translation across two or more ecosystems.
Encryption
Encryption is the process of encoding or scrambling sensitive data elements, known as plain text, into an unrecognizable and unreadable digital jigsaw puzzle, known as ciphertext.
During credit card processing, each time a transaction is initiated a customer’s payment information is automatically encrypted and the encryption key is sent to the recipient and/or financial institution to decrypt it.
While encryption provides a substantial layer of protection against unauthorized viewing, it doesn’t prevent the interception of the actual encrypted message. This weakness has led to hackers developing sophisticated programs that grant them access to encryption keys and their associated data to decipher.
Tokenization vs. Encryption
A common misconception is that tokenization and encryption are essentially the same and are therefore interchangeable, when in fact they affect data elements very differently and at different stages within transactions.
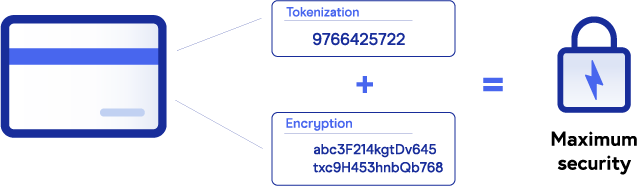
If tokenization protects data elements that are in use and at rest, it can be said encryption “masks” those elements while they are in transit across digital networks. Other differences between tokenization and encryption include:
- Method of data protection. Tokenization uses a token of no value to protect and replace sensitive data, whereas encryption creates ciphertext with an algorithm that can be unlocked and reversed with a key.
- Data transmission. Encryption allows for the secured data to be transmitted to trusted third parties, whereas tokenization doesn’t allow the original data to leave the organization.
- Range of use. Encryption can be used to protect any data set and any database volume, whereas tokenization is meant for more structured data like social security and credit card numbers.
Tokenization and encryption not only complement each other in building a formidable data defense but can also be seen as codependent entities that provide maximum protection when both are in place.
Storing Digital Assets
The actual location and storage of sensitive digital data can vary by organization, standards, and preference.
Some organizations store data in-house on local data servers which is rarely recommended by security experts, as it provides a centralized target for hackers. While others use online backup services that allow users to back up and restore files that may have been deleted, destroyed, or overwritten.
Storing digital assets on a cloud-based solution provides a more intangible virtual vault, making it a more difficult target for hackers. Cloud-based storage also allows remote user accessibility and functionality which can enhance productivity.
Businesses would be wise to use a variety of storage techniques like cloud-based solutions, external hard drives, off-site storage, secured networks, and more.
Credit card tokenization can provide customers with peace of mind
With data breaches becoming more common, customers are much more vigilant about where they input their payment information. Therefore, tokenization serves as an invaluable tool to protect your credit card data and prevent these attacks.
If a consumer knows a particular company uses PCI-compliant measures to secure customers’ information, they’re typically more inclined to shop or use the services provided by that company. This level of trust can give customers more peace of mind which can increase customer loyalty and improve sales for your business.
The Future of Tokenization
When properly implemented and enforced, tokenization and encryption will continue to play a major role in fending off advanced threats that seek to exploit sensitive data. For the most enhanced data security, both of these security measures can work together to bring about many benefits for companies and consumers in the digital age.
- What does tokenization mean?
- Data Tokenization
- Common forms of payment tokenization
- What roles do tokenization and encryption play in credit card processing?
- Encryption
- Tokenization vs. Encryption
- Storing Digital Assets
- Credit card tokenization can provide customers with peace of mind
- The Future of Tokenization