Blog > Understanding General and Administrative Expenses (G&A): Definition, Examples, and Management Strategies
Understanding General and Administrative Expenses (G&A): Definition, Examples, and Management Strategies
Navigating the intricate world of business finance requires understanding various expense categories, including general and administrative expenses (G&A). These costs encompass a company’s day-to-day operations and are essential to fiscal health.
This article illuminates aspects such as rent, utilities, and salaries to reveal the components and significance of G&A expenses. The ability to manage these expenditures efficiently is closely tied to a company’s profitability and operational efficiency.
The following sections will classify G&A expenses, their management, and the potential for leveraging technology to streamline these processes. Understanding G&A is crucial for decision-makers aiming to optimize their organizational expenses and ensure sustainable growth.
What are G&A expenses?
General and Administrative expenses, commonly known as G&A expenses, refer to the day-to-day operating overheads necessary to run a company. These expenses are not directly tied to producing goods or services. Still, they are essential for the company’s general operation and management. G&A expenses are categorized separately on income statements because they relate to the overall operation rather than individual departments or products. G&A is distinct from production or direct expenses incurred to create the company’s products or services.

Importance of G&A expenses in financial management
G&A expenses are integral in financial management. They are assessed regularly within financial statements to help evaluate a company’s efficiency and financial health. Monitoring these expenditures is crucial as they affect a company’s operating income and profitability.
Effectively managing G&A costs is, therefore, vital for any business. If these costs grow faster than the company’s revenue, they can significantly reduce profits. Conversely, well-managed G&A expenses can contribute to a company’s streamlined operation, leading to potential savings and improved financial outcomes.
While they may not be as attention-grabbing as direct costs or sales figures, administrative expenses are a vital component in any business’s strong foundation. Financial managers use G&A evaluations to create strategies that sustain growth and competitive advantage, ensuring long-term success.
Breakdown of G&A expenses
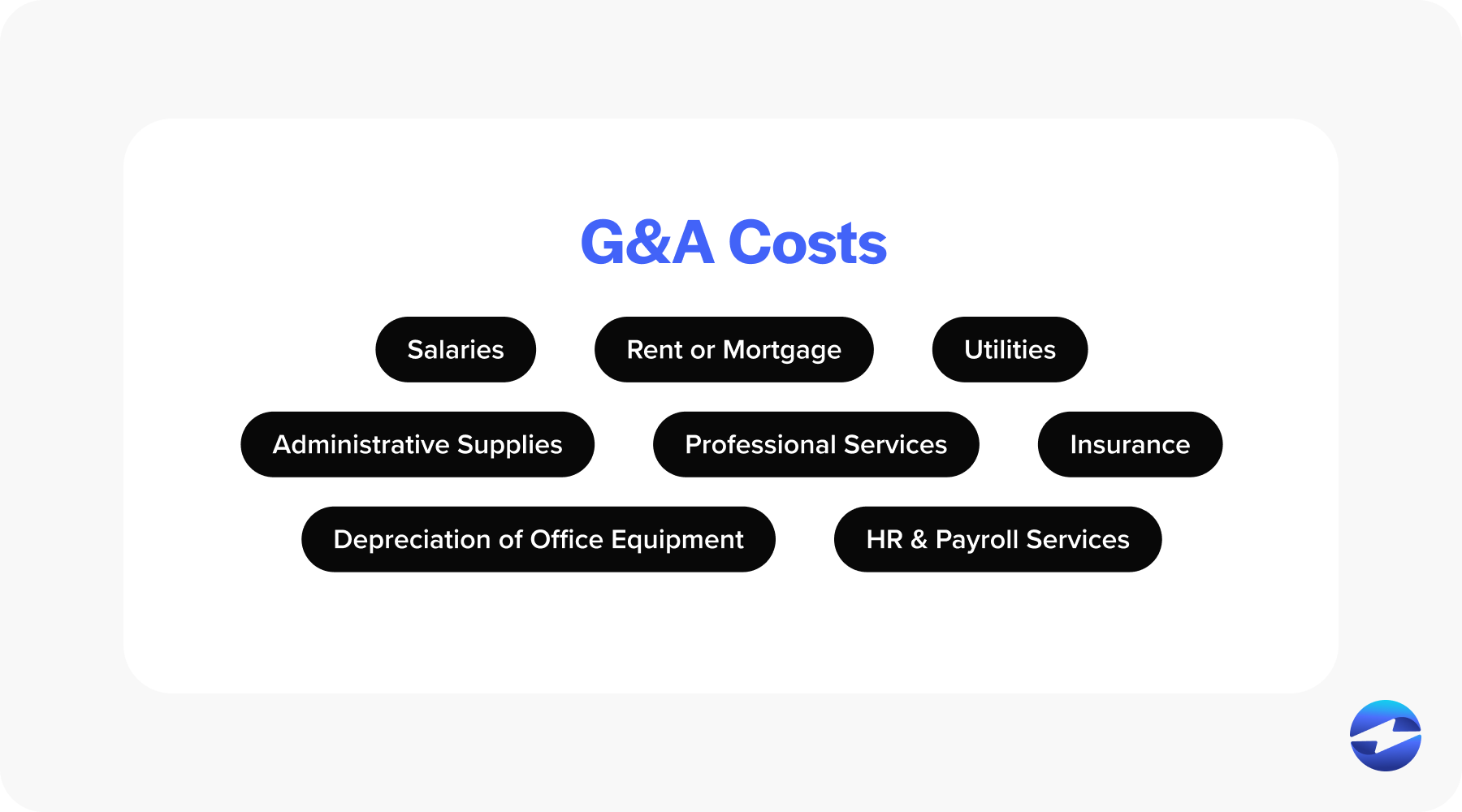
General & Administrative (G&A) expenses encompass a broad range of costs that businesses incur as part of their daily operations. These expenses, essential to the function of any enterprise, are not directly tied to any specific business activity or product but are necessary for overall operations. G&A costs often include:
- Salaries of executive and administrative personnel
- Office rent or mortgage payments
- Utilities for the office space, such as electricity and water
- Supplies and equipment for administrative staff
- Costs related to legal, accounting, and professional services
