Blog > Year-to-Date: What it Means and How to Calculate It
Year-to-Date: What it Means and How to Calculate It
Imagine you’re halfway through the year and want to gauge your financial progress. Year-to-date (YTD) is a crucial term in finance and accounting, but its relevance extends far beyond. It’s a simple yet essential concept that captures your financial activities from the start of the calendar year to the current date.
Whether you’re tracking investment performance or assessing a business’s health, YTD figures act as a snapshot of progress and financial dynamics. Understanding YTD can be the difference between making informed decisions and flying blind through the fiscal year.
This article will explain the meaning of YTD, why it’s important, how various professionals use it, and how to calculate it accurately for more precise financial insights.
What does YTD mean?
Year-to-date or YTD is often used when discussing the timeline or performance of an activity or the status of finances over the current year.
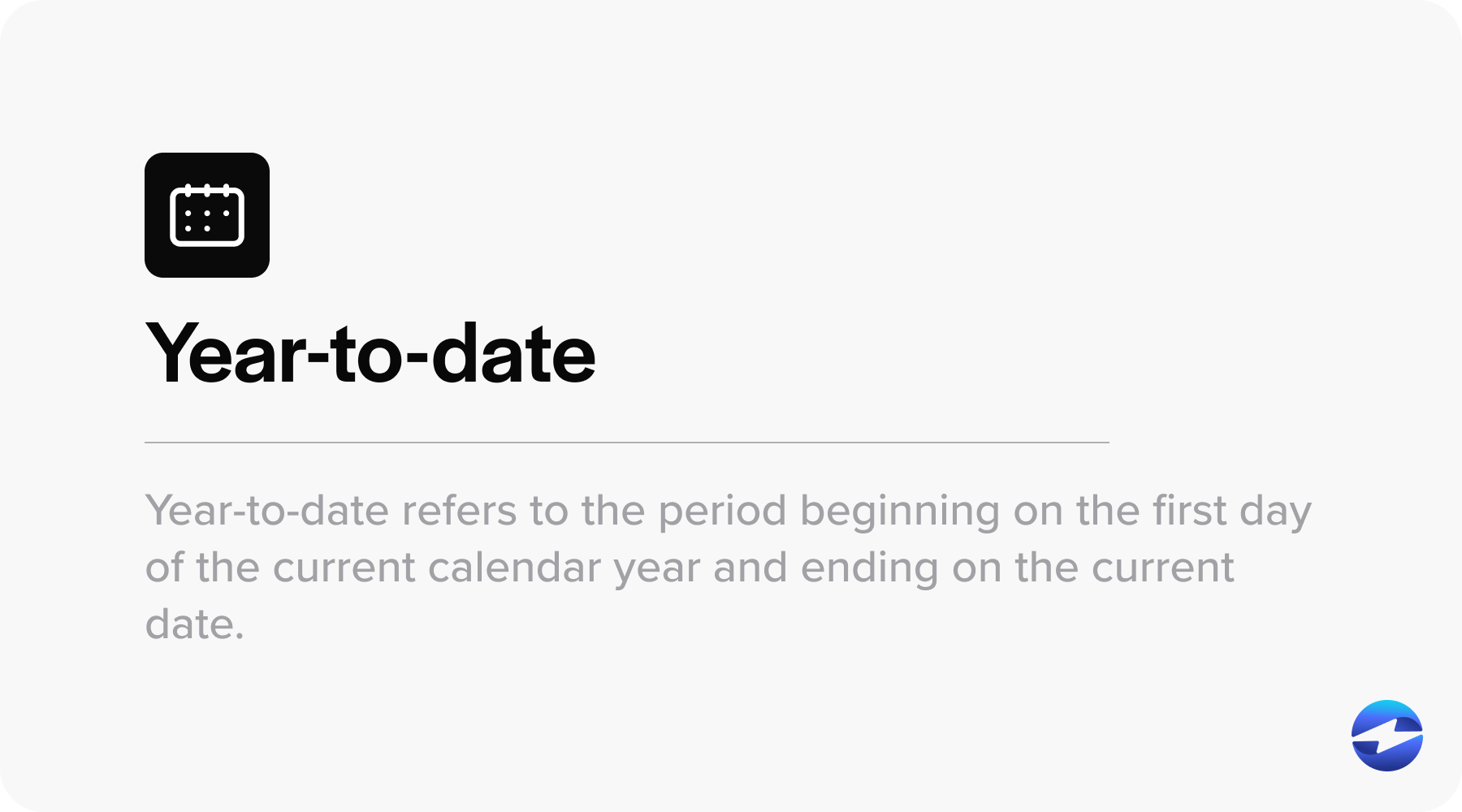
YTD refers to the period beginning on the first day of the current calendar year and ending on the current date. This can be aligned with either the calendar year, starting January 1, or the fiscal year for businesses, which doesn’t necessarily begin on this date.
