Blog > A Complete Guide to IoT Security: Issues, Risks, Standards, & More
A Complete Guide to IoT Security: Issues, Risks, Standards, & More
It seems like it was only a few years ago when we thought of computers, laptops, and smartphones as the only devices that used the Internet — maybe that’s because they were. Now, thanks to the massive explosion of IoT (Internet of Things) devices, staying connected has never been easier.
Everything from your smartwatch and car to the light bulbs and smoke alarms in your home can be IoT devices. Although this technology has made life easier for its users, it has also made a hacker’s job easier too. This increased risk has made it essential for businesses and personal users to ensure they implement the necessary IoT security to protect their data.
This article will cover a variety of important IoT security topics that include…
- The history of IoT devices
- What is IoT security?
- 4 security breaches to learn from
- The first IoT security legislation
- 6 company-wide strategies for your security model
- 9 IoT tools and solutions to secure your business
The history of IoT devices
According to IBM, the first IoT device was invented in 1982 when David Nichols, a Carnegie Mellon computer science grad student, was craving a Coke. Nichols didn’t want to make the long trek to see if there were any cold ones left in the vending machine, so he and his friends came up with the idea of installing micro-switches — connected to the department’s main computer via ARPANET — in the machine to notify them if any cold sodas were available.
Although Nichols’s invention and John Romkey’s 1990 Internet-connected toaster were some of the first to be reported, the term “Internet of Things” wasn’t coined until Kevin Ashton gave a presentation in 1999 where he referred to this technology as a connection of several devices via radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags. While this term has persisted, the IoT industry has expanded over the years to include a wide range of Internet- and network-based devices.
What is IoT security?
IoT security refers to the various modes of protection used to secure devices connected to the Internet and their associated networks. These safety measures are typically geared toward reducing vulnerabilities, preventing cyberattacks, addressing breaches, and eliminating any potential threats.
Although it may sound like a simple task to add protections to network-connected devices, several IoT security layers need to be accounted for, like sensors, data, servers, cloud platforms, and more. With a wide variety of devices, the framework of each may not look the same — there may be different physical barriers, network applications, protocols, and more. Nonetheless, your business needs to identify these components, functions, and operational procedures to ensure each is secure.

While IoT device architecture is not universal, here are some commonly accepted layers of security you may need to address:
- Application layer: This is where the user will interact with the device and its services.
- Network layer: This is where collected data is transmitted and processed. This layer connects devices to other servers and network devices.
- Perception (physical) layer: This is where devices and their sensors gather data for each operation or action taken.
Each layer leaves the possibility for malicious activity to occur, which is why businesses must build a comprehensive IoT security plan that addresses every device and network component.
IoT security benefits and challenges
There are always pros and cons of any technology or software, and network-connected devices are no different. With this industry expanding from everyday devices found in your home to extensive machinery used in major factories, there are an array of IoT security challenges and benefits that go along with it.
Challenges
As new devices are introduced into the market every year, businesses certainly have their work cut out for them when addressing IoT security challenges.
Some of the most common IoT security challenges include:
- Rapidly evolving trends, technology, and advanced threats
It’s extremely difficult to keep up with this fast-paced industry, evolving threats, and advanced viruses and breaches, especially when it comes to updating hardware and software in time. New technology like AI/machine learning, the cloud, and smart vehicles also open the door to attacks (stolen data, malware, ransomware, etc.) and can even put users in physical danger.
- Remote work as the new normal
With remote work comes remote access, which means the potential of unsecured home networks and public Wi-Fi for hackers to tap into.
- Internal human error
Human errors are one of the biggest IoT security challenges and cause the majority of breaches. Although it may be a hassle, scheduling consistent training on proper security protocols and updates will be crucial to reduce errors. Prioritizing device access to specific departments or staff will help too.
Benefits
While there are many challenges involved in implementing new Internet-connected devices into your business, there can also be many IoT security benefits with the right foundation.
Some of the most notable IoT security benefits include:
- Reduced operational costs
Secure IoT devices may be a little pricey to initially install, but they typically result in long-term savings for the business. This technology can reduce labor, improve production volumes and quality, and help teams put more focus on high-priority projects — all of which can save you money over time.
- Increased brand reputation, trust, and sales
Consumers want to do business with companies they trust to protect their information and produce top-notch products. By applying the necessary IoT security measures to your devices and communicating those efforts to your customers, you’re ensuring they can trust you. This trust can result in enhanced brand reputation by organic word-of-mouth recommendations and increased (new and return) sales.
