Blog > What is the Security Code on a Credit Card?
What is the Security Code on a Credit Card?
Ever wondered about the security code on a credit card? With the rise of online shopping and card-not-present transactions, codes are a common requirement during checkout. This security measure ensures online payments are legitimate and authorized. According to The Ascent, “Credit card fraud remains the most prevalent type of identity theft, with 318,000 reported cases in the first three quarters of 2023.”
With fraud extremely prevalent today, it is important to know what a card security code is and also where it is.
What is the security code on a credit card?
A card security code (CSC), also referred to as the card verification code (CVC) or card verification value (CVV), is a 3- or 4-digit number crucial for online credit card transactions. It’s not part of the credit card number itself but acts as an extra layer of security. This value adds additional verification that a customer is, in fact, the owner of the card they’re using. The security code is used in the card-not-present transaction space, which includes any transaction that occurs without the physical card present—online, phone, mail, and fax orders. The idea is that the more correct information needed to verify a credit card, the harder it is for a thief to match that information. In some transactions, the correct security code may not be needed to run a transaction. Therefore, when a fraudulent charge is made with an incorrect security code, it’s easier for a cardholder to prove that fraud has occurred.
When prompted to enter the code, it’s crucial to know where it is so you are not asking the question, “Where is the security code on a credit card?”
Where’s the security code on a credit card
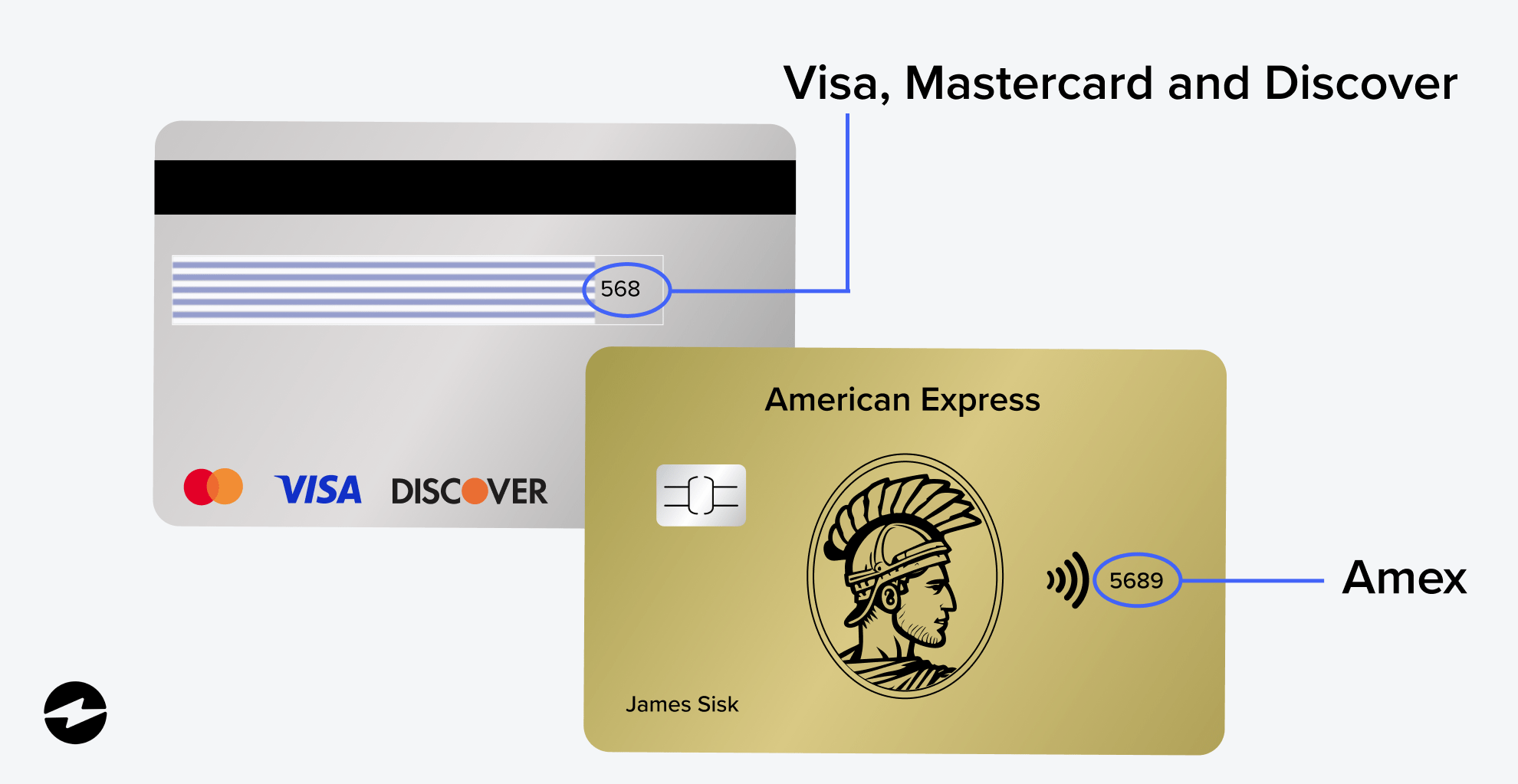
For MasterCard, Visa, and Discover cards, the credit card security code is the three-digit code located on the back of the card, typically in the signature field. For American Express cards, it’s the four-digit code located on the right side of the front of the card.