 Whether you’re looking at sales figures, financial statements, or paycheck stubs, the YTD figure helps to give context to business trends or personal finances by showing you cumulative totals for the time frame in question.
Whether you’re looking at sales figures, financial statements, or paycheck stubs, the YTD figure helps to give context to business trends or personal finances by showing you cumulative totals for the time frame in question.
Why is YTD important?
Understanding the meaning of YTD is crucial because it offers fresh and relevant insights into financial performance without waiting for year-end.
For business owners, tracking YTD sales, YTD profits, or overall YTD values can help them make timely decisions that can improve their financial health. It allows for monitoring trends over time, and when used in analyzing investment returns or portfolio performance, YTD returns provide a snapshot of how investments are doing in real-time.
For employees, YTD on a paycheck stub indicates how much they have earned from January 1 to the most current business day of the year. In the context of public companies, YTD figures can show progress and yield vital figures for investors.
Whether an individual tracks personal finances or a professional analyzes a company’s financial statements, YTD calculations can reveal a lot about performance and stability and often serve as a temperature check for economic well-being within that period.
Who uses YTD?
YTD is used by numerous business professionals trying to evaluate a company’s financial situation.
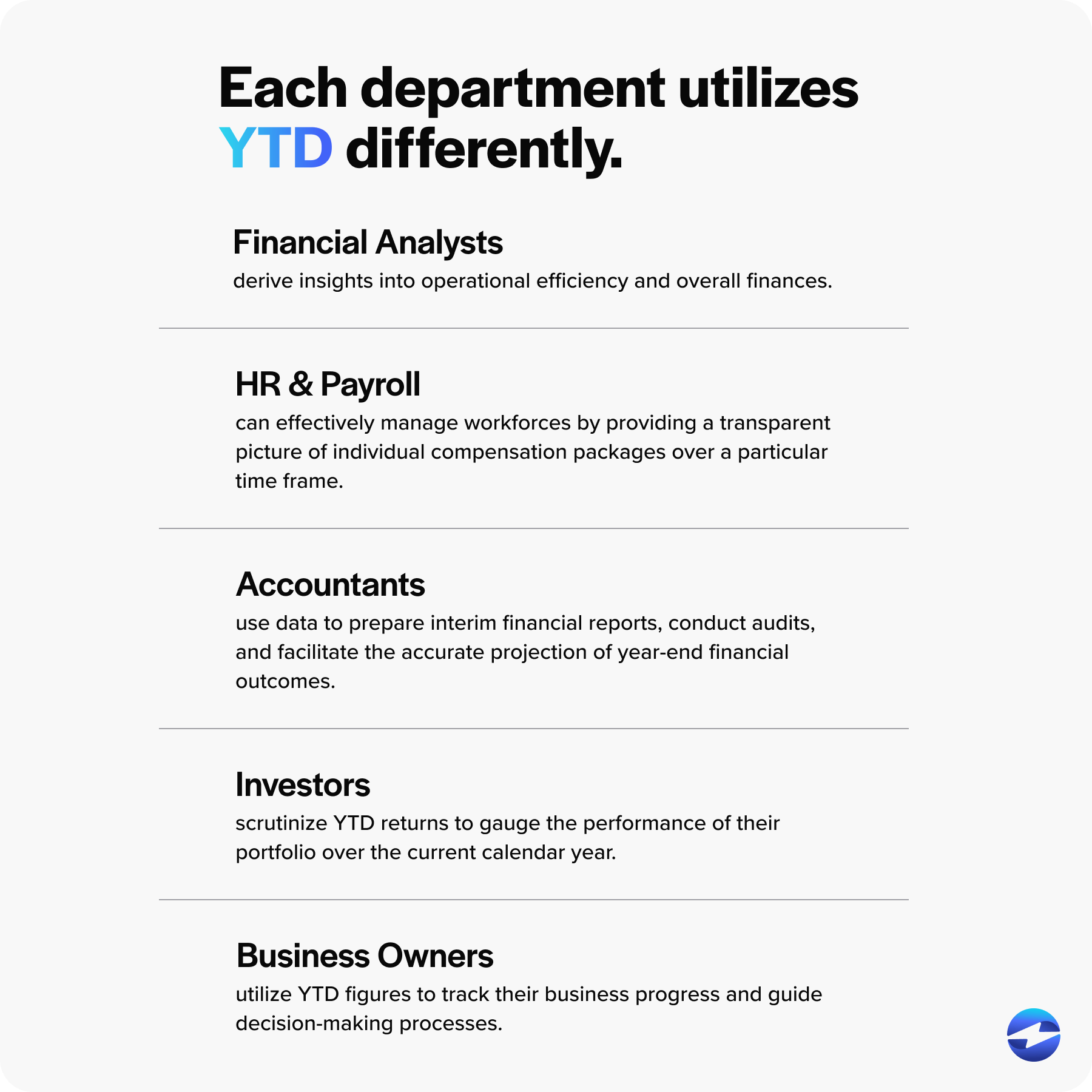
Some top departments and individuals using YTD include financial analysts, HR and payroll, accountants, investors, and business owners.