- Insurance expenses to protect company assets
- Depreciation of office equipment and furniture
- Human resources and payroll services
Understanding these G&A expenses is crucial, but it’s also important to distinguish them from other expense categories to ensure accurate financial management and reporting.
G&A vs other expense categories
When examining an organization’s financial statements, one will notice various line items categorizing expenses. General and Administrative (G&A) expenses stand out as one aspect of broader cost classifications. They differ from other types of expenses in that they are not linked directly to the sales or production of goods and services but to the company’s overall administration. Other categories may include selling expenses, research and development costs, and direct production expenses, each distinctly different from G&A. These categories collectively contribute to the total operating costs of a business and are instrumental for calculating the net income.
G&A vs SG&A (Selling, General, and Administrative)
General and administrative expenses (G&A) and Selling, General and administrative expenses (SG&A) are pivotal categories reflected in businesses’ income statements. While they both encompass operational costs that are not directly tied to creating a product or service, key distinctions exist between these two types of expenses.
SG&A includes all G&A costs and sales-related expenses. Selling expenses are costs incurred from the sales process and promotional activities, independent of general and administrative expenses.

Businesses’ primary goal is to manage and minimize these expenses without compromising efficiency or productivity to enhance overall profitability. Understanding the difference between G&A and SG&A allows for more accurate financial analysis and better cost-control strategies.
Difference between G&A and COGS (Costs of Goods Sold)
General and Administrative expenses (G&A) and Costs of Goods Sold (COGS) are two distinct categories on financial statements, each representing different costs a business incurs.
G&A refers to the overhead expenses necessary to run a company but are not directly tied to a specific product or service. These encompass various expenditures, from managerial salaries and office supplies to legal fees. G&A costs are typically categorized as indirect costs, meaning they do not fluctuate with the level of production or sales.
In contrast, COGS includes all the direct costs attributed to the production of goods sold by a company. This might cover raw materials, direct labor costs, and manufacturing overhead directly involved in creating the product. Unlike G&A, COGS varies proportionally with inventory production levels and is closely linked to sales activity.
Semi-variable vs. fixed expenses
Semi-variable expenses, also known as mixed or semi-fixed expenses, have both fixed and variable components. This means part of the expense stays constant up to a certain level of activity, while the other part changes with the level of activity. For instance, utility costs often have a base charge (fixed), plus charges for actual usage (variable).
