Blog > Boosting Business Productivity with Advanced ERP Payment Systems
Boosting Business Productivity with Advanced ERP Payment Systems
Businesses are always looking for ways to streamline operations and bolster their bottom line. Thankfully, they can turn to software like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, which revolutionize how they manage and integrate vital functions, especially financial transactions.
This article will explore the world of ERP payment solutions and how they fuel business productivity.
Understanding ERP systems
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are comprehensive software platforms designed to integrate all business processes and functions within an organization into a single, coherent system.

ERP systems help businesses manage complex operations and make data-driven decisions by centralizing data from departments like finance, human resources, supply chain, sales, and customer service. The core advantage is that these systems provide a holistic view of business operations, enabling real-time visibility into every aspect of the company’s activities. This leads to improved coordination and efficiency, as well as the ability to respond to changes in the business environment quickly.
What is ERP payment processing?
ERP payments are transactions processed within an ERP system. By using ERP payments, companies benefit from a streamlined approach to managing both inbound and outbound financial transactions.
This integration ensures that payment data is accurate, secure, and easily reconcilable with all other business operations data.
The payment functionalities embedded within an ERP payment processing system can support a range of ERP payment methods, including electronic funds transfers (EFTs), credit card processing, and even emerging digital payment options.
A timeline of ERPs
The evolution of ERP systems began in the 1960s with Material Requirements Planning (MRP) for inventory management. By the ‘70s and ‘80s, these systems expanded to include manufacturing processes and back-office functions like accounting and human resources, leading to ERP systems in the early 1990s as they moved beyond manufacturing into service industries.
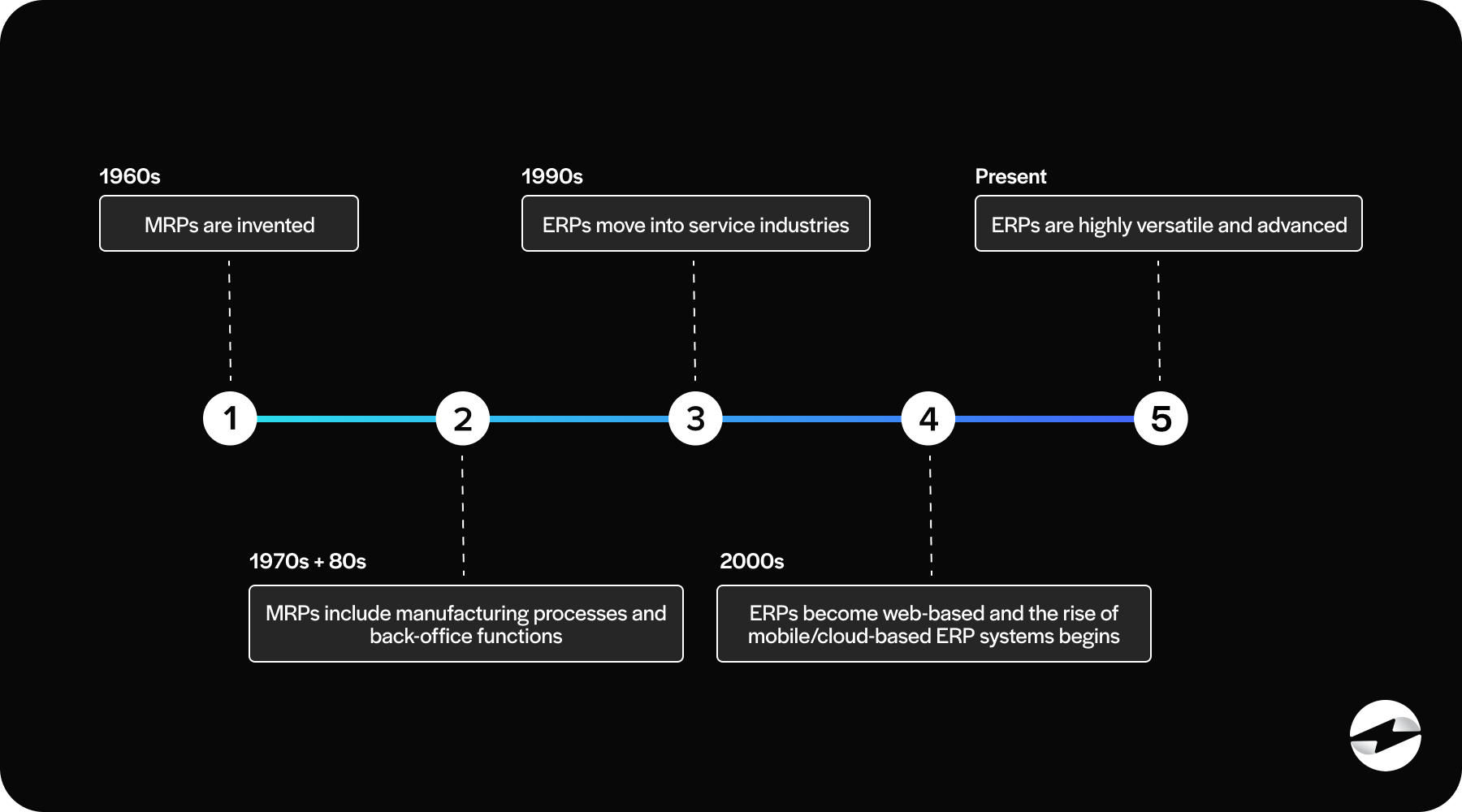
The 2000s saw ERP systems transition to web-based platforms for real-time data access, followed by the rise of mobile and cloud-based ERP solutions, enhancing accessibility and scalability. Today, modern ERP systems are highly versatile, incorporating advanced payment solutions to streamline transactions and boost business productivity.
Now that you know what ERP systems are, it’s essential to understand how they operate.
How ERP systems operate
ERP systems work by integrating various business processes and functions into a single unified system. Here’s a step-by-step explanation:

- Centralized database: All business data is stored in a centralized database, ensuring all departments can access the same information in real time.
- Modular structure: ERP systems are composed of various modules, each dedicated to specific business functions such as finance, human resources, sales, inventory, and supply chain management.
- Data entry: Information is entered into the system through the user interface or automated data feeds, updating the centralized database.
- Integration: Modules are interconnected, allowing data to flow seamlessly between departments. For example, an order entry in the sales module can trigger updates in the inventory, shipping, and accounting modules.
- Process automation: Routine business processes, such as order processing, payroll, and inventory management, are automated, reducing manual intervention and the potential for errors.
- Real-time updates: Any data entered, or changes made in one module are instantly reflected across the system, ensuring all departments have the latest information.
- Reporting and analytics: ERP systems provide robust reporting and analytics tools that generate real-time reports, dashboards, and insights to help management make informed decisions.
- Customization: ERP systems can be customized to meet businesses’ specific needs and workflows, including adding custom fields, workflows, and reports.
- User access and security: Role-based access controls ensure that users can only access data and functions relevant to their roles, enhancing security and data privacy.
- Scalability: ERP systems are designed to scale with the growth of the business, allowing additional modules and users to be added as needed.
It’s important to note that there are different kinds of ERP systems. Although these systems operate in similar ways, they have a few differences. Understanding these differences allows businesses to choose which structure works best for them.
3 types of ERP systems
ERP systems can be divided into three categories: on-premise, cloud-based, and hybrid. Factors such as company size, industry, budget, compliance requirements, and specific business processes can influence the type of ERP option a business may choose.
These variations in ERP options are designed to provide optimal operational efficiency while considering the organization’s technological infrastructure, control preferences, and flexibility requirements.
The following sections will provide you with a quick look at how these systems differ.

On-premise ERP systems
On-premise ERP systems are installed locally on a company’s hardware and servers and managed by its IT staff. This traditional model gives businesses complete control over their ERP infrastructure and data.