Financial analysts
Financial analysts rely heavily on YTD calculations to evaluate a company’s financial performance over the current fiscal year.
Analysts can derive insights into operational efficiency and overall finances by analyzing YTD figures such as sales figures, profits, and investment returns. Trends discerned from YTD data help make critical recommendations regarding investments and strategic planning, factoring in YTD returns and real-time market information.
HR and payroll
Human resources (HR) and payroll departments use YTD information to monitor and report employee earnings and deductions for the current year.
A clear understanding of YTD payroll data ensures accuracy in tax reporting, administration benefits, and compliance with financial regulations. It helps HR and payroll teams effectively manage workforces by providing a transparent picture of individual compensation packages over a particular time frame.
Accountants
Accountants incorporate YTD figures into financial statements to clearly and accurately represent their financial performance.
YTD values are critical in showing performance for the current calendar year, whether it’s the income statement, balance sheet, or cash flow statement. Accountants use this data to prepare interim financial reports, conduct audits, and facilitate the accurate projection of year-end financial outcomes.
Investors
Investors scrutinize YTD returns to gauge the performance of their portfolio over the current calendar year. This helps them compare investment returns against benchmarks and make informed decisions regarding asset allocation and investment strategy.
YTD returns reflect an investment’s appreciation, dividends, and interest earned, providing insight into return on investment and portfolio performance in a given period.
Business owners
Business owners utilize YTD figures to track their business progress and guide decision-making processes. The YTD information, such as profits, sales, and expenses, allows business owners to compare current performance against previous time periods.
YTD is crucial for managing cash flows, budgeting, and strategizing for market competitiveness. Business owners often analyze YTD data to adjust business objectives and forecast future trends.
How to calculate YTD
Calculating YTD involves summing up all relevant data or activity from the beginning of the current calendar year to the present day or a specified reporting date.
The methodology remains consistent whether you’re looking at financial performance, payroll figures, or sales numbers.
YTD formula and calculation
The YTD formula typically involves summing a particular metric’s total amount from the current year’s first day to the reporting day.
If it’s the income we’re talking about, the YTD calculation would be the total income earned from January 1 to the date in question.
Similarly, for measuring sales or expenses, the formula would involve adding up all sales or costs incurred over the same period.