In contrast, fixed expenses do not fluctuate with the production or sales volume level. They are consistent costs that a company must pay, irrespective of its business performance. These expenses include rent, salaries, insurance, and depreciation.

Understanding the nature of these expenses is crucial for budgeting and financial forecasting. Organizations aim to keep tight control over both to maintain profitability.
Effective financial management involves monitoring and adjusting these expenses to align with revenue and cost objectives.
Recording G&A expenses in your book
Accurately tracking and documenting general and administrative expenses is a cornerstone of effective financial management for any company. These expenses can be found in the income statements and are not directly tied to the production of goods or services. Therefore, they fall into the category of operating expenses.
To accurately reflect G&A costs in accounting records, each expense should be categorized as an indirect cost. Common G&A expenses include salaries for executive and administrative personnel, rent for office space, and utilities. Each of these should be recorded as they are incurred.
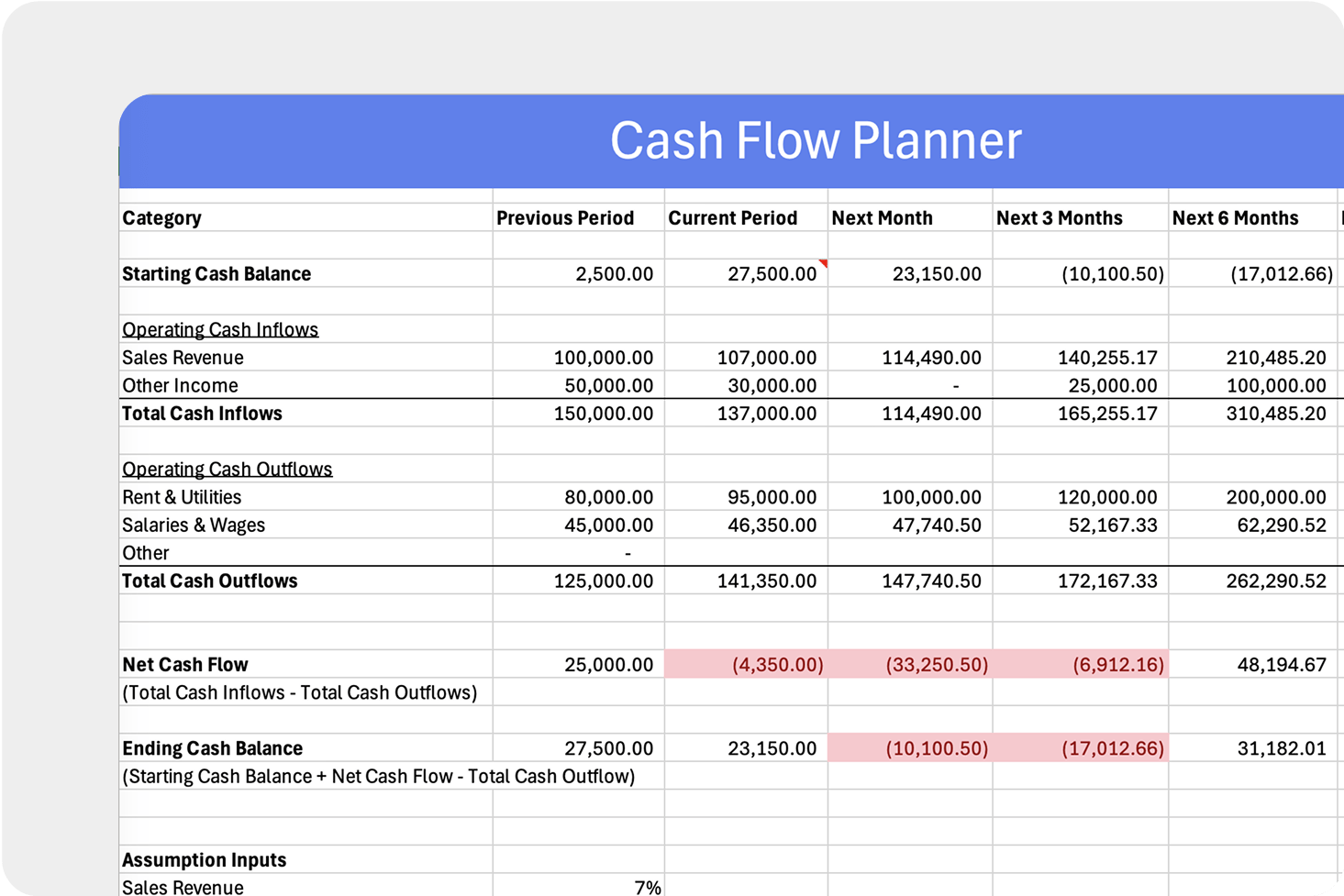
A simple table to depict the recording of G&A expenses might look as follows:
 These expenses are then summed up to represent the total G&A costs for a specific accounting period, contributing to the calculation of the company’s overall operating costs. It’s crucial to maintain accurate records to ensure the best reflection of the company’s financial health, adhere to applicable cost principles, and prepare for correct cost allocation across various cost objectives.