- Security standards and requirements met
Your business can automatically meet other industry-specific or national security requirements and PCI compliance standards with the right IoT security. This is because many of these protocols overlap with the safety measures that go along with protecting these devices.
The importance of IoT security
Statista projects that the IoT market will amass 75 billion devices worldwide by 2025, therefore strong security protocols and software have become a necessity for both businesses and private citizens.
Here are some of the important assets and operations IoT security can help protect:
- Sensitive customer data (credit card, home address, phone numbers, etc.)
- Medical devices and records
- Government classified information
- Industrial machinery
- Personal residences (home Wi-Fi networks, alarm detection systems)
- Transportation (cars, planes, etc.)
By failing to secure these devices and address IoT security vulnerabilities, you’re exposing your business to preventable damages and costly fines.
4 IoT security breaches to learn from
No organization wants to experience an IoT security breach, as it can be extremely detrimental to profits, consumers, and long-term success. Businesses that don’t properly secure their devices are putting their staff and customers at greater risk.
Teams would be wise to educate themselves on past mistakes to ensure they don’t repeat them. To help your business better protect its assets, here are four major IoT security breaches to learn from:
- SolarWinds Orion 2020 supply chain attack
- IoT malware and Ryuk ransomware attacks during COVID-19
- Mirai botnet attacks: hundreds of thousands of IoT devices accessed
- Stuxnet attack: IoT devices used to damage Iran’s nuclear program
1. SolarWinds Orion 2020 supply chain attack
SolarWinds is a Texas-based software provider that services many well-known organizations worldwide, including 425 of the Fortune 500 businesses and U.S. government agencies like the Pentagon, Department of Defense, and all military branches. It’s also home to one of the most recent large-scale attacks that compromised thousands of companies in 2020.

Orion, a network management system (NMS), is one of SolarWinds’ most widely used products. It monitors and manages professional systems like servers and IoT devices. This supply chain attack, which U.S. officials believe was carried out by groups tied to the Russian government, planted malware using a trojan software update that was distributed to users in March 2020. Once distributed, it gave hackers backdoor access into roughly 18,000 private networks.
The 2020 Solarwinds Orion supply chain attack left a huge impact on the world of IoT security, as well-known, compromised organizations like Microsoft, Deloitte, the National Nuclear Security Administration, and even the Department of Homeland Security were forced to rethink their cybersecurity strategies to better protect their devices and networks.
The response to this breach has been felt on a global scale. The U.S. government took legal actions against the hackers and imposed sanctions against Russia. SolarWinds has since removed the software and released emergency patches for affected companies to remove this malicious code and identify additional threats.
Private businesses should vet all third-party providers — even large corporations — to ensure their services are up to date with the newest precautions. The zero-trust approach (discussed below) will be highly useful in evaluating the different players involved. To prevent future attacks and address the top IoT security threats, you can also implement a data exfiltration prevention program and a supply chain risk management system.
2. IoT malware and Ryuk ransomware attacks during COVID-19
The 2021 SonicWall Cyber Threat Report found a 66% increase in IoT malware attacks in 2020 alone. Much of this rise is attributed to the pandemic, which forced businesses to work remotely and use home devices. This public health crisis gave hackers a better opportunity to access corporate networks through unsecured connections.

The healthcare sector bore the brunt of these attacks throughout the year, as the Department of Health & Human Services (HHS) reported a 50% increase in breaches within this industry. Over 100 of these incidents targeted network servers, desktop computers, laptops, email, and electronic medical record (EMR) systems.
Hackers also accessed healthcare networks using phishing emails, which can be seen in the spike in Ryuk ransomware aimed at hospitals involved in the COVID-19 response.
A Ryuk ransomware attack targets specific high-profile organizations that will pay larger sums of money, rather than going after multiple businesses for less. These attacks are usually carried out via phishing emails, using a BazarLoader trojan or Trickbot or Emotet botnets. The hackers gain access to private networks and encryption to block companies out of these systems until they pay the ransom requested.
Although Ryuk ransomware surfaced back in 2018, the pandemic brought a huge wave of these attacks against hospitals and healthcare organizations. In October 2020, U.S. ransomware attacks increased by 71% in the healthcare sector, with Ryuk being responsible for 75% of these attacks. This increase in activity prompted the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), FBI, and HHS to issue a joint warning for this industry.