Here’s the YTD formula:
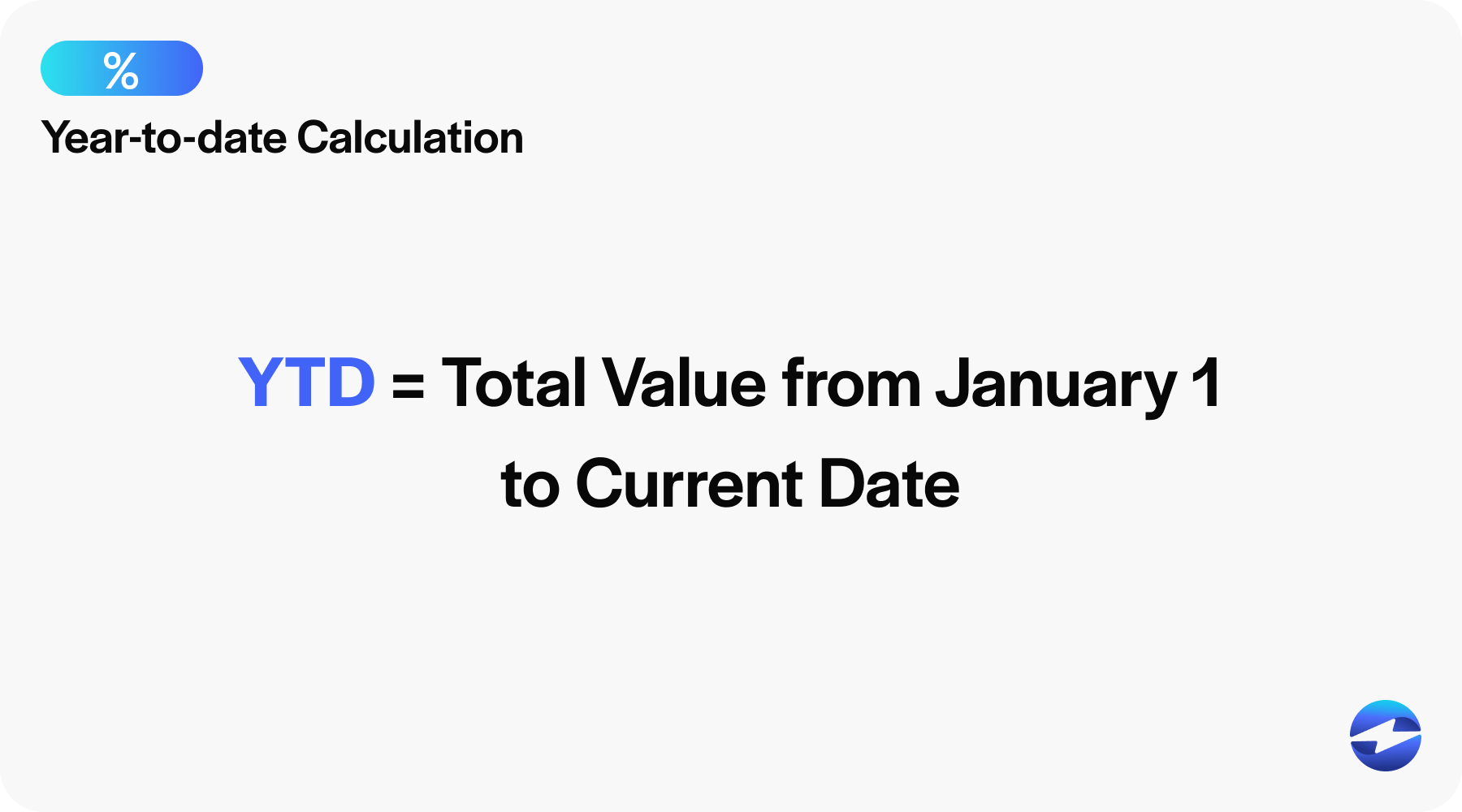
YTD = Total Value from January 1 to Current Date
Remember, the Total Value can refer to sales figures, financial profits, expenses, investment returns, or any other measurable data relevant to the YTD analysis.
Year to date example
A business owner wants to calculate the YTD sales to understand business trends over time. Imagine it’s currently the end of September, and they’ve compiled their monthly sales figures as follows:
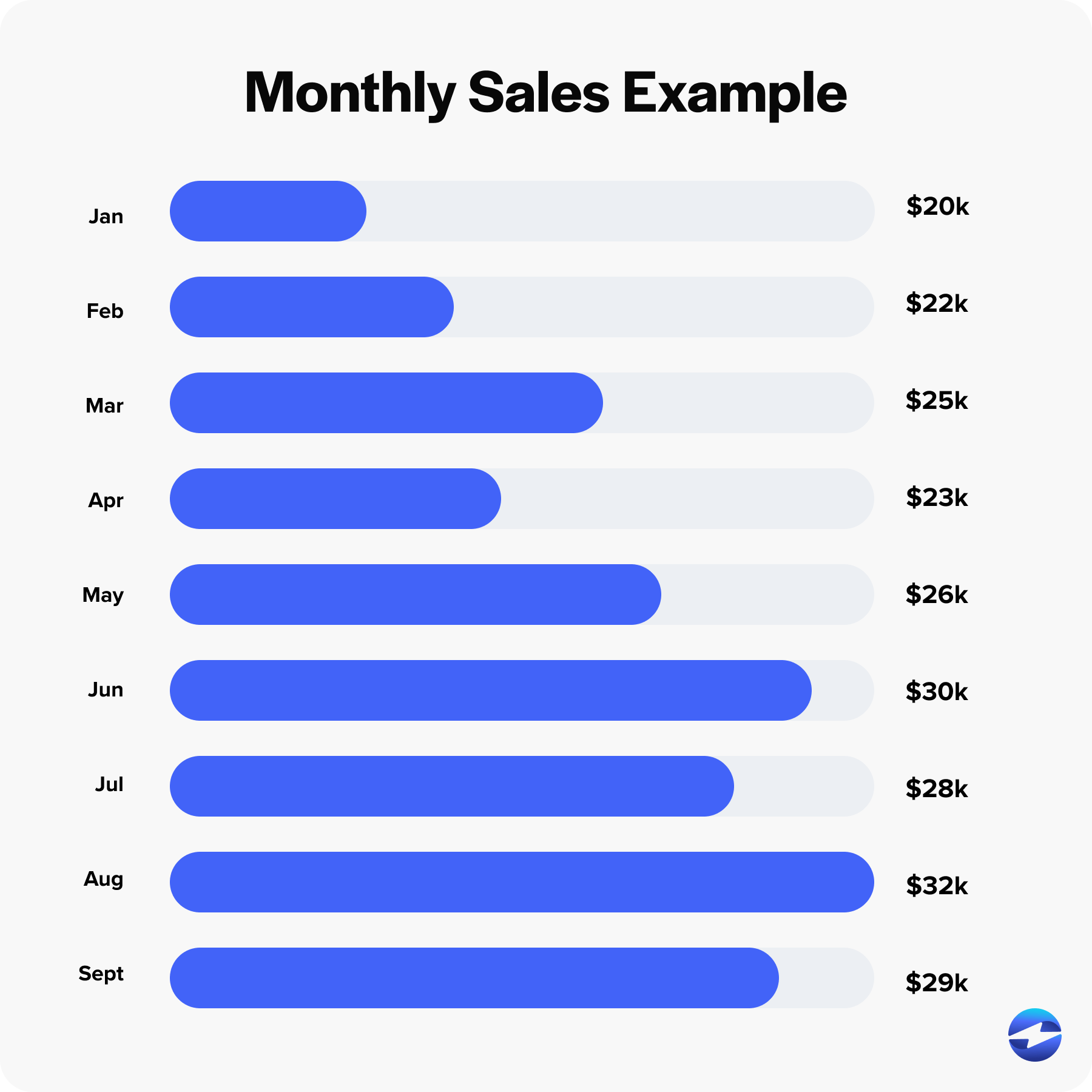
- January Sales: $20,000
- February Sales: $22,000
- March Sales: $25,000
- April Sales: $23,000
- May Sales: $26,000
- June Sales: $30,000
- July Sales: $28,000
- August Sales: $32,000
- September Sales (to date): $29,000
Using the YTD formula, the YTD sales would be calculated as follows:
YTD Sales = January Sales + February Sales + March Sales + April Sales + May Sales + June Sales + July Sales + August Sales + September Sales
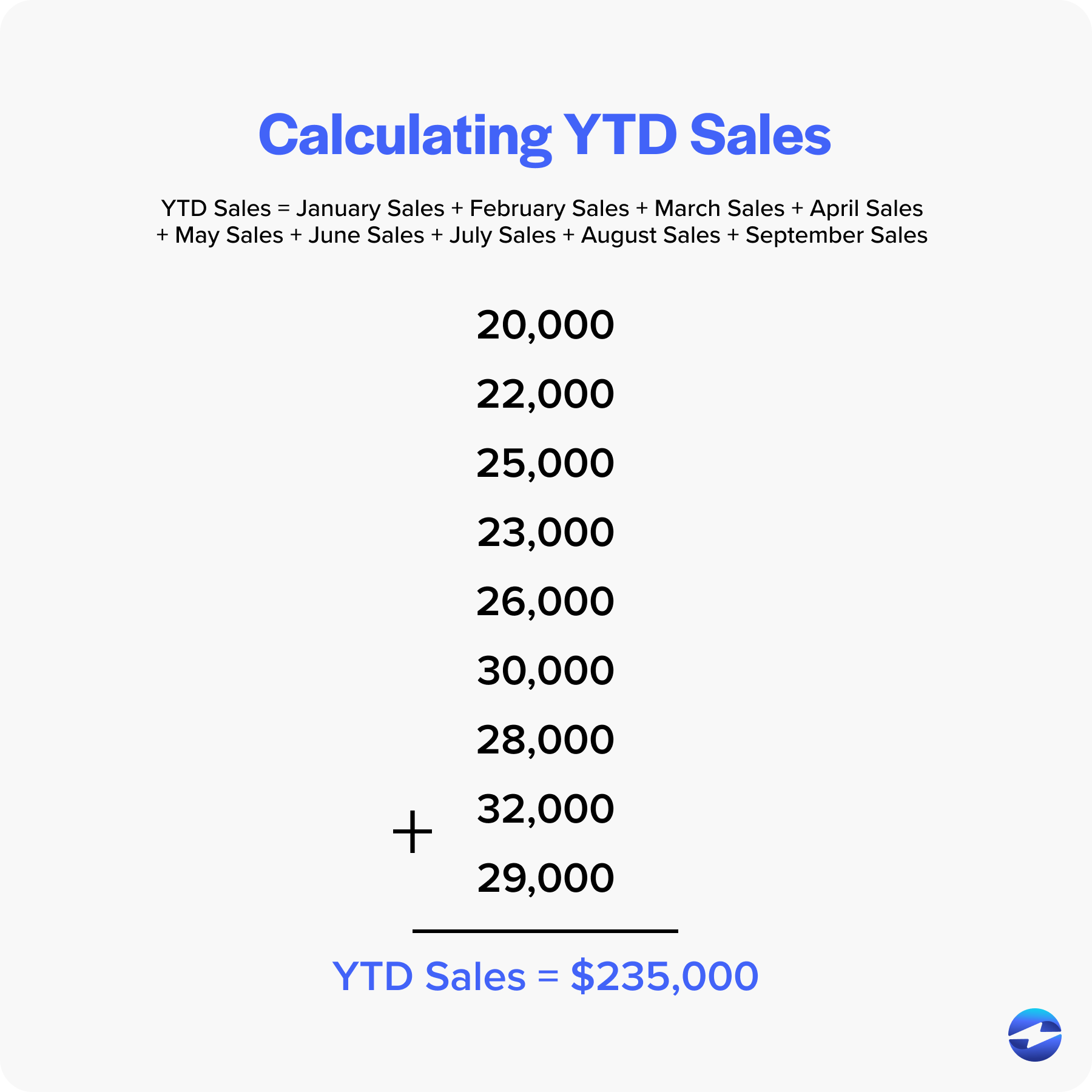
YTD Sales = $20,000 + $22,000 + $25,000 + $23,000 + $26,000 + $30,000 + $28,000 + $32,000 + $29,000 YTD Sales = $235,000
So, the YTD sales figure at the end of September would be $235,000.
This YTD figure gives the business owner an understanding of their sales performance throughout the current year and may influence their business decisions and strategy moving forward.
What does a high YTD mean?
Whether you’re glancing at a paycheck stub, scrutinizing financial statements, or assessing business trends, a high YTD figure can often signal strong financial performance or growth over the current calendar year up to the present moment.

Here are trends companies may see with a high YTD:
- Financial health: For a public company or small business, increased YTD sales, profits, or returns indicate robust business health.
- Investment performance: In personal finance, high YTD returns on an investment portfolio highlight successful investment strategies and potentially higher returns.
- Income growth: An individual’s paycheck with high YTD earnings reflects strong income growth, which could result from raises, bonuses, or overtime.
- Operational success: A company exhibiting high YTD cumulative sales or output values may outperform its forecasts and competitor trends over time.
Understanding YTD is crucial for business owners, investors, and employees, as it provides real-time insight into financial and operational progress within the current fiscal year.
Staying ahead of the game with YTD
Whether tracking personal finances, monitoring business trends, or evaluating investment returns, YTD is essential in providing a clear picture of your company’s financial standing.
YTD provides a snapshot of financial activity from the beginning of the current calendar year up to the present day and helps you analyze sales figures, profits, and other key performance indicators (KPIs).
Businesses that effectively leverage YTD data can set themselves up to apply better strategies for the rest of the fiscal year and long-term success.