These expenses are then summed up to represent the total G&A costs for a specific accounting period, contributing to the calculation of the company’s overall operating costs. It’s crucial to maintain accurate records to ensure the best reflection of the company’s financial health, adhere to applicable cost principles, and prepare for correct cost allocation across various cost objectives.
3 causes of bloat in G&A expenses
In business finance, vigilance is critical to controlling general and administrative expenses. While vital to operations, these costs can balloon due to oversight and mismanagement, hindering financial efficiency. Bloat in G&A expenses can often be attributed to three primary factors: zombie spend, SaaS sprawl, and shadow IT.

Zombie spend
Zombie spend refers to the unnoticed continuation of recurring costs for services or resources no longer in use or necessary for business operations. These stealthy expenses are like undead budget-eaters that drain company funds without adding value. The types of costs typically prone to becoming zombie spend include subscriptions, memberships, and software licenses that are auto-renewed without active assessment of their ongoing need. To fend off this undead expense, regular audits of recurring charges can identify and eliminate these unnecessary costs.
Common Sources of Zombie Spend
- Expired software licenses
- Unused service subscriptions
- Memberships not accessed by staff
Identifying and eliminating zombie spend is crucial for maintaining a healthy budget, but another significant challenge for businesses is managing Saas sprawl.
SaaS sprawl
The proliferation of Software as a Service (SaaS) solutions offers incredible business efficiency and productivity tools. However, SaaS sprawl occurs when these subscriptions multiply unchecked. Departments or teams may subscribe to overlapping services or similar tools, creating redundancy and underutilization of available features. The costs add up, generating a significant portion of administrative expenses. To mitigate SaaS sprawl, a centralized oversight of all SaaS licenses is recommended, alongside a detailed inventory and evaluation of tool utility across teams.
Steps to Manage SaaS Sprawl
- Conduct an inventory of SaaS tools
- Evaluate the utility per department
- Eliminate overlapping subscriptions
While managing SaaS sprawl is essential for cost efficiency, businesses must also address Shadow IT, where unauthorized software and tools are used without IT department approval, posing potential security and compliance risks.
Shadow IT
Shadow IT emerges when employees utilize non-approved technology or Software without formal consent from the IT department. This rogue adoption undermines company security protocols and adds to the G&A expenses through indirect costs. These covert operations can escape official procurement processes, thereby dodging any corporate discounts and leading to individual, unaccounted-for expenses. Combating shadow IT involves:
- Fostering clear IT policies.
- Providing approved alternatives that meet employee needs.
- Reinforcing the importance of adhering to standardized procurement procedures to control indirect costs.
Eliminating these causes of bloat in general and administrative expenses can streamline financial statements, improve cost efficiency, and contribute to more effective resource allocation.
Challenges in managing G&A expenses
Managing General and Administrative (G&A) expenses presents a variety of challenges for businesses, given that these represent an indirect cost pool essential for daily operations but do not directly contribute to profit generation. One of the primary difficulties is accurately categorizing expenses as either direct costs associated with specific products or services, or as overhead costs, which are more general. G&A expenses often encompass disparate elements ranging from salaries for human resources staff to rental costs for office space, making it tough to allocate and monitor them.
With G&A costs being a mix of variable and fixed expenses, businesses must be vigilant in their control to avoid unnecessary financial burdens. This is often compounded by the complexity of applicable cost principles and the need to adhere to regulations, which can vary significantly for different types and sizes of businesses, including nonprofit organizations.
To manage these expenses efficiently, businesses can face issues in defining an appropriate base period for allocating costs, determining actual costs, and deciding on acceptable cost allowances. Additionally, organizations must establish a balance between necessary expenditure for adequate administrative support and the risk of inflating their indirect costs, which can reduce the overall competitiveness.