One of the most notable Ryuk ransomware attacks during this timeframe was against 250 United Healthcare sites and hospitals. The affected hospitals immediately shut down their systems, redirected ambulances, and relocated surgery patients to nearby locations.
IoT security certainly has its work cut out for it, as the impacts of this past year are still being felt on a global scale. Some ways to prepare for these kinds of attacks in the future include:
- Secure email gateways
- Access control solutions
- Work from home risk models
- Regularly scan for shadow IoT devices
- Virtual patching
Cyber Talk also recommends that hospitals enhance their security by implementing cybersecurity products and services that offer full visibility into IoT devices, strong leaders to address vulnerabilities with device manufacturers, and zero trust identity and access management policies.
3. Mirai botnet attacks: hundreds of thousands of IoT devices accessed
The Mirai botnet is one of the largest known breaches and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. It used hundreds of thousands of IoT devices to breach well-known networks and even caused an Internet outage across much of the East Coast.
What looked like the workings of a foreign threat actually originated from three twenty-year-old men looking to make a quick buck off Minecraft. The creators of the Mirai botnet carried out the first attack in September 2016 by scanning big blocks of the Internet to hack into unsecured IoT devices — security cameras, home wireless routers, DVRs, etc. — using over 60 combinations of passwords and usernames. From there, they used these devices to launch DDoS attacks to flood and crash the systems of OVH, one of the largest global web hosting providers that owned a tool used by Minecraft servers, and Krebs on Security, a security blog written by Brian Krebs.
This malicious code was then posted online to the public a few days later to most likely hide where it came from and who created it. Unfortunately, it wasn’t long until another hacker got ahold of it and launched another massive attack.
In October 2016, the Mirai botnet was used to target Dyn, a large-scale domain name system (DNS) provider that services many well-known platforms. Using IoT webcams, this breach led to an Internet crash for much of the East Coast and compromised major sites like GitHub, Twitter, Reddit, Netflix, PayPal, Airbnb, etc.
Following these attacks, the Mirai botnet continued to strike in November 2016. The first breach was against Lonestar Cell, Liberia’s largest telecommunication provider, which knocked the entire country offline. Then, another targeted Deutsche Telekom, taking nearly a million routers down with it.
While figures vary by source, it’s believed that the Mirai botnet successfully breached over 600,000 IoT devices at its peak. To put it lightly, the impact of these breaches was massive — companies paid large amounts of money in damages, reputable businesses were left exposed and had to completely restructure, and sensitive customer data was compromised.
To better defend your IoT security model from Mirai malware, your business can:
- Use a managed approach that allows device communication in a secured cloud
- Update firmware and software continuously and look for vulnerabilities
- Change and strengthen administrative credentials
- Disable all remote wide-area network (WAN) access to devices
- Use IP devices only when necessary — not all devices need to have an IP address
4. Stuxnet attack: IoT devices used to damage Iran’s nuclear program
Stuxnet is arguably the most dangerous IoT breach that has ever taken place because it inflicted both virtual and physical damage to Iran’s nuclear program in 2010. It was also the first of its kind in the industrial space.

Stuxnet is a computer worm designed to target and disrupt programmable logic controllers (PLCs) that are found in industrial computers used for manufacturing. The malware developers used their intelligence on the Natanz nuclear facility in Iran to infect five companies that installed equipment at this location. Once technicians connected to this machinery, they downloaded the Stuxnet worm, and it spread throughout the system. The compromised PLCs were then used to damage the facility by reprogramming and destroying its nuclear centrifuges.
This breach is a bit different than the others previously mentioned, as it used PLC devices connected to equipment operating from Windows computers. In addition to exfiltrating data from these networks and their devices, it also destroyed roughly 1,000 centrifuges. Businesses and governments had never seen a cyber assault result in tangible harm, and especially not on a nuclear plant. Therefore, Stuxnet is known to be one of the first virtual weapons and IIoT (industrial internet of things) attacks.
While it’s believed Stuxnet malware can no longer be operated, its impact continues to live on. To improve your IoT security within this sector, McAfee recommends separating your industrial and generic systems. This separation can be accomplished with firewalls, segmentation, and even a demilitarized zone (DMZ) network. Stronger physical security protocols can also go a long way toward protecting machinery.
As device security continues to be at the forefront of business and federal affairs, the U.S. government has decided to get involved to help address IoT security issues in a legal capacity.
Rising threats lead Congress to pass the first IoT security act
According to a U.S. Government Accountability Office study, 56 of the 90 responding federal agencies reported using network-connected devices. With government entities now using this technology, new IoT security threats are bound to arise. As a result of this expansion, Congress acted by passing a bipartisan bill to better address IoT security concerns.
On December 4, 2020, President Donald Trump signed the Internet of Things Cybersecurity Improvement Act of 2020 (H.R. 1668) into law. The act requires the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) to publish a set of IoT security standards that any federal agency or manufacturer that owns or controls connected devices must follow.
This new legislation requires the NIST to produce step-by-step requirements for government organizations to safely operate and manage these devices. These IoT security standards should consider current best practices and protocols developed by relevant agencies, private businesses, and public-private partnerships, and should involve guidance related to:
- Secure development
- Identity management
- Patching
- Configuration management
The OMB will review the NIST’s guidelines and publish its own policies to ensure they align with each other. These IoT security standards will be reviewed and updated every five years. To better understand this new legislation, eSecurity Planet provides a great breakdown here.
You can also click here to read more about new IoT security laws in California and Oregon.
Impact of the new IoT Cybersecurity Improvement Act of 2020
While this legislation is meant for government agencies, it may also strengthen other industries’ IoT security standards. Since device manufacturers are now required to abide by these guidelines to sell to federal agencies, the hope is that they will use these same precautions and protocols for other devices. Therefore, industry professionals are optimistic that private sectors will adopt these new regulations to better address IoT security vulnerabilities in their systems.
Despite being a monumental law and a step in the right direction to address IoT security issues, there’s still a lot of work to be done to protect devices and their networks. In light of recent ransomware attacks on the U.S. Colonial pipeline and meat processing facilities, which caused food and gas shortages, the demand for more security has reached new heights. With the Department of Justice now issuing security guidance on par with previous terrorism models, it’s only a matter of time until new legislation goes into effect.
6 company-wide strategies you need to include in your IoT security model
The world of IoT has continued to evolve, and security measures have followed. As new devices come to market and existing ones consistently advance, there’s always a need for safety updates and new IoT security standards to be put in place.

To help your business protect its devices and address any IoT security threats, here are 6 company-wide strategies to implement:
- Cross-departmental security protocols and training
- Regular software updates and data backups
- Network segmentation and IoT device isolation
- Zero-trust approach
- Security by design
- Strong firewalls
Since IoT breaches continue to affect even the strongest of businesses, incorporating these six strategies into your security model can create a safer environment that protects your customers, employees, and partners moving forward.
1. Cross-departmental security protocols and training
Maintaining cohesive IoT security standards across all departments will help your business safely operate its devices and know what to look for if and when a threat arises.
There should be a strong emphasis on training teams on IoT security to understand new systems, implement routine virus scans, use secure Wi-Fi connections and third-party trusted applications, choose strong passwords, avoid phishing emails, and more.
2. Routine software updates and data backups
Businesses that actively monitor and test IoT device systems will maintain a stronger security model. Teams should apply any available software upgrades to address patching issues and bugs immediately. To ensure you don’t miss out on any news, you can set up web notifications or alerts (if possible) from device manufacturer websites.

It’s never a good idea to store all your data in one place, especially on Internet- or network-connected devices. To better prepare for any IoT security threats, businesses should implement off-site data storage systems to ensure they have access to sensitive data outside of their IoT devices.
3. Network segmentation and IoT device isolation
Network segmentation is the process of dividing networks into multiple, smaller fragments. This approach can reduce IoT security concerns by limiting access to a select group of authorized users, allowing your team to better control the flow of traffic and monitor devices more closely.
By segmenting IoT networks, you can narrow breaches to smaller areas rather than worry about multiple entry points for hackers, leading to more compromised data. Typically, businesses can strengthen security by keeping devices on a private network to ensure they’re not interacting with other critical files, customer information, classified trade secrets, etc.
Your business can further address IoT security risks by isolating devices to allow them to securely communicate with each other and transfer data across platforms. This isolation can be implemented using the following connection models:
- Device to device: IoT devices are within the same network, allowing them to communicate using PAN protocols (Bluetooth, Ethernet, etc.).
- Device to cloud: IoT devices are connected to the cloud, allowing them to share data and communicate on this platform.
- Device to gateway: IoT devices are connected to a network using a gateway, allowing them to securely transfer data to sensors, equipment, the cloud, and with each other.
- Cloud-to-cloud (back-end data sharing): Authorized third parties are given access to the cloud, allowing them to connect with IoT devices and obtain or export their data.
Some common ways to segment and isolate IoT devices include the use of VLANs (virtual local area networks), subnets, separate Wi-Fi networks, routers, firewalls, access controls, etc.
For a list of popular IoT networks, protocols, and technologies to implement, click here.
4. Zero-trust approach
Simply put, the zero-trust approach — “never trust, always verify” — means your business doesn’t trust any entity (either internal or external) until they’ve been verified. This strategy can reduce unwanted visitors, mitigate breaches, and eliminate some of the top IoT security threats by ensuring only authorized users (who’ve confirmed their identities) have access to your devices.
When implementing zero-trust into your IoT system, the National Cyber Security Centre recommends sticking to these basic security principles:
- Know your architecture (users, devices, and services)
- Create a single strong user ID
- Create a strong device ID
- Authenticate everywhere
- Know the health of your devices
- Focus monitoring on devices and services
- Set policies according to value
- Control access to your devices and data
- Don’t trust your network
- Choose services designed for zero trust
Although not all zero-trust models will be the same for every business and industry, some of the most common tools used to support this security measure include micro-segmentation, end-to-end encryption, and multi-factor authentication.
5. Security by design
Security by design refers to network-connected devices having built-in protection from day one. This means these infrastructures are fully equipped with the proper tools, safety features, and governance to defend against the top IoT security threats.

Businesses that incorporate or build these devices into their operations would be wise to confirm there’s a strong IoT security plan integrated into every facet — applications, tiers, life cycle, etc.
Although it’s nearly impossible to predict future attacks when implementing security by design, regular monitoring and testing will be imperative to address any IoT security vulnerabilities or threats in your device systems.
6. Strong firewalls
By incorporating a strong firewall into your IoT security model, your business can actively monitor network traffic and detect suspicious activity to prevent breaches on devices.
While this security measure may seem obvious, some firewalls are more reliable than others. Therefore, it’s important to ensure your system has the strongest barriers in place to stop hackers from accessing sensitive data. Although most IoT devices come with some form of initial firewall protection, businesses can supplement additional measures for stronger security.
Next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) have gained popularity in the world of IoT security, as they go beyond a traditional firewall to use application awareness that focuses on individual apps. They also include other features like intrusion detection, threat intelligence, website filtering, advanced malware detection, and more.
Some of the best NGFWs to incorporate into your IoT security plan include Fortinet, Cisco, WatchGuard, and Palo Alto Networks.
Implement these 9 IoT tools and solutions to keep your business safe
Now that you have the proper strategies in place to combat the most challenging breaches, you need to implement the right products to enhance those methods. IoT security solutions have become a hot commodity these days, especially when new threats seem to be coming from every direction. While it’s normal to want to implement every protective feature to secure your business, not every tool will be right for your infrastructure.
Before using any security solution, it’s important to assess which devices are in your network, their frequency of use, and what operations they perform to make the best decision for your business. Once you’ve analyzed these areas, you can research different safety measures to see what IoT security threats they address and how they will pair with your system.
To kickstart your research, here are 9 reliable IoT security solutions (and their benefits):
- API security management
- Cloud computing, AI, and machine learning technologies
- Password management
- Network access controls (NAC)
- Edge computing
- Endpoint security
- Public key infrastructure (PKI)
- Multi-factor or two-factor authentication
- Real-time (streaming) analytics
1. API security management
Application programming interfaces (APIs) allow connected devices to sync with a network to securely transmit data and communicate with other applications and devices. However, their connection to the public Internet opens the possibility for more IoT security problems.
To mitigate these IoT security risks, businesses should add an API management solution. This approach will be especially useful if devices contain weak, broken, or exposed APIs, as these factors can increase the chances of a breach and sensitive data being stolen.
API security management solutions can help you detect suspicious activity or gaps, monitor traffic, support growth, increase development, secure back ends, and more.
Some of the most reliable API managers to integrate into your IoT security model include MuleSoft, 3scale, Akana, and more.
2. Cloud computing, AI, and machine learning technologies
Some of the newer solutions, like artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and machine learning (ML), can greatly improve IoT security for your connected devices.

One of the main functions of network-connected devices is to collect and transfer large amounts of data. AI and ML systems can assist by analyzing this information to perform predictive analytics, report behavior patterns, address malicious activity, and better identify IoT security threats. They can also allow your infrastructure the flexibility to make real-time adjustments to prevent future attacks.
Switching to cloud computing can also help enhance your IoT security by reducing attack surfaces, better protecting stored data, and monitoring traffic through a secure API gateway.
3. Password management
While it may sound like a quick fix, misuse of passwords continues to plague the world of IoT devices. These mistakes are one of the biggest IoT security challenges for businesses when it comes to safeguarding their connected networks.
Businesses can implement password managers into their IoT security to avoid using default, weak, or duplicate passwords and usernames. These solutions can help protect your devices and their networks by offering advanced features like login audits, encryption, secure password sharing, and more.
Some of the best IoT password managers to address these IoT security issues include LastPass, Dashlane, and 1Password.
4. Network access controls (NAC)
Network access controls (NAC) help businesses improve their IoT security by building a stronger perimeter around device systems that only grants access to authorized devices.
In addition to tracking and keeping inventory of all IoT device connections, NAC solutions can detect and prevent any unwanted visitors from entering your network and restrict devices to specific networks and data. This technology protects both physical and cloud-based systems.
NAC solutions differ from traditional access controls in several ways, including the quantity and variety of systems they can detect — IoT devices, PCs, servers, routers, etc. They also implement additional preventative security features like firewalls and antivirus and spyware programs.
The best NAC solutions will include valuable features like:
- Vendor security: Uses a virtual private network (VPN) and secure channel to allow trusted third parties access to internal systems.
- Incident response: Automates this function to address issues in real-time and focus more time on restoring your infrastructure.
- BYOD (bring-your-own-device) protection: Restricts network access of any outside device (mobile phones, tablets, etc.) until this application can ensure the device complies with all the security protocols in place.
- IoT fortification: Identifies and groups IoT devices to specific networks to monitor and control what data or resources they have access to.
Some of the most reliable NAC solutions include Cisco, Forescout, and Impulse. Click for more.
5. Edge computing
Edge computing allows IoT devices to collect, store, and process data closer to the edge of their network, rather than sending it back to a centralized external server or cloud system to determine what actions to take.
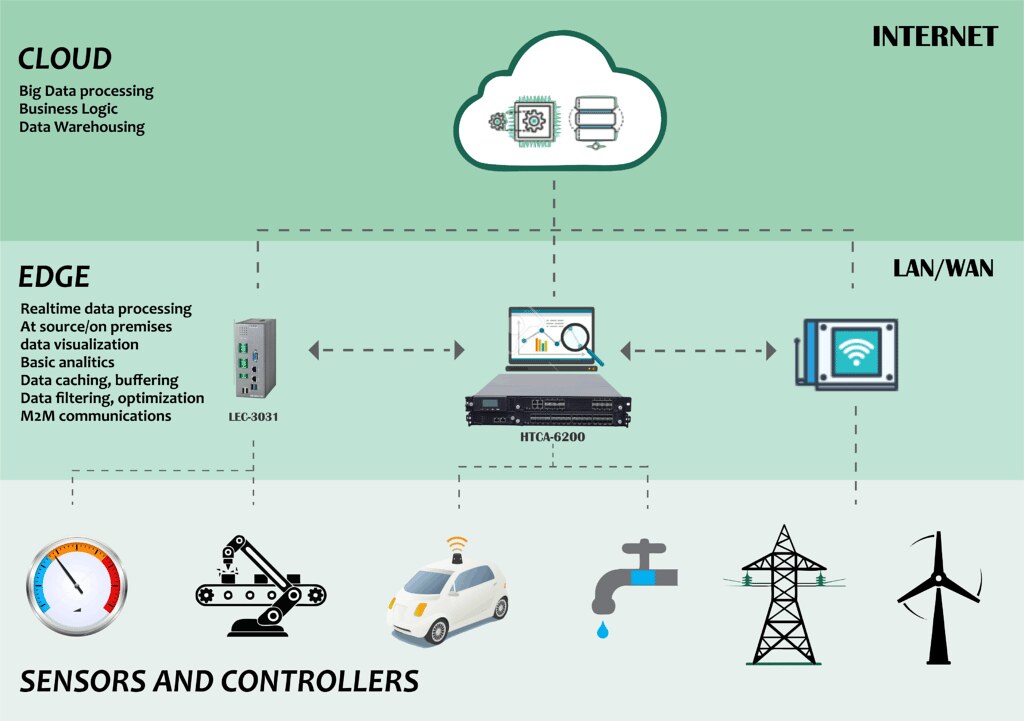
Implementing edge computing can improve your device security in a variety of ways. Applying this process to your infrastructure will help your business disperse its data, which can reduce and prevent large DDoS attacks and other IoT security threats. This solution also adds protective measures to defend local data points without hindering the entire network.
In addition to IoT security, edge computing can reduce latency, enhance performance and efficiency, improve data storage, and help businesses better manage their networks.
To help you better address these IoT security issues, STL Partners has compiled a list of 15 reliable edge computing solutions.
STL Partners provides valuable insights and expert guidance for businesses in the telecommunications space to help them grow their revenue, exceed customers’ expectations, and keep up with ever-changing trends.
6. Endpoint security
According to the 2020 Endpoint and IoT Zero Trust Security Report, 72% of businesses experienced an increase in endpoint and IoT security threats in the past 12 months, and over half anticipate an attack to compromise their system in the next year.
Endpoints are remote devices located at the edge of networks that communicate and transfer data back and forth to their associated server. As IoT technology has evolved, endpoints have expanded from traditional units like servers and desktops to lighting systems, sensors, industrial systems, medical devices, and more. While this growth is great for businesses to utilize different tools, it also opens the door for more attacks.
Implementing the proper security to protect these entry points from hackers can help decrease future breaches, safeguard sensitive data, and prevent malware or viruses from damaging your systems.
Endpoint solutions work to enhance your IoT security infrastructure by:
- Monitoring application activity and running updates to the cloud to protect assets.
- Securing sensitive information transmitted between partners and vendors.
- Sending alerts whenever any malicious or irregular activity is detected.
- Blocking unknown, third-party visitors from connecting with network devices.
- Expanding protections to each individual device and connected network.
Other capabilities of endpoint security include firewalls, URL filtering, browser isolation, encryption, secure email gateways, and more.
Some of the best endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions to tackle these IoT security concerns include McAfee, Symantec, and Bitdefender.
7. Public key infrastructure (PKI)
Public key infrastructure (PKI) is a combination of hardware, software, policies, and procedures to manage, create, distribute, and update digital certificates and public keys. While PKI has been a long-standing feature, it’s advanced over the years to meet the ever-changing standards of IoT security.
Using PKI, each IoT device is given a unique digital certificate to prove its identity, including security features like authentication and encryption methods to protect its network and data. This solution has transformed over the years to provide a more flexible and scalable approach by automating the device verification process to handle large device volumes and data storage.
Businesses can apply a variety of reputable PKI solutions to their IoT security, like DigiCert, OpenSSL, and Sectigo.
8. Multi-factor or two-factor authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and two-factor authentication (2FA) use several layers of security to verify a user’s identity before granting IoT device and network access.
Businesses can add MFA or 2FA to their administrative login procedure in addition to strong passwords to better protect their systems. This software can be applied using techniques like SMS codes (sent to a secondary device), fingerprints, facial recognition, hardware tokens, etc.
Since this is a popular IoT security technique, there are many software applications to choose from. Some of the top-rated MFA and 2FA solutions include Duo, LastPass, and OneLogin.
9. Real-time (streaming) analytics
Real-time analytics can greatly benefit your device security by preventing some of the top IoT security threats and monitoring suspicious behavior. Businesses that implement this tool can also improve their decision-making capabilities and safety protocols, which can lead to greater success moving forward.
To provide users with real-time analytics, device sensors work to detect activity that instantly triggers any associated data to be collected and stored for review. These insights can provide a leg up in the IoT security space, as they help businesses predict, prepare, address, minimize, and manage future attacks.
Much like authentication tools, you can use many real-time analytics solutions to improve your IoT security. Some of the most reliable platforms include Google Cloud, ThingSpeak, and Datadog.
Conclusion
As the world of connected devices continues to extend into every industry, home, and operation, advanced IoT security is no longer an option. With data becoming a desirable cyberweapon and hackers regularly targeting federal agencies and high-profile institutions, you don’t stand a chance without the proper protection in place. Luckily, businesses have access to a plethora of software innovations and security measures to prepare for any threat that comes their way.
 Is you business PCI compliant? Take this 1-min quiz to find out.
Is you business PCI compliant? Take this 1-min quiz to find out. 