On-premise ERP systems allow for customization and integration with existing in-house applications, making it a preferred option for organizations with complex business processes or those requiring a high level of data security.
However, these ERP solutions often involve a significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and IT personnel, and they can be more costly and time-consuming to upgrade.
Cloud-based ERP systems
Cloud-based ERP systems are hosted on the vendor’s servers and are accessed via the Internet. This model eliminates the need for businesses to invest in their own IT infrastructure, as the ERP provider handles the system’s maintenance, updates, and security.
Cloud ERP is often offered on a subscription basis, making it more cost-effective and scalable for growing businesses. Additionally, cloud-based systems are typically easier to implement and provide real-time data and access from any location, which supports remote or distributed workforces.
That said, businesses may have less control over cloud-based ERP system data and customization capabilities than on-premise solutions.
Hybrid ERP systems
Hybrid ERP systems blend elements of both on-premise and cloud-based solutions, allowing businesses to store some data and applications on local servers while others are hosted in the cloud. This model provides flexibility to leverage the scalability and accessibility of cloud services while maintaining critical functions or sensitive data on-premises.
Hybrid ERP systems may be ideal for companies transitioning from traditional to modern ERP solutions, allowing them to move to the cloud at their own pace. They also suit businesses with varying compliance or data sovereignty requirements. Since hybrid ERP systems combine the benefits of both models, they offer a balance between control, customization, and agility.
Now that you know the different ERP systems, you can learn more about some of the problems these systems aim to address.
5 common obstacles in B2B payments
Business-to-business (B2B) payments are fundamental to the operations of companies worldwide. However, in the process of transacting between businesses, several common obstacles can hinder efficiency and affect cash flow.
Here’s an overview of five primary challenges that businesses frequently encounter.

- Complex payment processes: Complex payment processes are a significant barrier in B2B payments due to their intricate nature involving multiple steps and parties. This complexity can result from a variety of factors, including the need for numerous approvals, manual data entry, differing payment terms, and the use of disparate systems that don’t communicate effectively with one another. This can lead to increased human error, slower transaction times, and difficulty maintaining consistent financial records.
- Delayed payments: Delayed payments are a prevalent issue in B2B transactions, often stemming from the previously mentioned complex payment process. The lag between issuing and receiving an invoice affects a business’s cash flow and can strain the relationship between trading partners.
- Fraud and security risks: With substantial sums of money often at stake and transactions typically occurring online, there’s an enhanced risk for cybercrime and payment fraud. Companies must apply secure payment practices to protect against unauthorized access, phishing attacks, or fraud. Compliance with industry standards and investment in secure payment technology are necessary to mitigate these risks.
- Compliance requirements: Local and international regulations, such as anti-money laundering (AML) and knowing your customer (KYC) laws, can complicate B2B transactions. Compliance demands meticulous record-keeping, reporting, and due diligence, which adds layers of administrative work and potential for error, further complicating the payment process.
- High transaction costs: High transaction costs can arise from bank fees, cross-border transaction fees, currency conversion fees, or fees associated with third-party payment services. For companies with large transaction volumes, these costs can significantly drain resources, eat into profit margins, and necessitate a more cost-effective solution for managing payments.
Recognizing these obstacles is the first step in seeking solutions that streamline payment processes, enhance security, ensure compliance, and reduce costs, ultimately improving business operations and partnerships.
5 advantages of integrated electronic payment options
Embracing integrated electronic payment options is a strategic move to enhance business productivity. ERP payment solutions are at the forefront of this movement, providing a unified platform that consolidates various business functions into one system.
Integrated electronic payment options offer advantages, including enhanced convenience and user experience, data security, reporting, cost savings, and more.
Enhanced convenience and user experience
Customer satisfaction is paramount to any business’s success. Integrated electronic payment options within ERP systems significantly enhance customer convenience by providing a seamless transaction experience.
A unified ERP payment system ensures quick and efficient transaction processing, reducing customers’ time spent making payments. This integration often allows for multiple ERP payment methods, catering to diverse customer preferences and ensuring a seamless payment process. The ease of completing transactions contributes to a positive user experience, which is crucial for fostering customer loyalty and trust.
Increased data security and compliance with regulations
Data security and regulatory compliance are critical concerns for businesses. Therefore, integrating electronic payment options within an ERP system strengthens data protection measures. With robust security protocols, these solutions safeguard sensitive payment data against unauthorized access and breaches.
ERP payment systems are also designed to adhere to industry standards and regulations, ensuring businesses comply with legal requirements.
This proactive approach to security and compliance protects the company and its customers and prevents potential financial penalties and reputational damage.
Improved tracking and reporting capabilities
An effective ERP payment gateway provides businesses with improved monitoring and reporting capabilities.
By enhancing financial transactions within a single ERP platform, companies can monitor payment activities with greater visibility. Real-time updates and comprehensive reports aid in identifying trends, pinpointing discrepancies, and making data-driven decisions.
This aspect of ERP transactions proves invaluable for managing everything from labor costs and inventory to supply chain management and financial planning.
Accelerated collections and cash flow management
Efficient cash flow management is crucial for any enterprise’s financial stability. With ERP payment integrations, businesses can accelerate the collections process.
Faster transaction processing times lead to quicker receipt of funds, thus enhancing the company’s cash flow. With real-time visibility into payment statuses, companies can proactively manage their receivables and payables, optimize working capital, and improve overall performance.
Cost savings and fee reduction
Integrating electronic payment options into ERP systems can yield substantial cost savings and fee reductions.
By automating and optimizing payment processes, businesses can eliminate expenses associated with manual and repetitive tasks, reduce human error, and decrease operational costs.
While ERP payment gateways and electronic payment portals offer streamlined operations and efficient payment processing, they also come with several potential risks that businesses must navigate.
Potential risks of ERP systems
Understanding the potential risks of using ERP systems is crucial because it helps businesses proactively address vulnerabilities, prevent costly issues, and enhance overall efficiency.
Here are a few potential risks to keep in mind:

- Security vulnerabilities and fraud risks: ERP systems are prime targets for cyberattacks and unauthorized transactions.
- Compliance issues: Failure to meet regulatory standards can result in hefty fines.
- System downtime: Technical problems can disrupt operations and result in lost sales.
- Integration challenges: Difficulties when integrating ERP systems can cause errors and inefficiencies.
- Transaction fees: High transaction fees can impact profit margins.
- Data privacy concerns: Protecting sensitive data is critical for maintaining customer trust.
- Reliance on third-party providers: Solely relying on third parties can lead to business interruptions, which can affect brand reputation, reliability, and customer trust.
By being aware of these risks, businesses can implement measures to mitigate them, such as robust security protocols and choosing reliable providers. Therefore, it’s essential to use trusted payment processors that can facilitate seamless integrations and payment collection processes.
Facilitate seamless integrations with EBizCharge
Integrating EBizCharge with popular ERP systems offers businesses a seamless solution for facilitating quick and easy transactions.
EBizCharge enhances business productivity by streamlining financial processes within the existing ERP framework. Its compatibility with systems such as QuickBooks, Sage, Microsoft Dynamics, and Acumatica ensures a straightforward integration process, minimizing downtime and enabling businesses to quickly benefit from improved transaction capabilities.
EBizCharge also provides real-time data synchronization to ensure all transactions are instantly reflected within the ERP system, which is crucial for accurate financial reporting and effective decision-making.
Additionally, EBizCharge automates payment processes, reducing manual data entry and minimizing the risk of human error, leading to more accurate financial records and smoother reconciliation processes. Its robust security measures adhere to the latest industry standards, protecting sensitive information and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
By adopting EBizCharge, companies can simplify complex payment processes, reduce transaction costs, and enhance overall operational efficiency, making it a strategic choice for optimizing financial management and driving growth.