Strategies for managing G&A expenses
Strategies for managing G&A expenses involve careful analysis and strategic planning to optimize costs without sacrificing the essential functions of an organization. The following are key tactics to effectively manage these expenses:

- Budget Review and Adjustment: Evaluate G&A costs during budget preparation and regularly throughout the year, adjusting for any unnecessary expenditures.
- Cost Allocation: Implement appropriate cost allocation methods to ensure that indirect costs are accurately distributed among different projects or departments.
- Technology Integration: Utilize technology to automate and streamline administrative functions, which can reduce labor costs and improve efficiency.
- Vendor Negotiation: Regularly review vendor contracts and negotiate better terms or discounts for services and supplies, which can directly lower overhead costs.
- Outsourcing: Consider outsourcing non-core activities to external providers who can often perform these functions more cost-effectively.
- Employee Training: Continuous training to improve the skills of administrative personnel can lead to greater productivity and reduced error rates.
- Lean Management Practices: Adopt lean management principles to identify and eliminate waste within administrative processes and operations.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can maintain effective control over G&A expenses, ensuring financial stability and operational efficiency.
Tools and Software for G&A expense management
In the realm of financial administration, managing general and administrative (G&A) expenses effectively is crucial. Various tools and Software have been developed to streamline this process, providing clarity and control over these often-indirect costs.
One key class of tools includes accounting software. Programs like QuickBooks, Xero, and Sage are equipped with features to categorize and track expenditures, making it easier to monitor G&A expenses. They provide detailed reports that can inform financial decision-making and help maintain accurate records for income statements. Pairing these platforms with a payment solution like EBizCharge can further reduce overhead. With credit card processing for QuickBooks, payment processing for NetSuite, and an Acumatica payment gateway, businesses can automate payment collection and reconciliation directly inside their accounting or ERP system.
For larger organizations, enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems integrate several business functions, including G&A expense management. ERPs like SAP and Oracle offer comprehensive solutions with modules that support the tracking of costs against different departments or cost centers.
Lastly, budgeting and forecasting software help in planning and predicting future G&A expenses while providing insights into areas where cost-saving measures can be applied.
It’s essential for businesses to choose the right mix of tools that align with their expense management needs and the complexity of their G&A cost structures.
Conclusion
G&A expenses are crucial for understanding a company’s financial health as they encompass all the necessary overhead costs that are not directly tied to the production or selling of goods and services. Effective management of these expenses is vital for maintaining a healthy bottom line. The goal is to strike a balance where the business runs smoothly without overinflating the indirect cost pool, thus safeguarding profitability and enabling potential for growth and investment.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you calculate General and Administrative expenses?
To calculate General and Administrative (G&A) expenses, you simply add up all the costs that go into running your business, aside from making or selling products. This includes things like:
- Salaries and wages for employees in roles like HR, management, and accounting
- Rent and utilities for your office space
- Insurance and other overhead costs
- Office supplies like paper, pens, and computers
- Professional services (like legal or accounting fees)
Basically, the formula is:
G&A Expenses = Salaries + Rent + Utilities + Supplies + Other Operating Costs
These are typically listed on your income statement, and knowing your G&A expenses can help you keep track of the day-to-day costs that keep your business running.
How do you calculate Selling, General, and Administrative expenses?
To calculate SG&A expenses, you simply add up all the costs related to selling, general operations, and administration. Here’s the breakdown:
- Selling expenses: Costs like advertising, marketing, and sales commissions.
- General expenses: Things like office supplies and utilities.
- Administrative expenses: Salaries for management and administrative staff, rent, etc.
The formula is:
SG&A = Selling Expenses + General Expenses + Administrative Expenses
These expenses are typically listed on the company’s income statement, and knowing how much you’re spending on SG&A can help you understand your company’s overall efficiency and cost management.
- What are G&A expenses?
- Importance of G&A expenses in financial management
- Breakdown of G&A expenses
- G&A vs other expense categories
- Semi-variable vs. fixed expenses
- Recording G&A expenses in your book
- 3 causes of bloat in G&A expenses
- Challenges in managing G&A expenses
- Strategies for managing G&A expenses
- Tools and Software for G&A expense management
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions