Blog > The Basics of EFTs: What is an Electronic Funds Transfer?
The Basics of EFTs: What is an Electronic Funds Transfer?
With the introduction of electronic funds transfers (EFTs), gone are the days of paper checks and manual money handling. EFTs revolutionize how money moves globally, quietly becoming the backbone of our financial infrastructure.
This article will dissect EFTs to help you understand their importance, how these transactions work, and the various payment methods involved.
What is an electronic funds transfer (EFT)?
An electronic funds transfer, or EFT, is a core pillar of modern banking and transactions. The term encompasses a broad range of electronic financial transactions in which funds are transferred from one bank account to another without physical exchange.

EFT payments are synonymous with efficiency and convenience, making them a go-to method for moving money domestically and internationally.
Why are EFTs important?
EFTs are particularly important because they present a range of benefits that traditional banking methods can’t match.
The significance of EFT transfers lies in their ability to facilitate immediate access to funds on nearly any given business day. This immediate access is essential for both individuals and businesses to manage cash flows, make timely payments, and maintain financial stability.

For businesses, EFTs simplify the payment process by allowing direct payments, reducing the administrative workload associated with handling paper checks and enhancing the speed at which transactions can be settled. EFTs enable businesses to execute payroll functions, vendor payments, and even customer refunds effortlessly.
For consumers, EFTs represent a secure, convenient, and fast way to conduct financial activities. They provide peace of mind for those making electronic payments, whether in the comfort of their home or through transactions across the globe. This electronic payment method is integral to modern life, supporting everything from online shopping to managing recurring bills through direct debit agreements.
EFT transactions can often be executed with low or even no fee credit card processing, especially when compared to traditional methods like international wire transfers or paper check processing. This cost efficiency, coupled with the heightened security features of modern electronic transfer systems, underscores the critical importance of EFTs in today’s financial ecosystem.
7 types of EFTs that businesses can use
