Blog > What are Discretionary Expenses? Definition and Examples
What are Discretionary Expenses? Definition and Examples
When running a business, teams constantly juggle various financial operations to ensure profitability and maintain growth. Among the numerous expenses that businesses incur, discretionary expenses play a significant yet often misunderstood role.
So, what exactly are discretionary expenses, and why are they important in budgeting?
What are discretionary expenses?
Discretionary expenses, or discretionary spending, relate to non-essential costs that businesses decide to spend on once their essential expenses have been met. These expenses might include items such as marketing campaigns, employee perks, training programs, and office upgrades, which, while not critical to basic operations, can enhance the company’s growth, employee satisfaction, and overall competitiveness. Managing these expenses effectively allows businesses to allocate resources to areas that can yield the most significant return on investment and support long-term strategic goals.

Fixed expenses vs. discretionary expenses
Understanding the difference between fixed and discretionary expenses is vital to effective budgeting.
Fixed Expense
Fixed expenses are predictable, recurring payments that must be made regularly, such as rent, utilities, salaries, and loan payments. These expenses are essential for the basic operation of the business and are generally non-negotiable.

Discretionary Expenses
On the other hand, discretionary expenses are non-essential costs that can vary based on the company’s financial situation and strategic priorities. These include spending on marketing, travel, employee perks, and office decor.
By carefully managing both types of expenses, businesses can ensure financial stability while also investing in areas that drive long-term success.
Why should you monitor discretionary spending?
Discretionary expenses hold considerable weight in the financial planning process because they allow businesses to invest in areas that can drive growth, innovation, and competitive advantage. Unlike fixed expenses, discretionary spending offers flexibility, enabling companies to allocate resources towards opportunities that can yield high returns.
For economies, discretionary spending can indicate consumer confidence; when discretionary expenses are high, it often suggests that people feel financially secure enough to spend on non-essential items. Businesses monitor discretionary expenses closely, as shifts in these spending patterns can impact market demand and influence marketing strategies. In personal finance, effectively managing discretionary expenses can increase savings and investment opportunities, improving long-term financial security.
Monitoring discretionary spending is crucial for businesses to ensure efficient resource use and financial stability. By tracking these flexible, non-essential expenses, companies can optimize investments in areas like marketing, employee perks, and innovation, ensuring they yield positive returns. This practice helps maintain financial health, especially during economic downturns, by allowing adjustments to conserve cash. Additionally, regular monitoring improves budgeting accuracy, fosters accountability, and promotes transparency within the organization, ultimately supporting strategic and thoughtful resource allocation for sustained growth and success.
Discretionary expenses can be subjective
Discretionary expenses for businesses can be subjective because they often depend on the company’s goals, priorities, and financial situation. What one business considers essential for growth, another might see as an unnecessary luxury. For example, spending on employee perks like free meals or wellness programs might be a high priority for a tech company looking to attract top talent, while a small retail business might view these as non-essential expenses. Similarly, a company focused on innovation might allocate significant funds to research and development, whereas another business might prioritize cost-cutting and consider such spending discretionary.
The subjective nature of these expenses means that their value and necessity can vary greatly between different businesses and even within the same company over time, depending on changing circumstances and strategic objectives.
Examples of discretionary expenses
Understanding what constitutes discretionary expenses can help businesses make informed financial decisions. Here are some common examples of discretionary expenses that companies might consider to enhance their operations and growth.
Marketing
Marketing expenses are often considered discretionary costs as they are typically adjustable. While essential for business growth, the extent of spending on advertising campaigns, public relations efforts, and promotional events can be increased or decreased depending on financial priorities and available resources. Investments in marketing must balance both potential returns and current affordability.
Client-specific requests
Funds allocated to fulfilling client-specific requests can also fall into the discretionary category. While meeting customer needs is crucial for maintaining business, the related expenses are often variable. Tailoring a product or creating custom solutions can incur additional costs, which may only be essential for some clients but could be approved to enhance client satisfaction and loyalty.
Investments
Allocations for investments represent a discretionary financial commitment. This broad category encompasses everything from stock market investments to purchasing new technology for a business. Given their nature, investment decisions are based on discretionary income or business revenue availability after all necessary expenses are covered.
Supplies and materials
Expenses for supplies and materials, beyond basic necessities, can be labeled as discretionary. For instance, opting for premium branded materials over generic ones constitutes a choice that reflects discretionary spending. These choices can enhance quality but also increase monthly expenses.
Employee perks
Offering employee perks is generally a discretionary decision for businesses. Perks such as gym memberships, company retreats, or gourmet coffee in the office are non-essential expenses. Although they may improve employee morale and retention, these expenses can be modified or omitted depending on the company’s financial health.
Travel expenses
Travel expenses can be discretionary, especially for purposes that could be considered non-essential, such as business-class flights or luxury accommodations. While some travel may be necessary, the level of spending associated with it is often at the discretion of the individual or company policy.
Workspace enhancements
Investing in workspace enhancements like ergonomic furniture, artwork, or advanced technology can be classified as discretionary. While such enhancements may improve the work environment and productivity, they are typically optional for the basic functioning of a workspace. These expenses are often subject to available budget after meeting essential costs.
What is discretionary expense budgeting?
Discretionary expense budgeting involves planning and allocating funds for non-essential items and activities. It is a method where individuals or businesses decide how much money can be spent on things beyond the necessities of living or operating. This type of budgeting gives room for flexibility and choice in spending, as it deals with costs that can be adjusted or eliminated without significant impact on day-to-day survival or essential operations.
How to budget for discretionary expenses
Effective budgeting for discretionary expenses is key to maintaining financial health while allowing for strategic investments. Here are six practical steps to help businesses plan and manage their discretionary spending.
Six ways on how to improve your discretionary expense budgeting

1. Measure expense ROI
When managing expenses, assessing Return on Investment (ROI) is crucial, especially in the context of discretionary expenses. ROI measurement evaluates the benefits received from the money spent. For discretionary expenses, determining ROI can help make informed decisions on whether to continue, increase, modify, or eliminate certain expenses.
Measuring the expense ROI involves several steps:
- Identify the expense.
- Determine the direct and indirect benefits gained.
- Quantify benefits in monetary terms when possible.
- Compare the benefits against the cost.
- Analyze the result to assess the efficiency of the expense.
For discretionary expenses like marketing efforts or employee perks, analyze the positive impacts, such as increased sales, improved employee satisfaction, or enhanced customer experience. If the expense produces a positive return, it may be deemed justifiable; a negative return might prompt reconsideration or strategic adjustments.
A simplified formula for calculating ROI is:
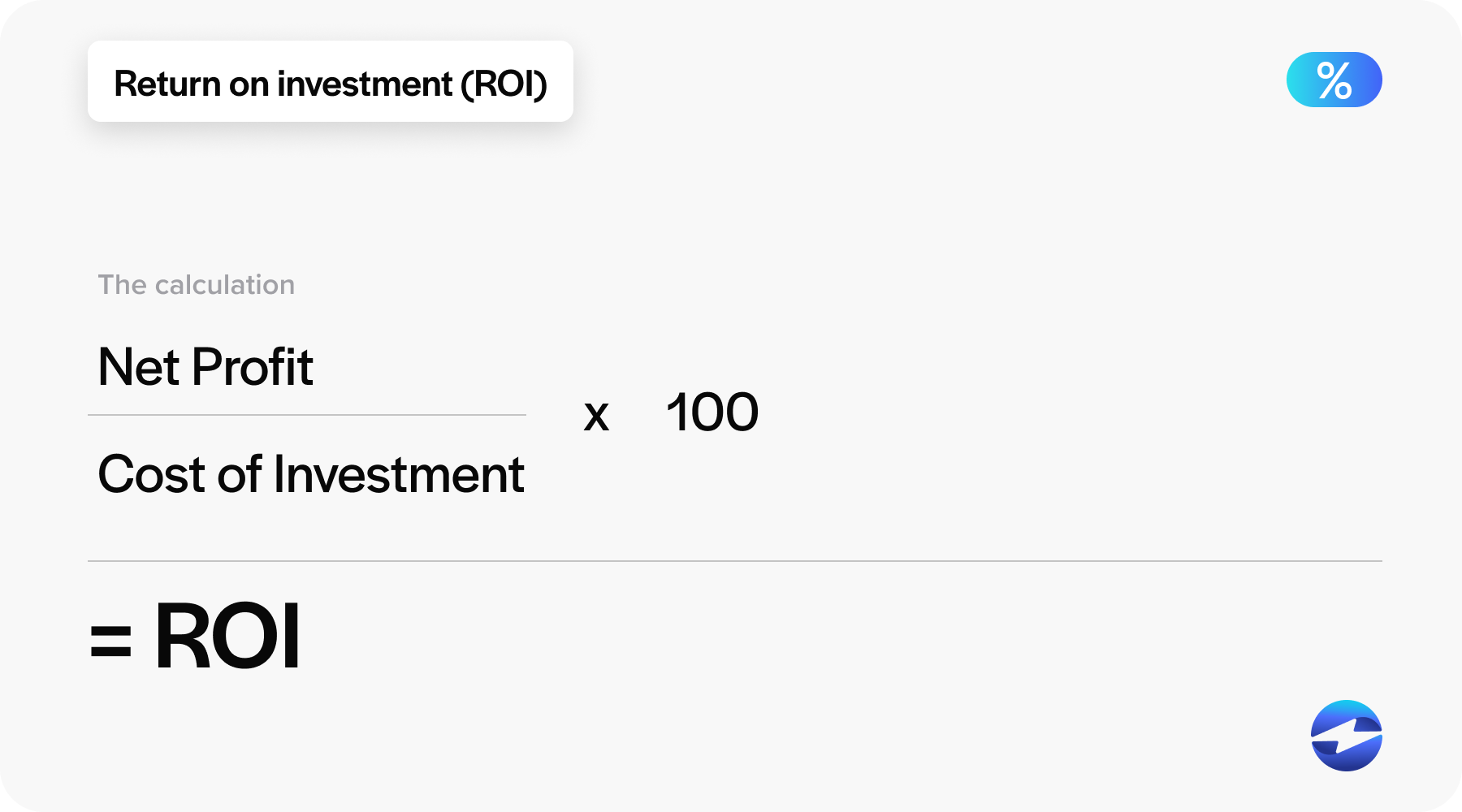
ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) x 100
Discretionary expenses with high ROI can be valuable investments for a business. In contrast, low ROI expenses should be scrutinized and possibly reduced to allocate resources more effectively.
2. Track and analyze spending
Tracking and analyzing spending can significantly improve your discretionary expense budgeting by providing detailed insights into where funds are being allocated and the impact of those expenditures. This process helps identify trends, highlight areas of overspending, and pinpoint opportunities for cost savings. By regularly reviewing spending patterns, businesses can make more informed decisions, adjust budgets in real-time, and ensure that discretionary expenses align with strategic goals and deliver a strong return on investment. Additionally, thorough analysis fosters accountability and encourages more judicious use of resources, ultimately leading to more effective and efficient financial management.
3. Set clear goals and priorities
Establishing clear goals and priorities can significantly enhance the management of discretionary expenses. By defining specific objectives, businesses can direct funds toward areas that provide the greatest impact, ensuring discretionary spending aligns with strategic goals. Prioritizing expenditures allows companies to identify essential investments versus non-essential costs, facilitating easier budget adjustments when needed without affecting critical initiatives.
4. Regularly review and adjust
Regularly reviewing and adjusting your discretionary expense budgeting is also crucial for maintaining financial efficiency and flexibility. Consistently monitoring spending, businesses can quickly identify deviations from the budget, assess the effectiveness of their expenditures, and make timely adjustments. This proactive approach helps in reallocating funds to high-priority areas, cutting unnecessary costs, and responding to changing financial conditions or strategic goals. Ultimately, regular reviews and adjustments ensure that discretionary spending remains aligned with the company’s objectives and maximizes return on investment.
5. Define and enforce expense policies
Expense policies are a critical set of rules that govern how funds are allocated and spent within an organization. These policies ensure that every disbursement falls within company budgets and is aligned with business objectives, creating a framework for accountable and responsible financial conduct.
To define an expense policy, companies must:
- Identify the types of expenses that are permissible.
- Establish clear limits for various categories of spending.
- Outline the procedures for submitting and approving expenses.
Enforcing these policies requires:
- Training employees to understand the expense guidelines.
- Implementing monitoring procedures to detect violations.
- Establishing consequences for policy breaches to discourage non-compliance.
Effective expense policies help organizations control costs by distinguishing between essential and non-essential expenses, thus promoting prudent financial management. They also reduce the likelihood of inappropriate spending, such as extravagant travel expenses or unjustified marketing expenses, ensuring that funds are utilized for necessary operations and strategic investments rather than discretionary costs.
6. Implement a waiting period
Implementing a waiting period before approving discretionary expenses can greatly improve your budgeting process. This approach encourages thoughtful consideration and evaluation of the necessity and potential impact of each expense. By introducing a pause before committing funds, businesses can avoid impulsive spending, prioritize more critical investments, and ensure alignment with overall strategic goals. This deliberate process helps in maintaining financial discipline, reducing unnecessary costs, and ultimately enhancing the effectiveness of discretionary expense budgeting.
Staying on top of your discretionary expenses
Discretionary expenses play a vital role in the strategic growth and flexibility of a business. While not essential for day-to-day operations, these expenses can significantly enhance a company’s competitive edge, employee satisfaction, and innovative capacity. Effective management of discretionary spending involves setting clear goals, prioritizing investments, regularly reviewing budgets, and implementing thoughtful spending practices like waiting periods. By closely monitoring and adjusting discretionary expenses, businesses can ensure their resources are used efficiently and align with their long-term objectives.