How To Protect Card Information
In order to ensure the highest level of data security, we recommend using payment card tokenization.
Tokenization provides several layers of protective armor to safeguard sensitive credit card information and shield against a potential data breach. Tokenization technology replaces credit card information with a unique token that is only decipherable with the proper payment system. With a tokenized credit card, businesses will never see the original credit card number. Instead, only the tokenized data is visible in the payment system. A tokenized credit card is completely different from the original credit card information and acts as the key for all future transactions. Businesses can use this token to house customer records and guarantee secure data storage. Tokenization helps make it difficult to hack or decipher your credit card data.
Safeguard Data with PCI Compliance
If you’re a business owner, we highly recommend that you don’t store your customers’ card security codes. Not only does this break PCI compliance—it also increases the risk of credit card fraud and defeats the purpose of the security code in the first place. PCI compliance applies to any business that accepts credit cards. In the event of a data breach, a lack of PCI compliance could result in steep fines by the PCI Security Standards Council. PCI compliance significantly decreases the liability for your business should a data breach occur. Using a tokenized credit card can help your business achieve PCI compliance. You can also use tokenization technology to secure business passwords, email addresses, employee files, and customer accounts.
Businesses can further protect themselves by using a payment solution that keeps sensitive card data off their systems entirely. With credit card processing for QuickBooks, transactions are tokenized and reconciled automatically within your accounting software, so your team never handles raw card numbers. Similarly, payment processing for NetSuite offers the same level of security within your ERP, ensuring every transaction is PCI compliant without adding extra steps to your workflow.
Frequently Askd Questions
What is a security code?
A card security code (CSC), also referred to as the card verification code (CVC) or card verification value (CVV), is a 3- or 4-digit number crucial for online credit card transactions. It’s an additional layer of security used to verify that the person making an online or over-the-phone purchase physically possesses the card.
Where is the security code on a credit card?
Discover, Visa, and Mastercard: The security code is a three-digit number on the back of the card in the signature panel.
American Express: The security code is a four-digit number on the front of the card, typically above the card number.
How to find CVV without a card?
Reach out to your credit card issuer to get your CVV number. They can look up your account and provide you with the information, making it a convenient way to retrieve your CVV if your card is not available.
If you’ve lost your card, Contact your card issuer immediately to report the loss and request a replacement. Do not attempt to find or use the CVV from a lost card.
What is SEC code on a credit card?
The Standard Entry Class Code (SEC) is a three-letter code exclusively used for ACH and ACH Prenote schedules to identify the NACHA payment type. This code describes the authorization method for ACH transactions, representing ‘Standard Entry Class’ (SEC) and offering insights into how the recipient authorized the payment, whether a consumer or a business.
What is a security code on a debit card?
A security code on a debit card is a three or four-digit number usually found on the back, near the signature strip. It’s there to add an extra layer of security when you’re making online or phone purchases, helping to confirm that you actually have the card in hand. It works the same way as the security code on a credit card, doing the same job for both.
 Is you business PCI compliant? Take this 1-min quiz to find out.
Is you business PCI compliant? Take this 1-min quiz to find out.