EFTs come in various forms, each catering to different needs and scenarios. These electronic transfers range from automated payments to on-demand transfers.
Here’s a brief overview of the prominent types:
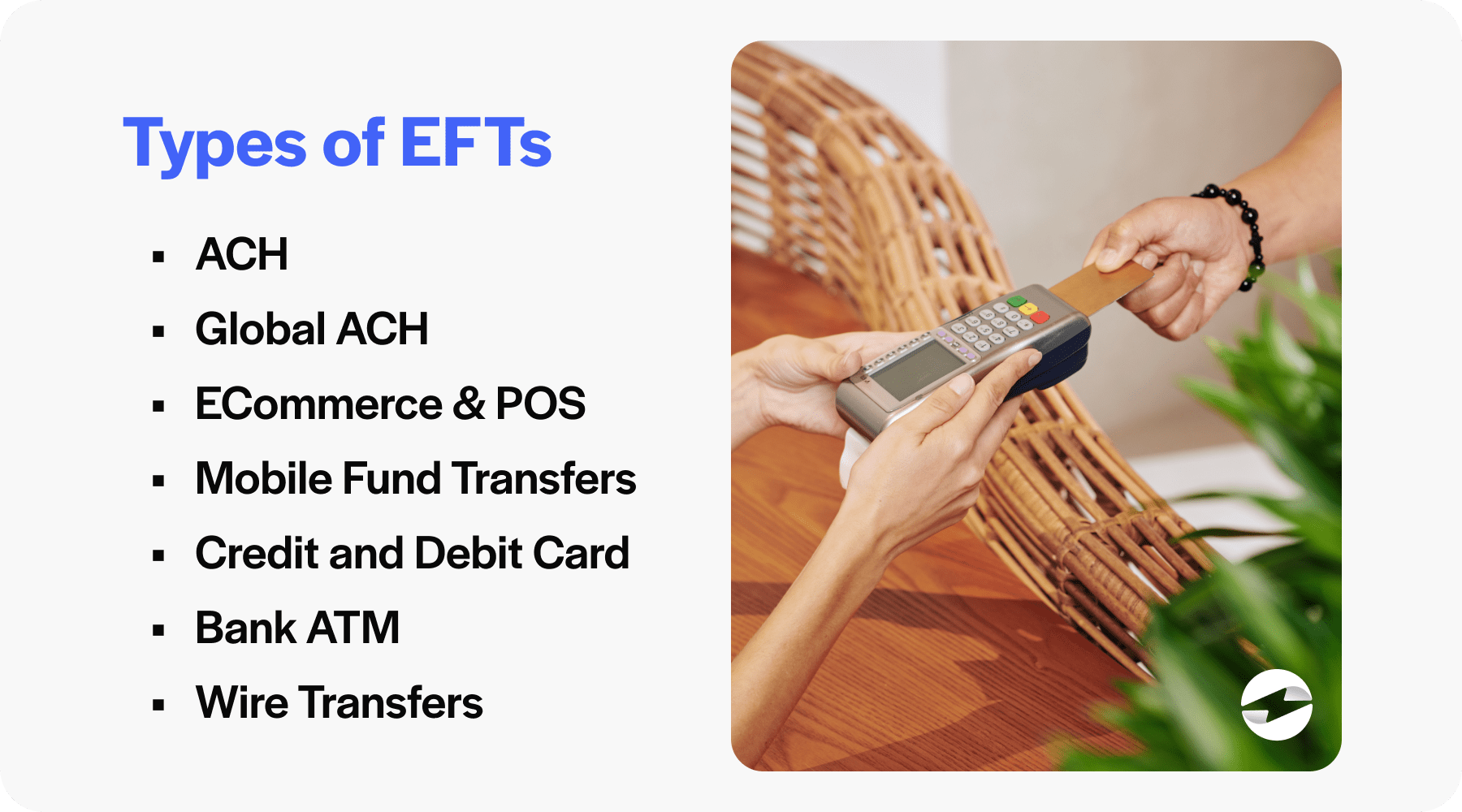
- Automated Clearing House (ACH): ACH transfers are a reliable and often-used form of EFT. ACH is designed to process batches of transactions, such as direct deposits of salaries or social security benefits and direct payments for bills. These transfers are usually domestic and are known for being cost-effective and efficient.
- Global ACH: Global ACH payments are like domestic ACH but cater to international transactions. They help with cross-border payments, making it convenient for businesses to pay overseas vendors or employees in a streamlined, cost-friendly manner.
- ECommerce & Point of Sale (POS): ECommerce and POS systems utilize EFT when customers purchase online or at retail outlets. When using a payment terminal to swipe a debit card or entering payment information on an eCommerce site, EFT is behind the scenes, processing card payments securely.
- Mobile fund transfers: Thanks to the introduction of smartphones, mobile fund transfers have become increasingly prominent. Through banking apps or specialized transfer services, users can send money anywhere directly from their mobile devices.
- Wire transfers: Wire transfers are another common EFT method for domestic and international transactions. This type of transfer is typically faster but more expensive and is often used for large or urgent funds transfers.
- Credit and debit card transactions: Credit and debit cards are everyday examples of EFTs. Whether a customer is shopping in-store or online, these transactions are processed through electronic systems, moving funds from the buyer’s bank account to the merchant’s bank.
- Bank ATM: Transactions conducted at bank ATMs also fall under the EFT category. Whether you’re withdrawing cash or transferring money between accounts, these payments are conducted electronically, providing customers with 24/7 banking capabilities.
These diverse EFT methods serve different purposes and collectively contribute to the fluidity of today’s financial transactions. Each type offers its balance of convenience, speed, and cost, shaping the global movement of money in the digital age.
How does an EFT work?
EFTs are a reliable and efficient method for electronically transferring money between bank accounts since they use computer-based systems without exchanging physical paper money or checks.
Here’s how EFTs work:
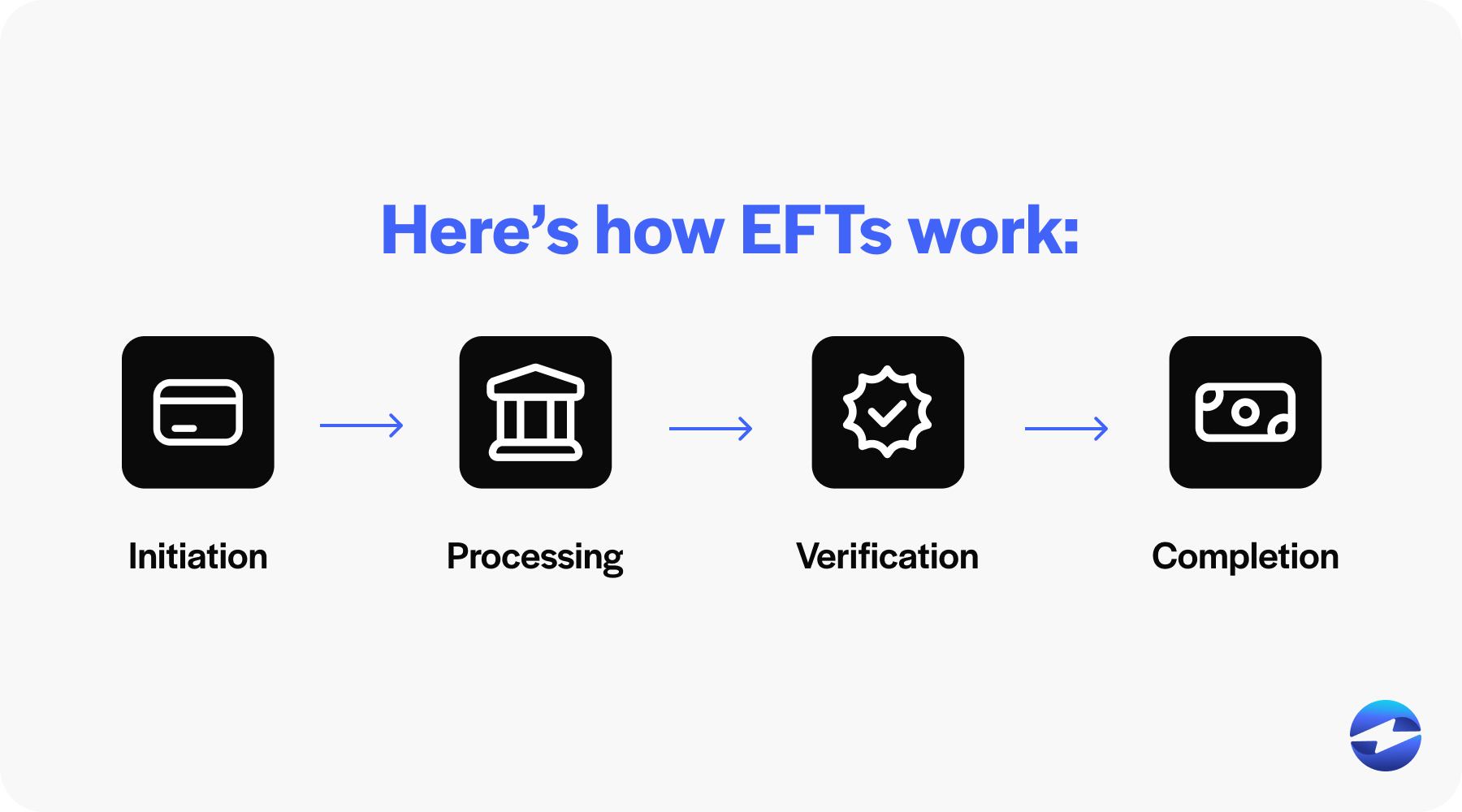
- Initiation: A party starts the EFT process by providing the necessary bank account information and authorizing funds transfer.
- Processing: The information then goes through a secure network, such as the ACH network, where transactions are batched and processed.
- Verification: Banks involved verify the transaction details to ensure accuracy and security.
- Completion: Upon confirmation, the funds are electronically deducted from the sender’s account and credited to the recipient’s account within one to two business days, depending on the type of EFT.
While it’s clear how EFT functions, there are also pros and cons of using EFTs.
Pros and cons of using ETFs
As with any technological advancement, EFTs come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages, which are crucial to consider for both individuals and businesses.
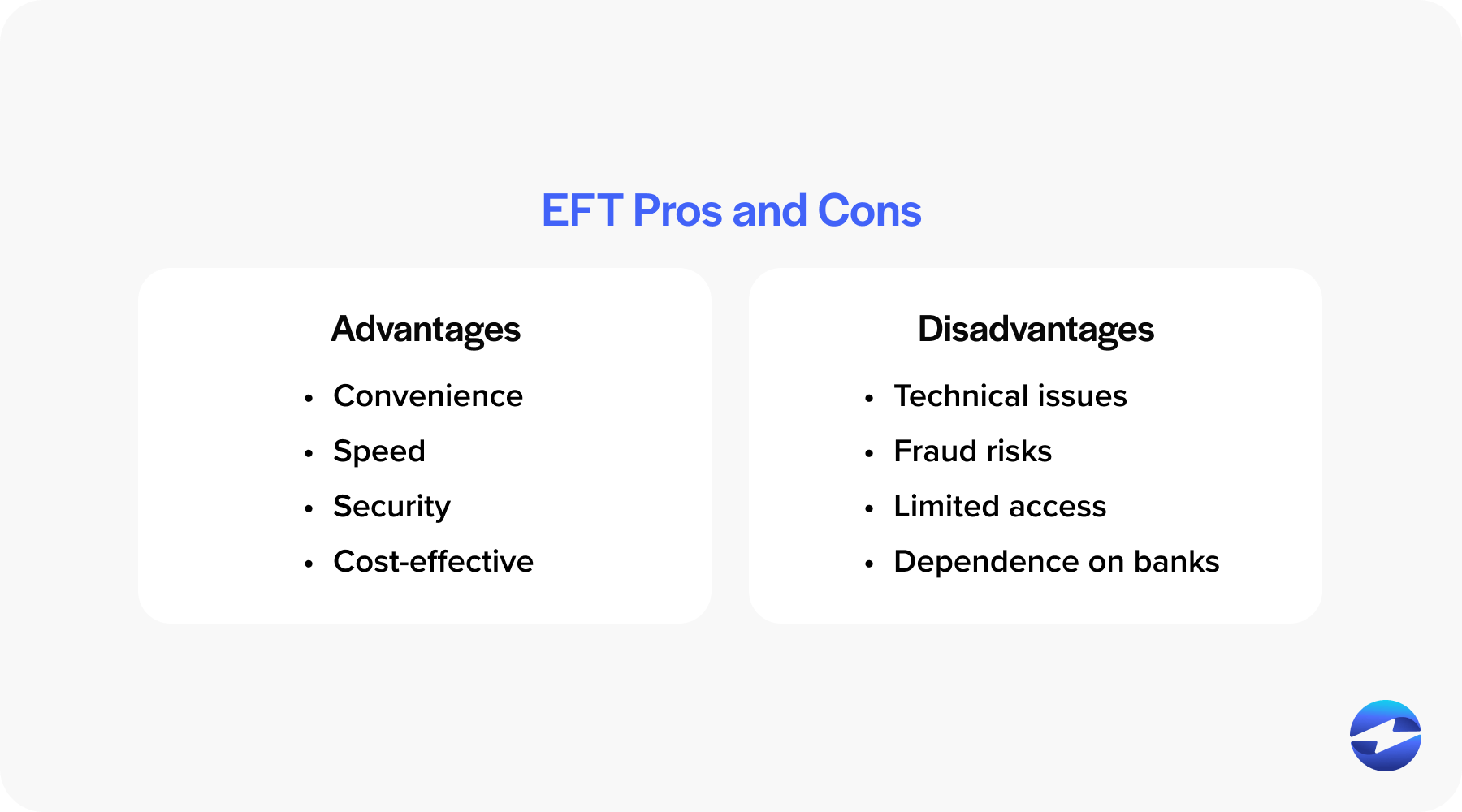
Advantages of using EFTs:
- Convenience: EFTs allow for quick and easy transfers of funds without the need to visit a bank, making financial transactions more efficient and accessible.
- Speed: Transactions are processed almost instantly, significantly reducing the time required for money to move between accounts compared to traditional methods.
- Security: EFTs are encrypted and monitored for fraudulent activities, offering a secure way to transfer funds.
- Cost-effective: EFTs often incur lower fees than other methods such as wire transfers or mailing checks.
- Automated payments: EFTs facilitate automated payments for recurring bills, reducing the risk of missed or late payments.
Cons of using EFTs:
- Technical issues: EFTs can be susceptible to technical problems, such as server outages or software glitches, which can delay transactions.
- Fraud risks: Despite security measures, EFTs can still be targeted by hackers and scammers, potentially leading to unauthorized transactions.
- Limited access: Not all individuals or businesses have access to the internet or necessary technology, limiting their ability to use EFTs.
- Dependence on banks: EFTs are reliant on the banking infrastructure, and any disruptions in the banking system can impact the ability to perform transfers.
Understanding the pros and cons of EFTs is essential for making informed decisions about managing and transferring funds in today’s digital economy. Another important aspect of EFTs is the time it takes to process the specific types of EFTs.
How long does an EFT take to process?
While the speed at which an EFT is processed depends on several factors, domestic transfers are generally quicker than international ones.
The table below outlines the typical timeframes for different types of EFTs.
| Type of EFT | Typical Processing Time |
|---|---|
| Direct Deposit | 1-2 business days |
| Automated Clearing House (ACH) | 1 to 3 business days |
| Wire Transfers (Domestic) | Within 1 business day |
| Wire Transfers (International) | 1-5 business days |
| Electronic Checks | 1-2 business days |
It’s important to note that EFT processing times can be delayed due to several factors. Transfers sent on weekends and holidays can take longer to process. Delays can also occur based on the institutions involved and if a transfer is initiated late in the day or after the end of a business day. In that case, processing will typically begin on the next business day.
What is the Electronic Funds Transfer Act (EFTA)?
The Electronic Funds Transfer Act (EFTA) is crucial for consumer protection in electronic payments and banking.

The EFTA provides a framework that ensures transparency and recourse for users engaging in EFTs. It outlines the rights, responsibilities, and remedies concerning electronic fund transfer activities for consumers and financial institutions.
How the EFTA works
When consumers initiate EFTs through direct deposits, ATM transactions, or debit card payments, they’re protected under the EFTA. This act mandates that financial institutions must provide detailed documentation of these transactions.
For each EFT, consumers should receive a record of the amount transferred, transfer date, and transfer type. These records help consumers track their transactions and verify their account activity.
The EFTA also stipulates procedures for reporting and resolving any unauthorized or incorrect transfers. Consumers have specific timeframes within which they must report discrepancies to their financial institution to receive protection from complete liability for the unauthorized transaction.
Overall, the EFTA ensures that EFTs are executed with maximum security and transparency, giving consumers confidence in using electronic payment methods.
Simplify your payments with EFTs
Understanding EFTs aids individuals and businesses in navigating today’s digital economy. With the continual growth of electronic payment methods, EFTs remain a vital part of personal and commercial financial landscapes, simplifying the process of electronic fund transfers while reducing the need for cash and checks.